This article is about the specific polity Second Polish Republic and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 11 November 1918 and 17 September 1939 (and de facto again in 1947 for a short time, before the proclamation of the Polish People's Republic). The state was established at the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of the Second World War.
Establishment
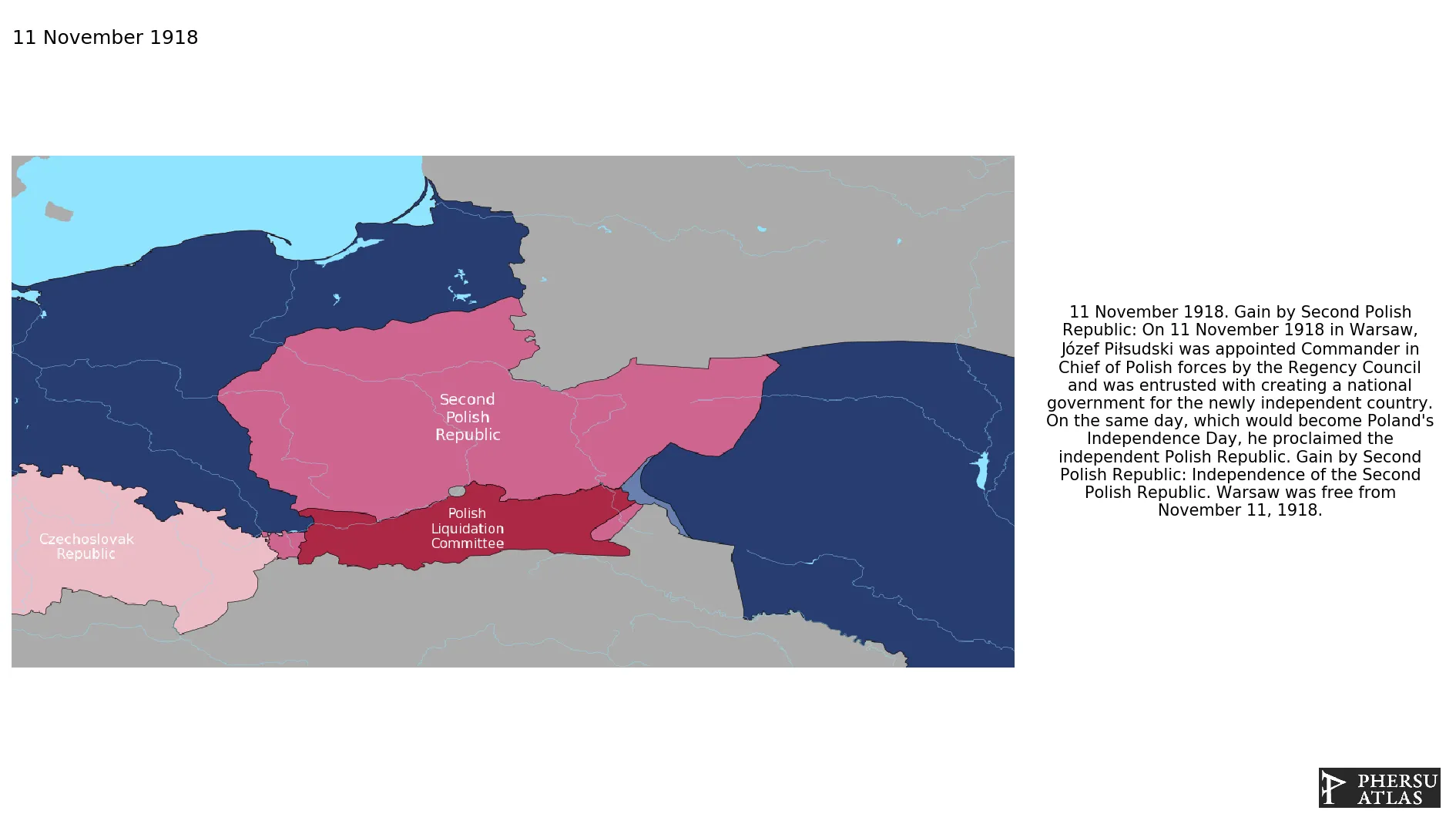
November 1918: Independence of the Second Polish Republic. Warsaw was free from November 11, 1918.
