This article is about the specific polity Nazi Germany and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
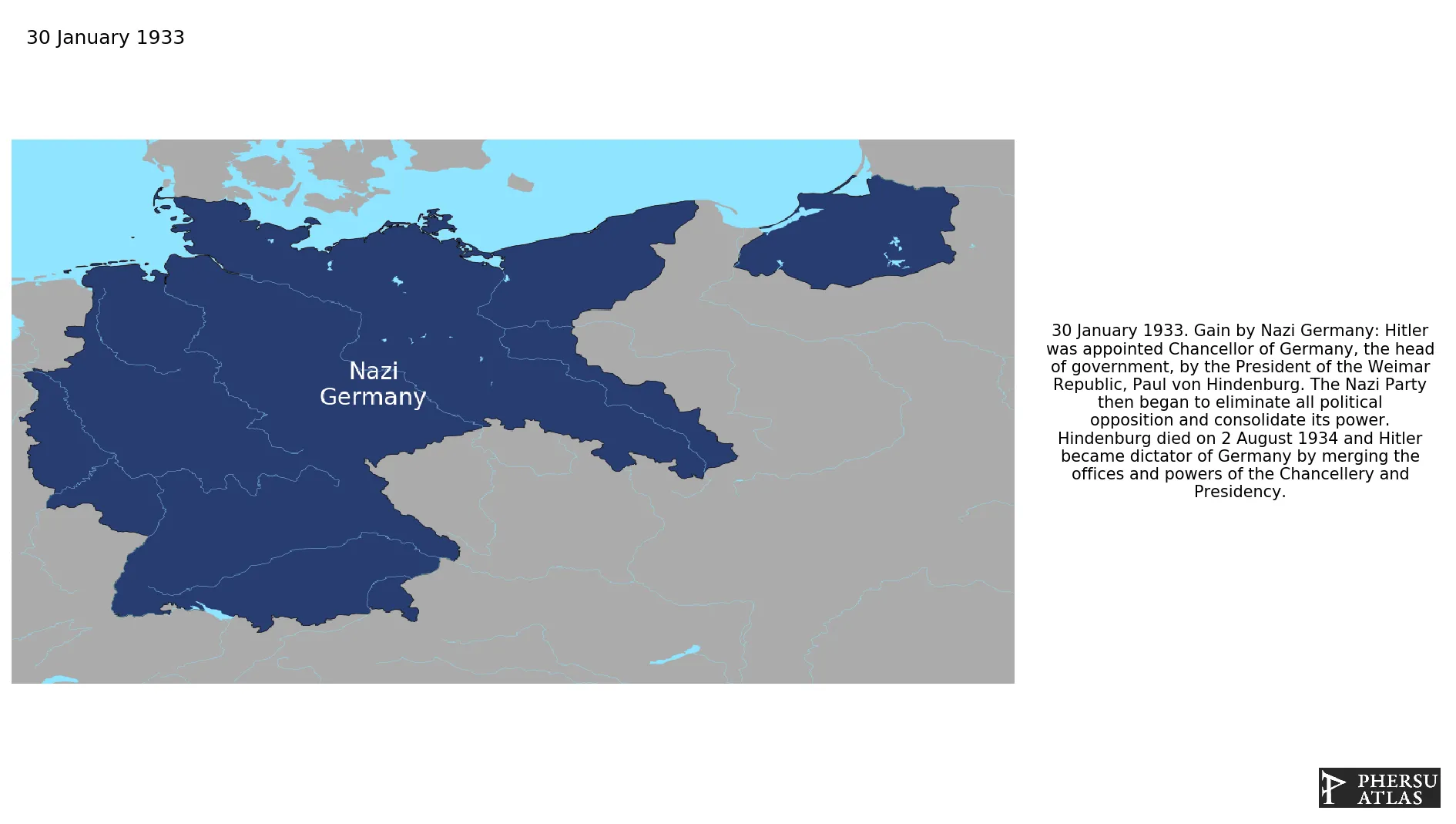
The far-right Nazi Party won the last elections of the Weimar Republic and Adolf Hitler became Chancellor of Germany. Shortly after the Death of president Paul von Hindenburg, Hitler took over also the presidential powers, becoming the so-called Führer of Germany and creating a new state, Nazi Germany (officially known as the German Reich). Dissatisfied with the outcome of the Treaty of Versailles, the other European countries initially allowed Germany to take over former territories of the German Empire or of the Austro-Hungarian Empire like Bohemia, Austria and Memelland. When Germany invaded Poland on 1 September 1939 this caused the start of World War II in Europe. After the defeat of Germany in 1945, the country was divided in military occupation zones and ceased to exist.
