This article is about the specific polity Rattanakosin Kingdom and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Siamese kingdom founded in 1782 with the establishment of Rattanakosin (Bangkok), which replaced the city of Thonburi as the capital of Siam. The Kingdom ended with the eastablishment of a constitutional monarchy after the Siamese revolution of 1932.
Establishment
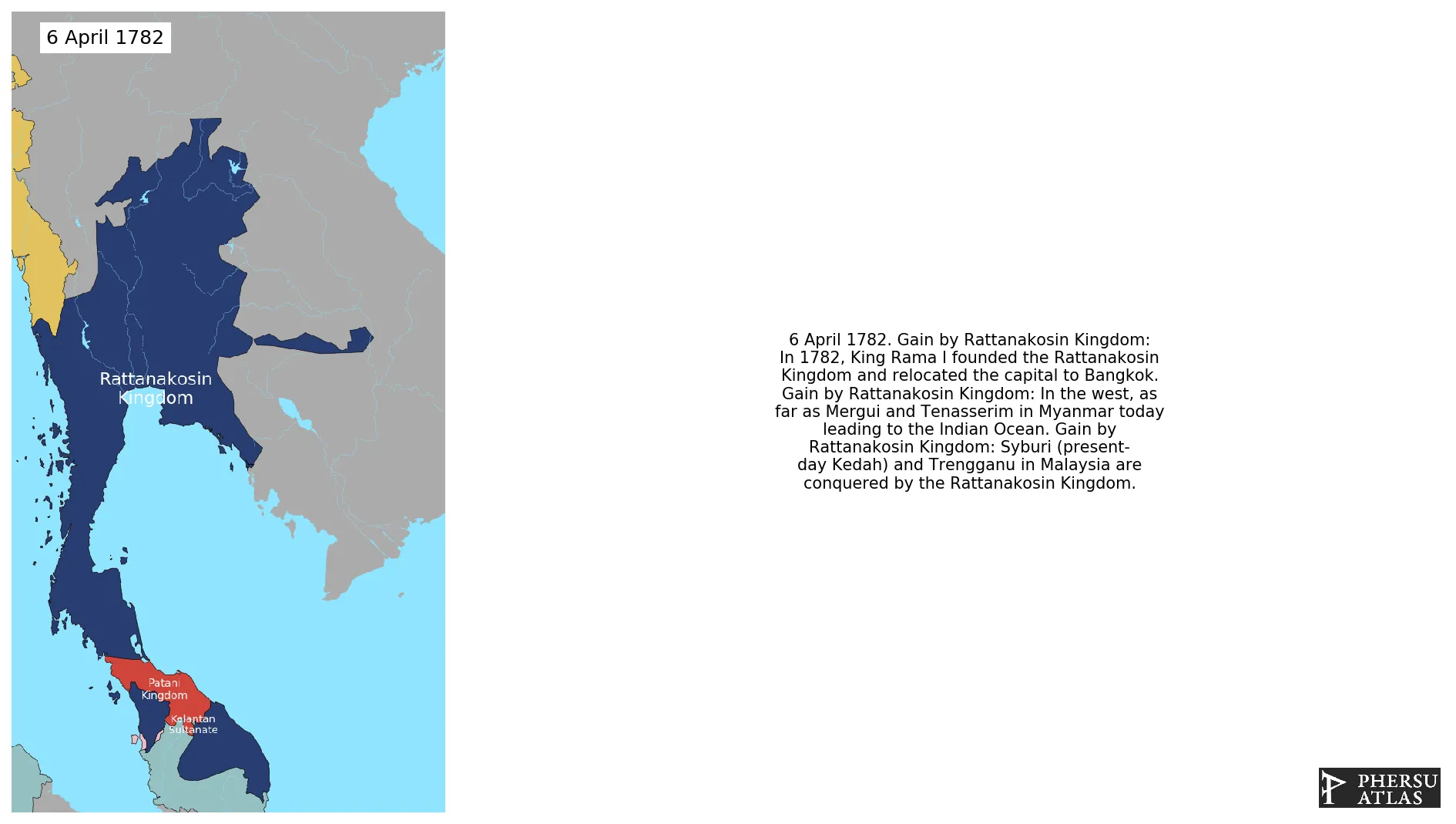
April 1782: In the west, as far as Mergui and Tenasserim in Myanmar today leading to the Indian Ocean.