November 1918: On 11 November 1918 in Warsaw, Józef Piłsudski was appointed Commander in Chief of Polish forces by the Regency Council and was entrusted with creating a national government for the newly independent country. On the same day, which would become Poland's Independence Day, he proclaimed the independent Polish Republic.
December 1918: The Polish uprising against German authorities broke out on 27 December 1918 in Poznań. Fighting also start in other towns: Szamotuły, Środa Wielkopolska, Pniewy, Opalenica, Buk, Trzemeszno, Września and Gniezno are captured.
December 1918: The Poles captured Grodzisk Wielkopolski, Kłecko, Kórnik, Wielichowo, Gostyń, Witkowo and other towns.
December 1918: In Poznań, the Poles forced the German 6th Regiment of Grenadiers from their barracks. After talks, the regiment leaved the city with their weapons.
December 1918: The Poles capture Wronki, Wągrowiec, Gołańcz.
December 1918: The Poles capture Kościan, Oborniki Wielkopolskie, Ostrów Wielkopolski.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
1.1.Aftermath of World War I
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
July 1920: Conference of Ambassadors in Spa, Belgium. Division of Orawa and Cieszyn between Poland and Czechoslovakia.
1.1.1.Aftermath of World War I in Poland
Events that happened shortly after the end of World War I in Poland.
1.1.1.Polish-Ukrainian War
Was a conflict between the Second Polish Republic and Ukrainian forces (both the West Ukrainian People's Republic and Ukrainian People's Republic).
February 1919: Ukrainians managed to surround Lviv on three sides.
March 1919: By March 18 the Poles had driven the Ukrainian forces from the Lviv-Przemyśl railroad, permanently securing Lviv.
May 1919: The Polish forces reached the Złota Lipa-Berezhany-Jezierna-Radziwiłłów line.
June 1919: By June 27 the Ukrainian forces had advanced 120 km along the Dnister river and on another they had advanced 150 km, past the town of Brody.
July 1919: The Ukrainian Galician Army and ZUNR leadership were pushed back to the line of the Zbruch river on 16-18 July, after which ZUNR was occupied by Poland.
1.1.2.Hungarian-Romanian War
Was a war between Romania and Hungary over territorial disputes after the dissolution of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I.
1.1.2.1.Hungarian-Romanian War Aftermath
The border between Romania and Hungary after World War I was decided in the The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919).
September 1919: The Treaty of St. Germain established the borders of the Czechoslovak Republic.
September 1919: The Treaty of St. Germain established the borders of the Kingdom of Romania with Poland.
1.1.3.Lithuanian War of Independence
Events that happened shortly after the end of World War I in Lithuania leading to the independence of the country.
January 1919: The German occupying army withdrew from Vilnius and turned the city over to local Polish self-defense forces.
1.1.3.1.Lithuanian-Soviet War
Was a war between Lithuania and the Russian SFSR. Russia considerd Lithuania, that had recently declared independence, a secessionist state. At the end of the war Russia recognized the independency of Lithuania.
January 1919: Vilnius was captured by the Soviet Red Army.
July 1920: Soviet-Lithuanian Peace Treaty signed between Lithuania and Soviet Russia. In exchange for Lithuania's neutrality and permission to move its troops in the territory that was recognised during its war against Poland, Soviet Russia recognized the sovereignty of Lithuania. Lithuania officially maintained that its de jure borders were those delineated by the treaty although a large territory, the Vilnius Region, was controlled by Poland.
1.1.3.2.Polish-Lithuanian War
Was a war between newly-independent Lithuania and Poland following World War I.
January 1920: On October 7, 1920, an agreement was signed by Poland and Lithuania, establishing a truce, known as the Suwałki Agreement: it temporarily accepted the Foch Line.
July 1920: Augustów conquered by RSFSR.
August 1920: Lithuanians conquered Suwalki.