Establishment
January 1933: Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany, the head of government, by the President of the Weimar Republic, Paul von Hindenburg. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934 and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the offices and powers of the Chancellery and Presidency.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
1.1.Aftermath of World War I
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
1.1.1.Territory of the Saar Basin
The Territory of the Saar Basin was a region of Germany occupied and governed by the United Kingdom and France from 1920 to 1935 under a League of Nations mandate.
March 1935: After a plebiscite was held in 1935, the Territory of the Saar Basin was returned to Germany.
Was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the German Reich on 13 March 1938.
March 1938: On 12 March, the German Wehrmacht crossed the border into Austria, unopposed by the Austrian military. The Germans were greeted with great enthusiasm. A plebiscite held on 10 April officially ratified Austria's annexation by the Reich.
On 29 September, the Munich Agreement was signed by Germany, Italy, France, and Britain. The Munich Agreement stipulated that Czechoslovakia must cede Sudeten territory to Germany. Germany dismembered Czechoslovakia.
October 1938: On 29 September, the Munich Agreement was signed by Germany, Italy, France, and Britain. The Munich Agreement stipulated that Czechoslovakia must cede the Sudeten territory to Germany. German occupation of the Sudetenland would be completed by 10 October.
By late 1938, Lithuania had lost control over the situation in the Memel Territory. In the early hours of 23 March 1939, after a political ultimatum had made a Lithuanian delegation travel to Berlin, the Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs Juozas Urbšys and his German counterpart Joachim von Ribbentrop signed the Treaty of the Cession of the Memel Territory to Germany in exchange for a Lithuanian Free Zone in the port of Memel, using the facilities erected in previous years.
March 1939: By late 1938, Lithuania had lost control over the situation in the Memel Territory. In the early hours of 23 March 1939, after a political ultimatum had made a Lithuanian delegation travel to Berlin, the Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs Juozas Urbšys and his German counterpart Joachim von Ribbentrop signed the Treaty of the Cession of the Memel Territory to Germany in exchange for a Lithuanian Free Zone in the port of Memel, using the facilities erected in previous years.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
5.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
December 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the eastern front of World War II in that date.
January 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
February 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
March 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
5.1.1.Invasion of Poland
Was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union. It marked the beginning of World War II.
5.1.1.1.German Annexation of Danzig
After the German invasion of Poland in 1939, the Nazis abolished the Free City of Danzig and incorporated the area into the newly formed Reichsgau of Danzig-West Prussia.
September 1939: After the German invasion of Poland in 1939, the Nazis abolished the Free City of Danzig and incorporated the area into the newly formed Reichsgau of Danzig-West Prussia.
5.1.2.German administration of eastern teritories during World War II
Refers to administrative acts of Germany on the organization of militarly occupied territories in eastern Europe during World War II.
October 1939: With two decresse on 8 and 12 October 1939, Adolf Hitler re-organized the occupied territories in Poland. West Prussia and the are of Poznan were annexed directly to Germany.
5.1.3.Operation Bagration
Was the Soviet offensive against German-occupied Belarus during World War II.
5.1.3.1.Šiauliai Offensive
Was an operation of the Soviet forces of the 1st Baltic Front, commanded by General Hovhannes Bagramyan, conducted from 5 July to 29 August 1944. It drove German troops from much of Lithuania, with the main tactical objective being the city of Šiauliai.
August 1944: Soviet advances during Operation Bagraton and Šiauliai Offensive.
