If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
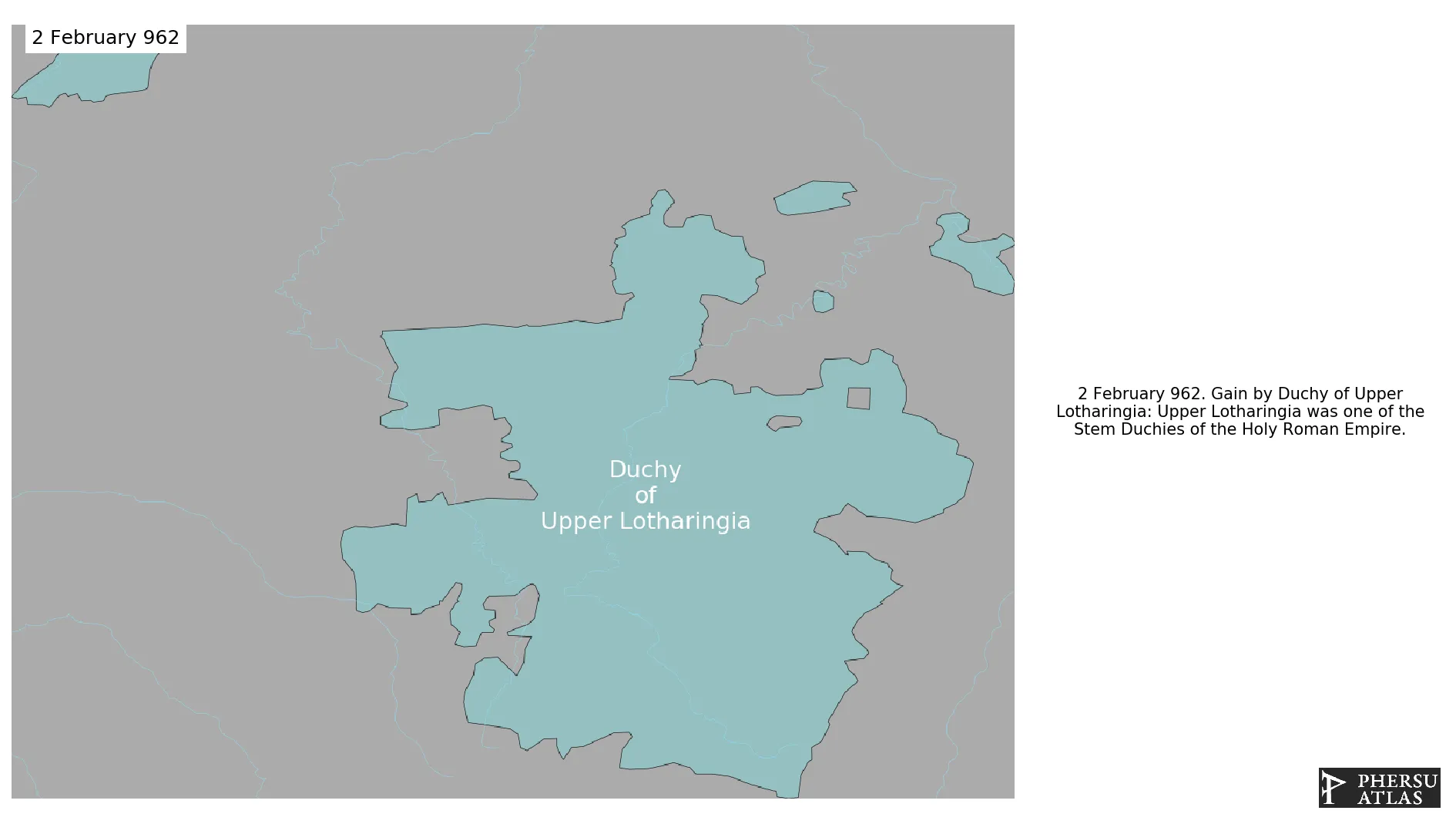
Was one of the stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom.
Establishment
February 962: Upper Lotharingia was one of the Stem Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Frankish Kingdom was partitioned and reuinited several times as the Frankish rulers used to divide their territories equally among their heirs. This lead also to a number of wars and revolts.
1.1.Incoronation of Otto I
East Frankish King Otto I was crowned first Holy Roman Emperor.
Was a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies.
January 1476: After the outbreak of hostilities in the Free County and in Savoy and the unsuccessful siege of Neuss, Charles had the Duchy of Lorraine occupied in 1475.
January 1477: The Duke of Lorraine Returns to his Duchy.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
3.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
January 1634: In 1633, the Duchy of Lorraine was occupied by France due to the hostile stance of its duke, Charles IV.
February 1661: The Peace of Vincennes in 1661 marked the end of the conflict between the Duchy of Lorraine and the Duchy of Upper Lotharingia. The French, under King Louis XIV, withdrew their forces from the territory as part of the peace agreement.
3.1.1.Thirty Years' War Minor Scenarios
A series of conflicts related to the Thirty Years' War.
3.1.1.1.Invasion of Franche Comté (Ten Years War)
Was French invasion of modern-day Franche-Comté, at the time a possession of the Habsburg, during the Thirty Years' War.
January 1645: Following a treaty concluded with Cardinal Mazarin in 1644, France committed to cease hostilities in Franche-Comté, in exchange for the considerable sum of 40,000 écus, thus guaranteeing the region's neutrality once again. The year 1644 thus marked the end of the Ten Years' War in Franche-Comté.