August 1920: The 1st Polish Infantry Regiment assaulted the Lithuanian defenders of the city of Augustów by surprise and disarmed a company of the 10th Lithuanian Infantry Regiment, securing control of the town.
August 1920: Polish Colonel Nieniewski entered the city of Suwałki with his soldiers.
August 1920: On August 31, Sejny was conquered by the Polish army.
September 1920: The Lithuanian army reached Augustów.
September 1920: The Lithuanian forces advancing from Sejny were routed and Augustów again fell into Polish hands.
September 1920: Polish forces recaptured Sejny.
September 1920: End of the Polish-Lithuanian War.
September 1920: Sejny is acquired by Poland at the end of the Polish-Lithuanian War.
1.1.4.Greater Poland uprising (1918-19)
Was a military insurrection of Poles in the Greater Poland region against German rule.
January 1919: The Second Polish Republic captured Jarocin, Krotoszyn and Mogilno.
January 1919: Czarnków, Jutrosin, Kruszwica, Nakło, Nowy Tomyśl, Miejska Górka, Rawicz, Strzelno and Wolsztyn are captured by the Poles.
January 1919: Inowrocław conquered by Second Polish Republic.
January 1919: The Germans recapture Chodzież and Czarnków.
January 1919: The Poles recaptured Chodzież Battle of Chodzież and Czarnków. They also win the Battle of Ślesin and capture Sieraków.
January 1919: The Poles lose Nakło to the Germans.
January 1919: The Germans recapture Sarnowa and win the Battle of Zbąszyń.
January 1919: Polish victory in the Battle of Szubin and capture Łabiszyn, Złotniki and Żnin.
January 1919: The Germans recapture Szamocin.
January 1919: Poles are forced to leave Potulice.
January 1919: Poles capture Babimost and Kargowa.
January 1919: In the Battle of Rynarzewo, the Germans capture Szubin.
February 1919: A Polish counterattack forced a German withdrawal to northern bank of the Noteć River. The Poles recaptured Rynarzewo and won the Battle of Kcynia.
February 1919: Poles recapture Szubin.
February 1919: Germans use an armoured train to capture Kargowa and Babimost, but their offensive is stopped near Kopanica.
June 1919: With the treaty of Versailles German eastern territories were officially ceded to Poland.
1.1.5.Polish-Czechoslovak War
Was a military confrontation between Czechoslovakia and Poland over the territory of Cieszyn Silesia in early 1919.
January 1919: Cieszyn Silesia was taken over by Czechoslovak forces on 27 January 1919. Polish troops retreated to the Vistula river.
February 1919: The Czechoslovak army withdrew to the new Green Line, established by the International Commission Agreement on the basis of the Czechoslovak-Polish Treaty, concluded on 3 February 1919 in Paris.
1.1.6.Aftermath of World War I in Pokuttya
Events that happened shortly after the end of World War I in the Pokuttya region.
August 1919: In late summer of 1919 Polish troops entered Pokuttya (see Polish-Ukrainian War) and the Romanians withdrew to their country.
1.1.7.Sejny Uprising
Was a Polish uprising against the Lithuanian authorities in August 1919 in the ethnically mixed area surrounding the town of Sejny.
September 1919: After several military skirmishes, Polish forces secured Sejny and the Lithuanians retreated behind the Foch Line.
1.1.8.Treaty of St Germain
Was a treaty that settled the dissolution of Austria-Hungary after World War I.
Was a Civil War in Russia that involved varios factions but mainly the Bolsheviks and the conservative White Army in the core Russian territories, as well as a multitude of local secessionist states. At the end of war the Bolsheviks were victorious and established the Soviet Union.
2.1.Pro-independence movements in the Russian Civil War
Local independence movement caused several secessions and revolts during the Russian Civil War.
2.1.1.Establishment of the Republic of Perloja
Was the creation of the small Republi of Perloja, in Lithuania, during the Russian Civil War.
January 1924: In 1923, Perloja was divided along the Merkys River, leaving one bank to Lithuania and another to the Second Polish Republic.
2.2.Ukrainian-Soviet War
Was a conflict between Ukrainian nationalist forces and the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War. It also included a multitude of ethnical and local factions.