April 1782: Syburi (present-day Kedah) and Trengganu in Malaysia are conquered by the Rattanakosin Kingdom.
April 1782: In 1782, King Rama I founded the Rattanakosin Kingdom and relocated the capital to Bangkok.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars fought between Burma and Siam from the 16th to 19th centuries.
1.1.Burmese-Siamese War (1785-1786)
Was a war between the Konbaung dynasty of Burma and the Siamese Rattanakosin Kingdom.
January 1786: The Burmese captured Songkhla.
January 1786: All of the Burmese invasion armies withdrew in disarray in late-January 1786.
1.2.Burmese-Siamese War (1791-1793)
Was a conflict between the Kingdom of Burma under Konbaung dynasty and the Kingdom of Siam under the Chakri dynasty over the town of Tavoy and the Tenasserim Coast.
April 1794: In a treaty, Siam formally cedes the Tenasserim coastal region to Burma.
1.3.Burmese-Siamese War (1802-1805)
Was a war between the Kingdom of Burma under the Konbaung dynasty and Kingdom of Siam under the Chakri dynasty over the Lan Na city-states.
1.3.1.Kengtung annexed by Chiang Mai
In 1802 Kengtung (northern Thailand) came under the rule of Chiang Mai.
January 1803: In 1802 Kengtung came under the rule of Chiang Mai.
1.4.Burmese-Siamese War (1809-1812)
Was a war between the Konbaung dynasty of Burma and the Rattanakosin Kingdom of Siam.
1.4.1.First Burmese invasion (Siam)
Was the first Burmese invasion of Siam during the Burmese-Siamese War (1809–1812).
September 1809: The second column, led by British Lieutenant Colonel Herbert, embarked on ships and captured Takua Pa in 1809 during the Burmese military occupation. This marked a significant victory in the Anglo-Burmese War.
November 1809: In October 1809, Bodawpaya, the king of Burma, sent his chamberlain with a large force to conquer Ranong and Na Toei. The force consisted of 30,000 soldiers, 60 war ships, and 200 swivel guns. The successful campaign resulted in the territory falling under Burma's military occupation.
January 1810: The Burmese forces, led by Prince Bagyidaw, managed to regroup after initial setbacks and received reinforcements. They successfully captured the city of Phuket on 13 January 1810.
1.4.2.Second Burmese invasion (Siam)
Was the second Burmese invasion of Siam during the Burmese-Siamese War (1809–1812).
April 1810: In March 1810, the combined Siamese-Kedahan forces, led by Governor Phraya Surin Phakdi, successfully retook the island of Phuket from the invading Burmese forces. The invaders were pushed into Pak Chan, marking a significant victory for the Rattanakosin Kingdom.
1.4.3.Third Burmese invasion (Siam)
Was the third Burmese invasion of Siam during the Burmese-Siamese War (1809–1812).
June 1810: The Burmese King Bodawpaya sent his army, led by his son Prince of Tharrawaddy, to invade Phuket in late May 1810. The Burmese forces aimed to conquer the island and expand their territory in the region.
June 1810: In 1810, a Siamese counter offensive led by Phuket Governor Phraya Thammarat expelled the Burmese invaders from the island.
Expansion during the rule of Bodawpaya of the Konbaung Dynasty.
January 1815: With the help of the Burmese the Kengtung ruling dynasty was reinstated in 1814.
Was an attempt by King Anouvong (Xaiya Sethathirath V) of the Kingdom of Vientiane to end the suzerainty of Siam and recreate the former kingdom of Lan Xang.