5.1.3.2.Kaunas Offensive
Was an offensive of the Soviet Red Army to clear the area of Kaunas from German forces.
July 1944: The German resistance on the approaches to the Neman was broken.
5.1.4.Baltic Offensive
Was the campaign between the northern Fronts of the Red Army and the German Army Group North in the Baltic States during the autumn of 1944 that resulted in the Soviet re-occupation of the Baltic States.
5.1.4.1.Battle of Memel
Was a battle which took place on the Eastern Front during World War II resulting in the Soviet conquest of Klaipėda (Memel).
January 1945: German forces abandon Memel, which is occupied by Soviet forces shortly after.
5.1.5.Gumbinnen Operation
Was a Soviet offensive on the Eastern Front late in 1944, in which Soviet forces attempted to penetrate the borders of East Prussia.
October 1944: Gumbinnen was reached by the Soviets by 22 October.
October 1944: Gumbinnen was retaken by German forces on the 24 October.
October 1944: The Germans lost Gumbinnen on October 25th.
November 1944: The town of Gumbinnen was again taken by the German 5th Panzer Division.
5.1.6.Vistula-Oder Offensive
Was a Soviet offensive were German-held territories of Kraków, Warsaw and Poznań were conquered.
January 1945: First White Russian Front takes Łódź.
January 1945: The Red Army reached the Baltic coast of the Vistula delta.
January 1945: The Red Army reached Katowice.
January 1945: The Soviet 2nd Guards Tank and 5th Shock Armies reached the Oder almost unopposed. A unit of the 5th Shock Army crossed the river ice and took the town of Kienitz as early as 31 January.
5.1.7.Soviet Invasion of Slovakia
Was the Soviet invasion of Slovakia near the end of World War II.
March 1945: On March 3-5 the Soviets took northwestern Slovakia.
March 1945: In Czechoslovakia, troops of Second Ukrainian Front take communications center of Banska Bystrica.
April 1945: Important communications center of Bratislava (Czechoslovakia) falls to troops of Second Ukrainian Front.
5.1.8.East Prussian Offensive
Was a strategic offensive by the Soviet Red Army against the German Wehrmacht in East Prussia during World War II.
January 1945: Second White Russian Front seizes Allenstein and Deutsch-Eylau.
January 1945: Rokossovsky's leading tank units had reached the shore of the Vistula Lagoon.
March 1945: Some 15 divisions of the German 4th Army had become encircled on the shore of the Vistula Lagoon in what became known as the Heiligenbeil Pocket. After bitter fighting, these units were finally overcome on 29 March.
April 1945: Organized resistance in East Prussia ends as Königsberg fortress falls to troops of Third White Russian Front
April 1945: In East Prussia, troops of Third White Russian Front overrun Pillau, at tip of Samland Peninsula.
5.1.9.Battle of Küstrin
Was the Soviet offensive against German forces in the area of Küstrin (today Kostrzyn nad Odrą in Poland).
February 1945: On February 2, 1945, Soviet troops occupied the fortress of Küstrin.
5.1.10.Siege of Breslau
Was a three-month-long siege of the city of Breslau in Lower Silesia, Germany (now Wrocław, Poland) by Soviet Troops at the End of World War II.
February 1945: In German Silesia, Soviet forces gain ground North-West of Breslau.
May 1945: After a three-month-long siege of the city of Breslau in Lower Silesia, Germany (now Wrocław, Poland), fell to the Soviets.
5.1.11.East Pomeranian Strategic Offensive
Was an offensive by the Soviet Red Army against the German Wehrmacht in Pomerania and West Prussia from 10 February to 4 April 1945.
February 1945: Red Army overruns Schneidemuehl (North-East Prussia).
February 1945: In checkered fighting, Deutsch-Briesen fell into Soviet hands on February 16.
March 1945: As early as March 1, the Soviets had again penetrated east of Koslin to the Baltic Sea.
March 1945: Russian troops reach coast at Koeslin.
March 1945: On March 5th the Red Army reached the Baltic coast and occupied Kammin.