January 1919: The Komancza was suppressed by the Polish government as part of the Polish-Ukrainian War.
April 1920: The Lemko Republic was ended by the Polish government in March 1920.
2.3.Soviet westward offensive of 1918-25
Was a military campaign by the Russian SFSR into regions that had been evacuated by the German forces in eastern Europe after World War I.
2.3.1.Soviet westward offensive in Poland
Was a military offensive by the Russian SFSR in Poland after the German army left the area.
February 1919: The Soviet westward offensive came to a halt by late February.
May 1919: In April the Bolsheviks captured Grodno and Vilna.
2.4.Polish-Soviet War
Was a war between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic in the aftermath of World War I and during the Russian Civil War.
April 1919: Polish forces under General J. Lasocki recaptured Lida.
April 1919: French General A. Mokrzecki captured Nowogródek and Baranowicze.
April 1919: The major city of Vilnius was taken by Polish cavalry units.
June 1919: By May units of Rydz-Śmigły had advanced to the north and east and reached the line of Łyngmiany-Ignalino-Hoduciszki-Narocz lake.
June 1919: Polish General Mokrzecki engaged Russians east of Baranowicze.
July 1919: Polish armies attacked Mołodeczno and captured it on 4 July.
July 1919: Łuniec in the Polesie region was captured by Polish forces.
July 1919: In mid-July, the Soviet counteroffensive near Naliboki was stopped.
August 1919: Polish forces continued their push and captured Minsk.
August 1919: Dubno and Krzemieniec in the Wołyń region were captured by Polish forces.
August 1919: The town and fortress of Równe was captured by Polish forces.
August 1919: On 18 August Zasław was occupied by Polish forces.
August 1919: Borysów conquered by Second Polish Republic.
August 1919: After heavy fighting, the Polish army captured fortress Bobrujsk near Berezyna.
October 1919: Polish forces reached Daugava River and secured the region from Dzisna to Dyneburg.
October 1919: Borysów conquered by Second Polish Republic.
January 1920: By early January 1920, Polish forces had reached the line of Uszyca-Płoskirów-Starokonstantynów-Szepietówka-Zwiahel-Olewsk-Uborć-Bobrujsk-Berezyna-Dyneburg.
April 1920: By March, Polish forces had driven a wedge between Soviet forces in the north (Bielorussia) and south (Ukraine), capturing the towns of Mozyrz and Kalenkowicze.
July 1920: The RSFSR captured Brodno.
July 1920: Supported by Lithuanian forces, the Poles captured Wilno on 14 July.
July 1920: The Galician Soviet Socialist Republic was a Bolshevik's self-declared and short-lived political entity that existed from 15 July to formally 21 September 1920. The communist state was established during a successful counter-offensive of the Red Army in the summer of 1920 as part of the Polish-Soviet War.
July 1920: The Polish 1st Army had to retreat behind Neman River.
July 1920: On 19 July Grodno fell to the Red Army.
August 1920: Brest-Litovsk conquered by RSFSR.
August 1920: Łomża and Ostrołęka conquered by RSFSR.
August 1920: Polish forces managed to recapture Brody.
August 1920: The fortress of Brześć Red Army in the first attack.
September 1920: Sovietic Offensive in Poland of August 1920.
September 1920: The Galician Soviet Socialist Republic is absorbed by Poland.
October 1920: Polish counteroffensive of October 1920.
2.4.1.Russian Offensive (Polish-Soviet War)
Was an offensive by the Russian SFSR against Poland during the Polish-Soviet War.
February 1919: The first serious armed conflict of the Polish-Soviet War took place around 14 - 16 February, near the towns of Manevychi and Biaroza in Belarus.
March 1919: In early March 1919, Polish units opened an offensive and forces under General Stanisław Szeptycki captured the cities of Słonim.
March 1919: Polish forces under General A. Listowski took Pinsk.
2.4.2.Battle of Warsaw
Were a series of battles during the Polish-Soviet war that resulted in the defeat of the invading Russian SFSR.