February 1827: In January 1827 the Lao armies of the kingdoms of Vientiane and Champasak (ruled by Anouvong's son) moved south and west across the Khorat Plateau, advancing as far as Saraburi, just three days march from the Siamese capitol of Bangkok. .
July 1827: The Siamese quickly mounted a counterattack, forcing the Lao forces to retreat.
January 1829: In 1828, King Anouvong of Vientiane rebelled against Siam, leading to the Siamese invasion and subsequent annexation of Vientiane and Champasak. This marked the consolidation of control by the Rattanakosin Kingdom over the territories of the Vientiane Kingdom.
January 1829: In 1828, King Anouvong of Vientiane rebelled against Siam's control, leading to the Siamese invasion of Vientiane and Champasak. The Champasak Kingdom was subsequently absorbed into the Rattanakosin Kingdom, solidifying Siam's control over the region.
Were a series of armed conflicts between the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom and Rattanakosin Kingdom and the various dynasties of Vietnam mainly during the 18th and 19th centuries.
4.1.Siamese-Vietnamese War (1831-34)
Was a war between the Nguyen Dynasty of Vietnam and the Rattanakosin Kingdom of Siam caused by the Siamese attempt to conquer Cambodia and southern Vietnam.
4.1.1.Vietnamese offensives
Were a series of offensive by the Vietnamese Nguyen Dynasty against the Siamese invasion during the Siamese-Vietnamese War (1831-1834).
July 1834: Siamese army to capture Muang Phuan, defeating the Vietnamese forces.
4.2.Siamese-Vietnamese War (1841-45)
Was a war between the Nguyen Dynasty of Vietnam and the Rattanakosin Kingdom of Siam caused by the Siamese attempt to conquer Cambodia and southern Vietnam.
January 1846: After four years of attritious struggle, Siam and Vietnam agreed to a compromise peace and placed Cambodia under joint rule.
4.3.Franco-Siamese War
Was a conflict between the French Republic and the Kingdom of Siam.
October 1893: The Siamese found they had no British support and surrendered to France, ceding Laos during the Treaty of Bangkok of October 3, 1893.
Was a French military campaign to conquer Tonkin and Annam, in Vietnam, that became French protectorates.
5.1.Treaty of Huế
The 1883 and 1884 Treaties of Huế divided the remaining Vietnamese territory into the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin under nominal Nguyen dynasty rule.
August 1883: The 1883 and 1884 Treaties of Huế divided the remaining Vietnamese territory into the protectorates of Annam and Tonkin under nominal Nguyen dynasty rule.
January 1786: In 1785, a resurgent Siam sent an army led by Prince Surasi (Viceroy Boworn Maha Surasinghanat), younger brother of King Rama I, to seek the submission of Patani.
January 1786: Territorial cessions of Siam to the British in 1785.
January 1801: In 1800 Kelantan became independent from Trengganu rule
January 1809: Sultan Dziaddin was forced to abdicate in 1803 by the King of Siam and was replaced by his nephew Sultan Ahmad Tajuddin II. This sparked a succession crisis as crown prince, Tunku Bisnu claimed to be the rightful heir to the throne. Fearing civil war, the Siamese Kingdom reconciled the two parties by appointing Tunku Bisnu as ruler of Setul, thus establishing the Kingdom of Setul Mambang Segara in 1808.
January 1809: The Kingdom of Setul Mambang Segara was established in 1808 in wake of the partition between the rulers in the Royal House of Kedah.
January 1811: The Kingdom of Setul Mambang Segara looses Terang (Trang) to Siam in 1810.
January 1811: The state of Reman was founded in Patani between the older principalities of Pujut, Jalor and Legeh. It emerged as a single polity under Tuan Tok Nik Tok Leh in 1810. Tuan Tok Nik, also known as Tuan Mansor, a Patani nobleman, was appointed to observe the mining-activities in the area during the reign of Muhammad Raja Bakar, the Sultan of Patani.