March 1945: Soviet forces led by Marshal Georgy Zhukov occupied Stolpmünde, a town in present-day Poland.
March 1945: On March 8, the 1st Guards Tank Army was temporarily assigned to Rokossovsky's front, parts of the 3rd Guards Tank Corps and the 132nd Rifle Corps of the 19th Army (General Koslow) jointly occupied the town of Stolp.
March 1945: Sopot fell into Soviet hands on March 23.
March 1945: On March 28, the Red Army took Gotenhafen (modern-day Gdynia).
March 1945: Troops of Second White Russian Front complete capture of Danzig.
April 1945: The German formations north-west of Danzig on the Oxhöfter Kämpe and on the Hela peninsula, as well as the German units stationed near Stutthof, continued to resist until April 9, 1945.
5.1.12.Vienna Offensive
Was an offensive launched by the Red Army in order to capture Vienna, Austria, during World War II. .
April 1945: The Red Army penetrated Klosterneuburg with the 20th and 22nd Guards Tank Brigades.
April 1945: On April 8, Soviet forces also landed on the left bank of the Danube opposite Orth and near Mannsdorf.
April 1945: The German 96th Infantry Division and the 101st Jäger Division had to evacuate Gänserndorf and Angern on April 10th.
April 1945: The Soviet 23rd Panzer Corps (Lieutenant General Akhmanov) occupied Deutsch-Wagram on April 11.
April 1945: Second Ukrainian Front gains ground North of Vienna. Troops of Third Ukrainian Front continue to clear region West of Vienna and overrun Fuerstenfeld, East of Graz.
5.1.13.Battle of Berlin
The German Ninth Army, encircled in a large pocket in the Spree Forest region south-east of Berlin, attempted to break out westwards through the village of Halbe but was defeated.
May 1945: Battle of Halbe: The German Ninth Army, encircled in a large pocket in the Spree Forest region south-east of Berlin, attempted to break out westwards through the village of Halbe but was defeated.
May 1945: Fighting between German and Soviet forces in Berlin.
5.2.World War II (Western Front)
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
May 1940: Hitler announced the re-integration of Eupen-Malmedy into Germany while the rest of Belgium remained under military occupation.
August 1942: Luxembourg was annexed by Germany into Gau Moselland.
5.2.1.Saar Offensive
Was the French invasion of Saarland, Germany, in the first stages of World War II.
September 1939: The French army advanced to as far as 8 kilometres in some areas of Germany, and captured about 12 towns and villages unopposed: Gersheim, Medelsheim, Ihn, Niedergailbach, Bliesmengen, Ludweiler, Brenschelbach, Lauterbach, Niedaltdorf, Kleinblittersdorf, Auersmacher, and Sitterswald.
September 1939: The French occupied most of the Warndt Forest.
September 1939: The French 32nd Infantry Regiment made further gains on 12 September, seizing the German town of Brenschelbach.
September 1939: The French held German territory along all of the Rhine-Moselle front, but after the collapse of Poland, General Maurice Gamelin on 21 September ordered French units to return to their starting positions on the Maginot Line. On 17 October the withdrawal was complete.
5.2.2.German Invasion of France
The Battle of France was the German invasion of France during World War II that ended with the French Armistice of Compiègne on 22 June 1940.
5.2.2.1.French Armistice
Was the Armistice of 22 June 1940 when France surrendered to Germany during World War II.
5.2.2.1.1.Franco-German Armistice
The French Armistice of 22 June 1940 was signed at 18:36 near Compiègne, France, by officials of Nazi Germany and the French Third Republic. The armistice partitioned France: northern and central France were militarly occupied by Germany, Alsace-Lorraine was inglobated into the German State, and the remainder of France became Vichy France, a regime loyal to Germany.
June 1940: The Armistice of 22 June 1940 was signed at 18:36 near Compiègne, France, by officials of Nazi Germany and the French Third Republic. It did not come into effect until after midnight on 25 June. Northern and coastal France fell under direct German occupation, whereas a French government aligned with Germany ("Vichy France") was established in the south. Alsace-Lorraine was annexed to Nazi Germany.