August 1920: Soviet assault at Radzymin.
August 1920: Polish forces recaptured Radzymin.
August 1920: By the end of August, the 4th and 15th Red Armies had been defeated in the field, and their remnants crossed the border into East Prussia.
August 1920: Russian Budionny's cavalry moved through weakly defended areas, reached city of Zamość and attempted to take it.
September 1920: What was left of Buidonny's 1st Cavalry Army retreated towards Włodzimierz Wołyński.
September 1920: Battle of the Niemen River.
September 1920: On 18 September Polish forces recaptured Równe.
September 1920: Petliura's Ukrainian forces defeated the Bolshevik 14th Army and on 18 September took control of the left bank of the Zbruch river.
September 1920: The Second Polish Republic Captured Lida and Pińsk.
October 1920: The soviet Tukhachevski managed to reorganize the eastward-retreating forces and in September established a new defensive line running from the Polish-Lithuanian border to the north to the area of Polesie, with the central point in the city of Grodno in Belarus.
October 1920: After the mid-October Battle of the Szczara River, the Polish Army had reached the Tarnopol-Dubno-Minsk-Drisa line.
October 1920: After the mid-October Battle of the Szczara River, the Polish Army had reached the Tarnopol-Dubno-Minsk-Drissa line.
March 1921: A ceasefire was signed between Poland and Soviet Russia on 12 October and went into effect on 18 October. Borders were settled in the Peace of Riga, signed in Riga on 18 March 1921.
On 29 September, the Munich Agreement was signed by Germany, Italy, France, and Britain. The Munich Agreement stipulated that Czechoslovakia must cede Sudeten territory to Germany. Germany dismembered Czechoslovakia.
October 1938: As Czechoslovakia was being absorbed into the German Reich, Zaolzie, the Czech half of Cieszyn, was annexed by Poland in 1938 following the Munich Agreement and the First Vienna Award. At noon on September 30, Poland gave an ultimatum to the Czechoslovak government. It demanded the immediate evacuation of Czech troops and police from Zaolzie and gave Prague until noon the following day. At 11:45 a.m. on October 1 the Czech foreign ministry called the Polish ambassador in Prague and told him that Poland could have what it wanted.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
4.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
4.1.1.Invasion of Poland
Was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union. It marked the beginning of World War II.
September 1939: The German armies opened their offensive on September 1 at 5:45 AM, crossing the Polish frontiers on all fronts. Athe Fourteenth army attacked with two groups, one in the Mahrisch Ostrau towards Cracow, and the second group from the Sillein area of northern Slovakia. At the same time the the Fourth Army reached the line Konitz-Nakel.
September 1939: Polish forces at Wieluń surrender to the German 10th Army.
September 1939: Advancement of the German campaign in Poland by September 3rd.
September 1939: Battle of Mława.
September 1939: Polish forces around Piotrków surrender to the German 10th Army.
September 1939: On September 6, without opposition, the Mahrisch Ostrau group of the Fourteenth Army captured Cracow, principal city of southern Poland.
September 1939: The siege of Westerplatte concludes with the surrender of its remaining garrison to the Germans. Tarnów falls to the 14th Army.
September 1939: The pocket at Radom is reduced by the German 14th Army.
September 1939: On September 9 the army had reached the line Dukla-Rzeszow-Kolbuszowa.
September 1939: By the 10th the German forces reached the the east bank of the San at Radymno and Jaroslav. The 1st German Mountain Division forced a crossing of the San at Sanok, in the Carpathian foothills.
September 1939: On the 11th, German forces were south of the Fort of Przemysl, and has also reached Sambor and Lemberg.
September 1939: Advancing rapidly on the 12th, the Third Army cut the railroad lines leading from Warsaw to Bialystok and Siedlce.
September 1939: Advancement of the German campaign in Poland by September 13th.
September 1939: The German Third Army captured Brest Litovsk on the 14th.
September 1939: Przemyśl is captured by the German Army.
September 1939: Advancement of the German campaign in Poland by September 15th.
September 1939: The Red Army invades eastern Poland.