January 1813: Kelantan falls under Thai sovereignty.
January 1815: Manglon becomes tributary to Hsenwi State.
January 1817: Perak falls under Thai sovereignty.
September 1821: In 1821, Perlis came under the sovereignty of the Rattanakosin Kingdom, ruled by King Rama III.
February 1826: Territorial change based on available maps.
January 1840: The state was established in 1839 as an honour for Tunku Anum, a member of Kedahan nobility after his efforts of restoring the diplomatic ties between Kedah and Siam during the Perang Musuh Bisik (The War of Whispering Enemies) of 1821.
May 1843: On 20 May 1843, the Siamese made Sayyid Hussain Jamalulail, the paternal grandson of a Hadhrami Arab Sayyid immigrant and maternal grandson of the Sultan of Kedah, became the first Raja of Perlis. This made Perlis as a sovereign state. His descendants still rule Perlis, but as rajas, instead of as sultans.
August 1863: With the establishment of the French protectorate, the borders of Cambodia wer fixed. Several minor territories were de facto annexed by the Rattanakosin Kingdom and by Vietnam.
August 1863: The protectorate was established in 1863 when the Cambodian King Norodom requested the establishment of a French protectorate over his country, meanwhile Siam (modern Thailand) renounced suzerainty over Cambodia and officially recognised the French protectorate on Cambodia.
November 1864: Following various resistant movement by the populace during his 10-year reign, the king was forced to abdicate his position as a monarch and reunifying the area into Kedah on 10 November 1864, effectively marking the end of the Kubang Pasu Kingdom.
January 1874: British protectorate established in Perak.
January 1893: The sovereignty of the Kingdom of Setul Mambang Segara effectively ended in 1916, following the dissolution by the Siamese government. Its borders were largely inherited to its successive province, the present-day Satun, Thailand.
January 1893: In 1892, Setul was returned to Kedah.
October 1893: Franco-Siamese War: Kingdom of Luang Phrabang ceded to French Indochina.
October 1894: Final Boundary Treaty for the Siam-Burma border between Thailand and Britain.
January 1900: Chiang Mai became part of the Phayap province of Thailand.
January 1905: In 1904, to get back Chantaburi, Siam had to give Trat and Koh Kong to French Indochina.
January 1905: France forced Siam to cede control of a territory on the west bank of the Mekong opposite Luang Prabang and around Champasak in southern Laos, as well as of western Cambodia.
January 1907: Siamese authorities abolished all tributary kingdoms in the Pattani region and annexed them to the Pattani province (Thai: มณฑลปัตตานี).
March 1907: Trat became part of Thailand again on 23 March 1907.
July 1909: A British protectorate (an unfederated Malay state) is established in Kelantan.
July 1909: A British protectorate (an unfederated Malay state) is established in Perlis.
June 1932: The 1932 Siamese revolution resulted in a nearly-bloodless transition of Siam into a constitutional monarchy system of government.
Disestablishment
June 1932: The 1932 Siamese revolution resulted in a nearly-bloodless transition of Siam into a constitutional monarchy system of government.
.svg.png.webp)
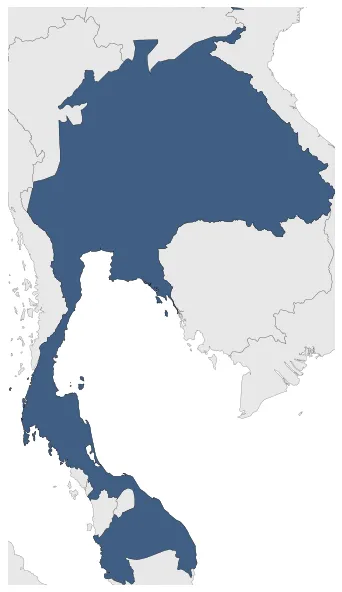
 Rattanakosin Kingdom
Rattanakosin Kingdom