5.2.3.Ardennes Counteroffensive
Was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II.
5.2.3.1.Allied Counteroffensive
Allied military operations to liberate Belgium and Luxembourg during World War II.
January 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
5.2.4.Siegfried Line campaign
Was a phase in the Western European campaign of World War II which involved actions near the German defensive Siegfried Line.
September 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
5.2.4.1.Battle of the Scheldt
Was a series of military operations led by the First Canadian Army, with Polish and British units attached, to open up the shipping route to Antwerp so that its port could be used to supply the Allies in north-west Europe.
October 1944: Allied advances by October 16th in the Low Countries and Belgium, during the Battle of the Scheldt.
5.2.5.Lorraine campaign
Was the operation of the U.S. Army to liberate German-occupied Lorraine during World War II.
December 1944: Allied forces accept surrender of last of the Metz forts.
5.2.6.Western Allied invasion of Germany
Was the invasion of the western territories of Germany mainly by the United States, United Kingdom, France and Canada at the end of World War II.
March 1945: Frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
March 1945: American forces clear large part of Wesel in street-to-sreet fighting.
March 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
April 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
April 1945: Allied advance in Germany in that date.
April 1945: Allied reduction of Ruhr Pocket.
April 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
May 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
5.2.6.1.Battle of Aachen
Was a battle of World War II, fought by American and German forces in and around Aachen, Germany, between 2-21 October 1944.
October 1944: The German commander of Aachen garrison surrenders at 12:05 of 21 October 1944 ot American forces.
5.2.6.2.Operation Clipper
Was an Allied offensive by the British XXX Corps (which included the American 84th Infantry Division) to reduce the Geilenkirchen salient in mid-November 1944.
November 1944: Allied forces arrive 2 miles Sout-West of Geilenkrichen.
5.2.6.3.German Offensive on the Western Front during the Allied invasion
Was a offensive of Germany against the Allies that were invading German-occupied Europe during World War II.
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 16th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 20th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 25th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
5.2.6.4.Operation Blackcock
Was an operation to clear German troops from the Roer Triangle, formed by the towns of Roermond and Sittard in the Netherlands and Heinsberg in Germany during the fighting on the Western Front in the Second World War.
January 1945: Allied forces complete capture of Heinsberg.
5.2.6.5.Operation Veritable
Was an Allied military operation in the Reichswald Forest, in Germany, towards the end of World War II.
February 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
February 1945: Allied forces complete capture of Cleve.
March 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
5.2.6.6.Operation Grenade
Was the crossing of the Roer river between Roermond and Düren by the U.S. Ninth Army which marked the beginning of the Allied invasion of Germany.
5.2.6.7.Operation Lumberjack
Was a military operation with the goal of capturing the west bank of the Rhine River and seizing key German cities, near the end of World War II.
March 1945: At Bitburg, the Soviet 5th Infantry Division cut through the German lines.
March 1945: Allied forces entered Euskirchen on 4 March.
March 1945: Allied conquest of Cologne.
5.2.7.Battle of Vianden
Took place November 19, 1944 in the small town of Vianden, in northern Luxembourg. It was one of the most important battles of the Luxembourg Resistance during World War II.
November 1944: One of the most important battles of the Luxembourg Resistance during World War II took place November 19, 1944 in the small town of Vianden.
5.2.8.Colmar Pocket
Was an Allied military operation to liberate central Alsace from German forces.
January 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
February 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
5.3.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
May 1945: The entire territory of Germany is occupied by Allied forces.
5.3.1.The Surrender of German forces
Surrender of German forces at the end of World War II.
May 1945: Soviet forces complete capture of Berlin. German forces surrender.
May 1945: German forces in North West Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands surrender.
May 1945: German forces in Bavaria surrender.
May 1945: The Soviets forced the German units in Army Group Centre, that were located in Bohemia, to capitulate by 11 May.
5.3.2.Austrian State Treaty
The Austrian State Treaty re-established Austria as a sovereign state after World War II.