September 1939: Kutno falls to the German 8th Army and Brest-Litovsk falls to the 3rd Army.
September 1939: Soviet forces capture Wilno.
September 1939: Advancement of the German campaign in Poland by September 18th.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 19 September.
September 1939: Advancement of the German campaign in Poland by September 20th.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 20 September.
September 1939: Advance of the German Invasion of Poland until 21 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 21 September.
September 1939: Advance of the German Invasion of Poland until 22 September.
September 1939: The Red Army occupies Lviv.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 23 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 24 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 25 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 26 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 27 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 28 September.
September 1939: German capture of Modlin.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 29 September.
September 1939: Advance of the German Invasion of Poland until 30 September.
October 1939: The garrison of the Hela Peninsula, besieged by land and naval forces, surrendered to German forces on October 1.
October 1939: Warsaw surrendered to German forces on September, 27. German forces occupied the city ca. on October, 1st.
October 1939: The Battle of Kock ends with the surrender of defending Polish forces. This is the final significant military resistance to the German or Soviet invasions.
4.2.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
August 1945: At the Potsdam Conference the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union placed the German territories (within the 1937 Nazi Germany borders) east of the Oder-Neisse line, and with the exception of parts of East Prussia, as formally under Polish administrative control. The 1919 Versailles Treaty created Free City of Danzig was also placed under Polish administration.
February 1947: Creation of the Polish People's Republic.
Disestablishment
February 1947: Creation of the Polish People's Republic.
Selected Sources
Campaign In Poland, 15-22 September 1939. United States Military Academy of Westpoint. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope07.jpg
Cook, C. / Stevenson, J. (2006): The Routledge Companion to World History since 1914, Routledge, p.20
Kamp wrzesn9-03. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-03.png
Kamp wrzesn9-13. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-13.png
Kamp wrzesn9-17. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-17.png
Kamp wrzesn9-18. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-18.png
Kamp wrzesn9-19. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-19.png
Kamp wrzesn9-21. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-21.png
Kamp wrzesn9-22. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-22.png
Kamp wrzesn9-23. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-23.png
Kamp wrzesn9-24. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-24.png
Kamp wrzesn9-25. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-25.png
Kamp wrzesn9-26. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-26.png
Kamp wrzesn9-27. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-27.png
Kamp wrzesn9-28. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-28.png
Kamp wrzesn9-29. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-29.png
Kamp wrzesn9-30. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-30.png
Kennedy, R.M. (1956): The German Campaign in Poland, 1939, Department of the Army, p. 108
Kennedy, R.M. (1956): The German Campaign in Poland, 1939, Department of the Army, p. 113
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. Map No. 3. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/Germany/DA-Poland/maps/DE-Poland-3.jpg
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. p.17
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. p.18
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. p.22
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. p.26
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. p.31
The German Campaign in Poland: September 1 to October 5, 1939. Chief of Staff, US Army: Digests and Lessons of Recent Military Operations. United States Government Printing Office Washington: 1942. pp. 12-13
.svg.png.webp)
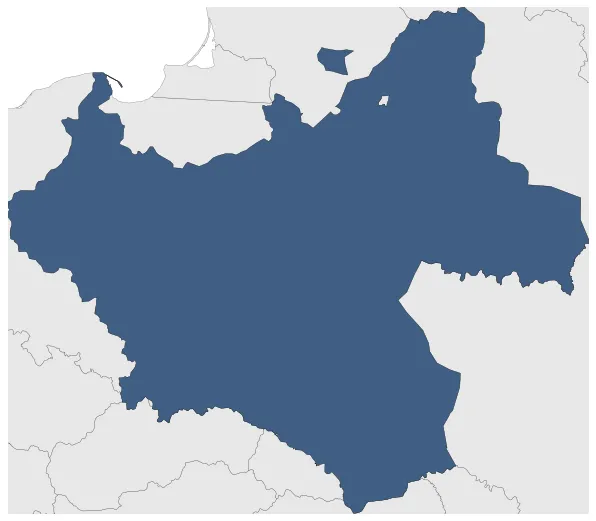
 Second Polish Republic
Second Polish Republic