3.1.2.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
August 1632: Occupation of Trier by the French.
March 1635: The Spaniards recapture Trier from the French.
3.1.3.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
3.1.3.1.Low Countries Front (France)
Was the Low Countries front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
January 1636: Spanish occupation of Philippsbourg, Speyer, Landau and Treviri.
Was a war between France and Spain. The French armies of Louis XIV occupied the Franche-Comté and large parts of the Spanish Netherlands.
4.1.Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668)
Was the treaty that ended the War of Devolution. France returned much of his gains.
May 1669: At the end of the War of Devolution France kept Armentières, Bergues, Charleroi, Courtrai, Douai, Furnes, Lille, Oudenarde, and Tournai.
Was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland.
5.1.French invasion of the Rhineland
Was the French invasion of the Rhineland during the War of the Polish Succession.
November 1733: The Duchy of Lorraine was invaded by France.
5.2.Treaty of Vienna (1738)
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Polish Succession. Augustus III was officially confirmed as King of Poland.
November 1738: Stanisław Leszczyński, a Polish nobleman who was briefly King of Poland was compensated with the Duchy of Lorraine in 1738 after losing the Polish throne.
February 1766: The acquisition of Lorraine for the former Polish king, however, proved of lasting benefit to France, as it passed under direct French rule with Stanislaus' death in 1766.
January 993: Otto I, was the first count of Chiny.
January 1001: The Gau counts in the Nahegau assumed the title Wildgrave.
January 1001: The Lordship of Commercy is a feudal entity formed from the 10th century around the town of Commercy.
January 1001: The county of Vaudémont (now in the Meurthe-et-Moselle department) was already known as the county of Saintois in the 9th century. It belonged to the county of Toul, from which it broke away in the 10th century.
January 1001: Independence of the Metz Prince-Bishopric from the Dukes of Lorraine.
January 1034: Bar County is partitioned from Lotharingia.
January 1036: The county of Salm-en-Ardenne, of which Vielsalm was part, was established around the year 1000.
January 1049: The Toul Prince-Bishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1051: In the course of the Middle Ages, Boppard developed into a free imperial city, already under Emperor Henry III. the city received market rights in 1050.
January 1061: In 1060, the title Count of Luxembourg was first used by Conrad I of Luxembourg.
January 1081: Saarbruecken County was established when the region of Saargau was given to Sigebert I, founder of the line of Saarbrücken.
January 1086: In 1085, the Palatinate emerged from the County Palatine of Lotharingia.
January 1091: A Comes de Vianne named Bertolf was first mentioned in 1090, who probably belonged to the house of the Counts of Hamm and Bailiffs of Prüm, which in turn descended from the Counts of Bidgau.
January 1101: Establishment of the Ligny Lordship.
January 1101: The Counts of Flanders from the 11th century onward also held land east of the Scheldt river as a fief of the Holy Roman Empire, an area called "Imperial Flanders" (Rijks-Vlaanderen or Flandre impériale).
January 1101: Finstingen Lordship is mentioned for the first time in 1100.
January 1123: In the Middle Ages, Püttlingen was owned by Bishops of Metz. During the Investiture Controversy (1075-1122), the bishops of Metz, who were loyal to the emperor, transferred the area around Püttlingen to the Lords of Forbach.
January 1151: The male representatives of Dagsuburg now held the titles of Counts of Dagsburg and Counts of Egisheim.
January 1201: The fortified castle was built on the Schlossberg hill at the end of the 12th century.
January 1201: Blankenberg belonged to the family which took its name (Blankenberg in German), then became a fief of the Counts of Salm in the 12th and 13th centuries. They attributed it to one of their youngest, Ferry de Blâmont, youngest son of Henri III de Salm.
January 1221: Establishment of the Imperial city of Oberwesel.
January 1355: In 1354 the County of Bar was raised to a duchy.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
January 1420: The German half of the Duchy of Bar was reunited with the Duchy of Lorraine in 1419.
January 1459: The Finstingen Lordship is acquired by the Duchy of Upper Lotharingia.
January 1467: Since 1466 Épinal belonged to the Duchy of Lorraine.
January 1474: René of Lotharingia inherited the County of Vaudemont.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
January 1486: The Duchy of Bar fell to the Duchy of Lorraine in 1485.
January 1500: The Lordship of Blankenberg was bequeathed to the Duke of Lorraine in 1499.
January 1548: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of the Reformation.
January 1573: The Hanau County is acquired by the Duchy of Upper Lotharingia.
January 1630: Saarwerden is acquired by the Duchy of Upper Lotharingia.
January 1727: Duchy of Upper Lotharingia merged with Wied-Runkel.
February 1766: Based on Gustav Droysen's Holy Roman Empire Maps.
Disestablishment
February 1766: Based on Gustav Droysen's Holy Roman Empire Maps.
February 1766: The acquisition of Lorraine for the former Polish king, however, proved of lasting benefit to France, as it passed under direct French rule with Stanislaus' death in 1766.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany)
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 38-39
Livet, G. (1994): La Guerre de Trente Ans, Paris (France), p. 37
Zeller, O. (2024): La Bresse et le pouvoir: Le Papier journal de Jean Corton, syndic du tiers état (1641-1643), Dijon (France), p. 12

 Duchy of Upper Lotharingia
Duchy of Upper Lotharingia