May 1945: In the immediate aftermath of World War II, Austria was divided into four occupation zones and jointly occupied by the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France.
Disestablishment
January 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
January 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
January 1945: First White Russian Front takes Łódź.
January 1945: Second White Russian Front seizes Allenstein and Deutsch-Eylau.
January 1945: Allied forces complete capture of Heinsberg.
January 1945: Rokossovsky's leading tank units had reached the shore of the Vistula Lagoon.
January 1945: The Red Army reached the Baltic coast of the Vistula delta.
January 1945: The Red Army reached Katowice.
January 1945: German forces abandon Memel, which is occupied by Soviet forces shortly after.
January 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
January 1945: The Soviet 2nd Guards Tank and 5th Shock Armies reached the Oder almost unopposed. A unit of the 5th Shock Army crossed the river ice and took the town of Kienitz as early as 31 January.
February 1945: On February 2, 1945, Soviet troops occupied the fortress of Küstrin.
February 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
February 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
February 1945: Allied forces complete capture of Cleve.
February 1945: In German Silesia, Soviet forces gain ground North-West of Breslau.
February 1945: Red Army overruns Schneidemuehl (North-East Prussia).
February 1945: In checkered fighting, Deutsch-Briesen fell into Soviet hands on February 16.
February 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
March 1945: As early as March 1, the Soviets had again penetrated east of Koslin to the Baltic Sea.
March 1945: At Bitburg, the Soviet 5th Infantry Division cut through the German lines.
March 1945: Allied forces entered Euskirchen on 4 March.
March 1945: On March 5th the Red Army reached the Baltic coast and occupied Kammin.
March 1945: Allied conquest of Cologne.
March 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
March 1945: On March 3-5 the Soviets took northwestern Slovakia.
March 1945: Russian troops reach coast at Koeslin.
March 1945: Frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
March 1945: Soviet forces led by Marshal Georgy Zhukov occupied Stolpmünde, a town in present-day Poland.
March 1945: On March 8, the 1st Guards Tank Army was temporarily assigned to Rokossovsky's front, parts of the 3rd Guards Tank Corps and the 132nd Rifle Corps of the 19th Army (General Koslow) jointly occupied the town of Stolp.
March 1945: Sopot fell into Soviet hands on March 23.
March 1945: American forces clear large part of Wesel in street-to-sreet fighting.
March 1945: In Czechoslovakia, troops of Second Ukrainian Front take communications center of Banska Bystrica.
March 1945: On March 28, the Red Army took Gotenhafen (modern-day Gdynia).
March 1945: Some 15 divisions of the German 4th Army had become encircled on the shore of the Vistula Lagoon in what became known as the Heiligenbeil Pocket. After bitter fighting, these units were finally overcome on 29 March.
March 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
March 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
March 1945: Troops of Second White Russian Front complete capture of Danzig.
April 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
April 1945: Important communications center of Bratislava (Czechoslovakia) falls to troops of Second Ukrainian Front.
April 1945: Allied advance in Germany in that date.
April 1945: The Red Army penetrated Klosterneuburg with the 20th and 22nd Guards Tank Brigades.
April 1945: On April 8, Soviet forces also landed on the left bank of the Danube opposite Orth and near Mannsdorf.
April 1945: Organized resistance in East Prussia ends as Königsberg fortress falls to troops of Third White Russian Front
April 1945: The German formations north-west of Danzig on the Oxhöfter Kämpe and on the Hela peninsula, as well as the German units stationed near Stutthof, continued to resist until April 9, 1945.
April 1945: The German 96th Infantry Division and the 101st Jäger Division had to evacuate Gänserndorf and Angern on April 10th.
April 1945: The Soviet 23rd Panzer Corps (Lieutenant General Akhmanov) occupied Deutsch-Wagram on April 11.
April 1945: Second Ukrainian Front gains ground North of Vienna. Troops of Third Ukrainian Front continue to clear region West of Vienna and overrun Fuerstenfeld, East of Graz.
April 1945: Allied reduction of Ruhr Pocket.
April 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
April 1945: In East Prussia, troops of Third White Russian Front overrun Pillau, at tip of Samland Peninsula.
May 1945: Battle of Halbe: The German Ninth Army, encircled in a large pocket in the Spree Forest region south-east of Berlin, attempted to break out westwards through the village of Halbe but was defeated.
May 1945: Soviet forces complete capture of Berlin. German forces surrender.
May 1945: Fighting between German and Soviet forces in Berlin.
May 1945: German forces in North West Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands surrender.
May 1945: German forces in Bavaria surrender.
May 1945: After a three-month-long siege of the city of Breslau in Lower Silesia, Germany (now Wrocław, Poland), fell to the Soviets.
May 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
May 1945: In the immediate aftermath of World War II, Austria was divided into four occupation zones and jointly occupied by the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France.
May 1945: The Soviets forced the German units in Army Group Centre, that were located in Bohemia, to capitulate by 11 May.
May 1945: The entire territory of Germany is occupied by Allied forces.
Selected Sources
Battle of the Scheldt. Canadiansoldiers.com. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://www.canadiansoldiers.com/history/campaigns/northwesteurope/scheldt.htm
Crossing Of The Rhine, 22-28 March 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope79.jpg
Dollinger, Hans. The Decline and the Fall of Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan, Library of Congress Catalogue Card Number 67-27047. p. 239
Encirclement Of The Ruhr, 29 March-4 April 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope80.jpg
Erich Kuby: Die Russen in Berlin 1945, Scherz Verlag, München 1965, S. 24.
Final Operations, 19 April-7 May 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope82.jpg
German Ardennes Counter-Offensive, 26 December 1944 16 January 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope73.jpg
Ian Kershaw (trad. de l'anglais), La Fin : Allemagne, 1944-1945, Paris, Seuil, 2012, p.137
Kennedy, R.M. (1956): The German Campaign in Poland, 1939, Department of the Army, p. 127
Operation Bagration, 22 June-19 August 1944. United States Military Academy of West Point. Retrieved on 6 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope30.jpg
Pursuit To The West Wall, 26 August-14 September 1944 United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope66.jpg
Reduction Of Ruhr Pocket And Advance To the Elbe And Middle Rivers, 5-18 April 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope81.jpg
Russian Balkan And Baltic Campaigns, 19 August-31 December 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope31.jpg
Soviet Offensive To The Oder, 12 January-30 March. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope32.jpg
Sullivan, G.R.: Ardennes-Alsace p.23. U.S. Army Center of Military Hisotry. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://www.history.army.mil/brochures/ardennes/aral.htm
The Rhineland Campaign, Operations 8 February-5 March & Operations 6-10 March 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope76combined.jpg
U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/ardennes/p49(map).jpg
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 323
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 386
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 400
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 402
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 450
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 455
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 463
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 483
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 498
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 516
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 523
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 528
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 530
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.308
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.351
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.378
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.381
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.382
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.424
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.425
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.459
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.473
.svg.webp)
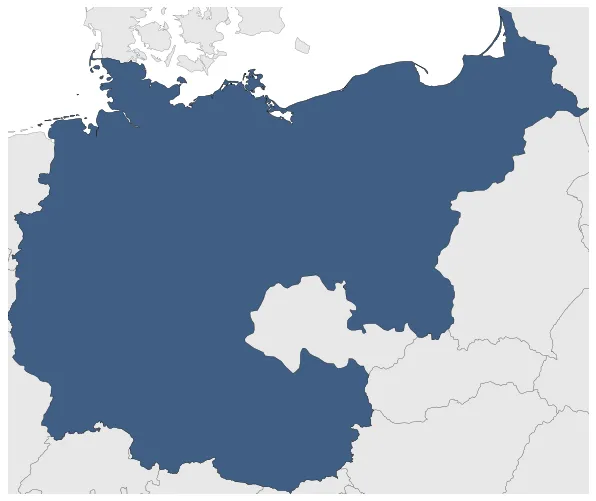
 Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany