This article is about the specific polity Song Dynasty and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an imperial dynasty of China. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.
Establishment
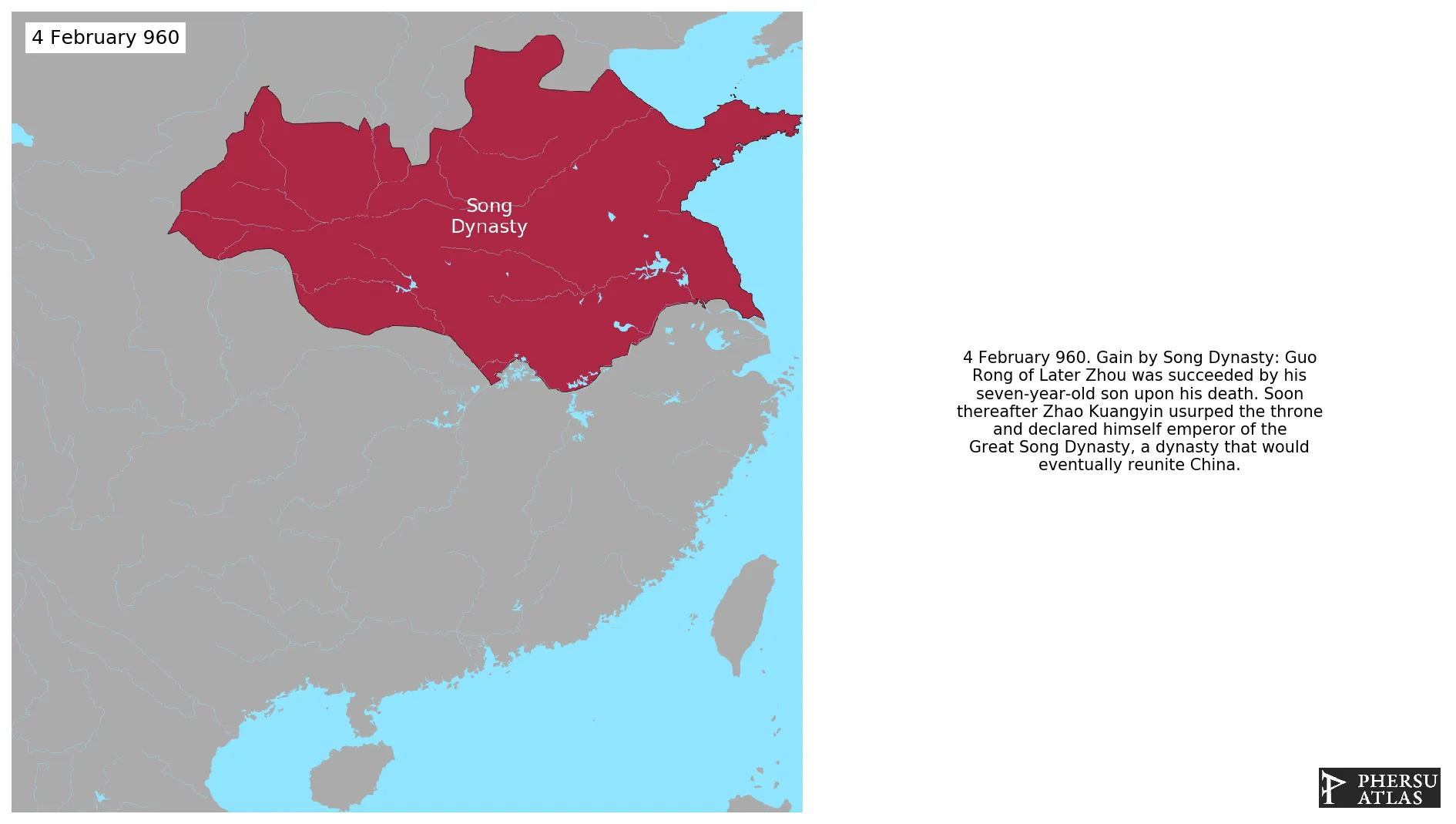
February 960: Guo Rong of Later Zhou was succeeded by his seven-year-old son upon his death. Soon thereafter Zhao Kuangyin usurped the throne and declared himself emperor of the Great Song Dynasty, a dynasty that would eventually reunite China.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military conflicts fought by the Northern Song dynasty, Western Xia dynasty, and Liao dynasty from the late 10th century to early 12th century.
January 1006: Western Xia Expansion by 1005.
January 1033: In 1032, Western Xia emperor Yuanhao annexed the Tibetan confederation of Xiliangfu.
January 1104: In 1103, the Song dynasty annexed Tsongkha.
January 1137: Western Xia Expansion by 1136.
1.1.Jiqian's rebellion
Li Jiqian, did not agree to this and refused to submit to Song administration.
January 983: Li Jiqian refused to submit to Song administration and established the Western Xia.
January 986: The Western Xia capture Yinzhou.
1.2.Shenzong's invasion
In 1081, the Song dynasty launched a military attack on the Western Xia.
January 1082: In 1081, the Song dynasty launched a five-pronged attack on the Western Xia.
Was an era of disunity in Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three provinces of Tibet in 1253, under the Yuan dynasty.
January 1073: The Song dynasty gains control of Wushengjun.
Was a military conflict between the Lý dynasty of Đại Việt and the Song dynasty of China between 1075 and 1077. .
November 1075: In the October 1075, Nùng Tông Đản led 23,000 soldiers advancing into Song territory in Guangxi.
March 1076: In the early spring of 1076, Lý Thường Kiệt and Nùng Tông Đản defeated the Song reinforcements to Yongzhou and, during a battle at Kunlun Pass, their forces beheaded the Governor-General of Guangnan West Circuit, Zhang Shoujie. Afterwards, the Vietnamese forces then marched towards the city of Yongzhou, where they were temporarily held up by a fierce resistance led by the Yongzhou governor Su Jian, who with three thousand soldiers prevented the city from falling for forty-two days.
April 1076: When Song forces attempted to challenge Lý Thường Kiệt's forces, the latter retreated from Yongzhou, with their spoils of war and thousands of prisoners.
January 1083: As a result of mounting casualties on both sides, Thường Kiệt made peace overtures to the Song in 1077. Captured territories held by both Song and Vietnamese were mutually exchanged in 1082, along with prisoners of war.
3.1.Chinese Counterattack
Was a counterattack by the Chinese Song Dynasty against the invading armies of Đại Việt.
January 1078: By 1077, the Song had destroyed two other Vietnamese armies and marched towards their capital at Thăng Long. Song forces were halted at the Nhu Nguyệt River.
January 1078: The Song regained Quảng Nguyên prefecture.
Were a series of conflicts between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty (1115-1234) and the Han-led Song dynasty (960-1279).
September 1123: One month after the Song had recovered Yanjing, Zhang Jue, who had served as military governor of the Liao prefecture of Pingzhou about 200 kilometres east of Yanjing, killed the main Jin official in that city and turned it over to the Song.
December 1123: The Jurchens defeated the armies of Zhang Jue and took Pingzhou.
4.1.Jin-Song Alliance against Liao
In 1114 the chieftain Wanyan Aguda (1068-1123) united the Jurchen tribes and led a revolt against the Liao. .
June 1123: The Song tried to help the Jin but had several military failures. They wanted the sixteen prefectures that they had ceded to the Liao in the past but the Jin due to the "poor support" gave them only a part of it. In the spring of 1123 the two sides finally set the terms of the first Song-Jin treaty. Only seven prefectures (including Yanjing) would be returned to the Song.
4.2.First Jurchen campaign against the Song Dynasty
Was a military campaign by the Jin Dynasty against the Song Dynasty.
December 1125: Zongwang (Jin Dynasty) took Yanjing, where Song general and former Liao governor Guo Yaoshi switched his allegiances to the Jin.
January 1126: By the end of December 1125, the Jin army had seized control of two prefectures and re-established Jurchen rule over the Sixteen Prefectures.
January 1126: Jin armies besieged the city of Taiyuan in mid January 1126.
January 1126: The Jurchen forces reached the Yellow River.
January 1126: Kaifeng, the capital of the Northern Song Dynasty, was besiegedby the Jin dynasty.
March 1126: The Song recognized Jin control over three prefectures. The Jurchen army ended the siege of Kaifeng in March after 33 days.
March 1126: The Song recognized Jin control over three prefectures. The Jurchen army ended the siege of Kaifeng in March after 33 days. The prefectures of Hejian, Taiyuan, and Zhongshan and the sixteen prefectures went to the Jurchen, all the other occupied regions remained to the Song
March 1126: Almost as soon as the Jin armies had left Kaifeng, Emperor Qinzong reneged on the deal and dispatched two armies to repel the Jurchen troops attacking Taiyuan and bolster the defenses of Zhongshan and Hejian.
October 1126: Taiyuan fell in September 1126, after 260 days of siege by the Jin dynasty.
4.3.Second Jurchen campaign against the Song Dynasty
Was a military campaign by the Jin Dynasty against the Song Dynasty.
December 1126: The Jin assaulted Kaifeng in mid-December 1126.
January 1127: The Song emperor offered his unconditional surrender to the Jurchen, who occupied the northern areas of Song.
4.4.Third Jurchen campaign against the Song Dynasty
Was a military campaign by the Jin Dynasty against the Song Dynasty.
November 1127: After reigning for barely one month in Da Chu, Zhang Bangchang was persuaded by the Song to step down as emperor of the Great Chu and to recognize the legitimacy of the Song imperial line.
January 1130: In December 1129, the Jin started a new military offensive, dispatching two armies across the Huai River in the east and west. On the western front, an army invaded Jiangxi, the area where the Song dowager empress resided, and captured Hongzhou.
January 1130: On the eastern front, Wuzhu commanded the main Jin army. He crossed the Yangtze southwest of Jiankang and took that city when Du Chong surrendered.
January 1130: The Song disbandment of the Great Chu and execution of Zhang Bangchang antagonized the Jurchens and violated the treaty that the two parties had negotiated. The Jin renewed their attacks on the Song and quickly reconquered much of northern China.
January 1130: The Jin seized Hangzhou.
February 1130: Shaoxing conquered by Jin dynasty (1115-1234).
April 1130: The Jin captured Kaifeng in early 1130.
November 1130: Reluctant to let the war drag on, the Jin decided to create Da Qi (the "Great Qi"), their second attempt at a puppet state in northern China. Da Qi was formed late in 1130, and the Jin enthroned Liu as its emperor. Some territories in northern Song were evacuated by the Jin.
January 1131: Wuzhu's troops came back south of the Yangtze one last time to Jiankang, which they pillaged, and then headed north. Yet the Jin had been caught off guard by the strength of the Song navy, and Wuzhu never tried to cross the Yangtze River again.
February 1131: Wuzhu's troops came back south of the Yangtze one last time to Jiankang, which they pillaged, and then headed north. Yet the Jin had been caught off guard by the strength of the Song navy, and Wuzhu never tried to cross the Yangtze River again.
December 1133: With Jin support, Da Qi invaded the Song in November 1133. Xiangyang and nearby prefectures were defeated by his army.
January 1135: The armies of Qi and Jin won a series of victories in the Huai valley, but were repelled by Han Shizhong near Yangzhou and by Yue Fei at Luzhou.
January 1135: In 1134, Yue Fei defeated Li and retook Xiangyang and its surrounding prefectures.
January 1136: With the death of Jin Emperor Taizong, the Song reconquered the Huai valley.
April 1140: An invading Jurchen army led by Wizhu retreated Kaifeng, allowing Song forces to take Zhengzhou and Luoyang.
July 1140: On July 8, 1140, at the Battle of Yancheng, Wuzhu launched a surprise attack on Song forces with an army of 100,000 infantry and 15,000 horsemen. Yue Fei directed his cavalry to attack the Jurchen soldiers and won a decisive victory.
January 1141: In 1140, Song general Yue was forced to withdraw from Zhengzhou and Luoyang after the emperor ordered him to return to the Song court.
January 1141: Song forces recaptured Zhengzhou and Luoyang.
4.5.Treaty of Shaoxing
Was the agreement that ended the military conflicts between the Jin dynasty and the Southern Song dynasty.
October 1142: On October 11, 1142, after about a year of negotiations, the Treaty of Shaoxing was ratified, ending the conflict between the Jin and the Song. By the terms of the treaty, the Huai River, north of the Yangtze, was designated as the boundary between the two states.
4.6.Wanyan Liang's war
Was a military invasion of the Song Dynasty by the Jurchen ruler of the Jin Dynasty Wanyan Liang.
November 1161: Wanyan Liang, emperor of the Jin Dynasty, began the invasion of Song in 1161 without formally declaring war. The Song lost the Huai to the Jurchens.
November 1161: A few Jin prefectures in the west were captured by the Song Dynasty.
January 1163: On December 15, Wanyan Liang was assassinated in his military camp by disaffected officers. He was succeeded by Emperor Shizong (r. 1161-1189). Shizong was pressured into ending the unpopular war with the Song, and ordered the withdrawal of Jin forces in 1162.
4.7.War of 1206 -1208
Was an unsuccesful military invasion of the Jin Dynasty by the Song Dynasty.
September 1206: The Jin repelled the Song in Sizhou 泗州 (on the north bank of the Huai River across from modern Xuyi County).
December 1206: The Jin initiated an offensive against Song prefectures in the central front of the war, capturing Zaoyang and Guanghua (on the Han River near modern Laohekou).
November 1208: In 1208, the peace treaty was signed between the Jin Dynasty and the Song Dynasty in China. The treaty was signed after both sides agreed to return to the status quo ante bellum, ending the conflict between the two dynasties.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
January 1259: In 1258, Mongol forces captured Chengdu.
5.1.Conquest of Western Xia
Was a series of conflicts between the Mongol Empire and the Tangut-led Western Xia dynasty in northwestern China. Western Xia was finally annexed to the Mongol Empire.
5.1.1.Second Mongol Invasion of Western Xia
Was the second Mongol military campaign in Western Xia. Western Xia was inglobated in the Mongol Empire.
August 1225: Genghis Khan lay siege to Suzhou, which fell after five weeks.
5.2.Conquest of Song China
Was the Mongol conquest of the Chinese Song Dynasty.
January 1232: The Song patrols were under the command of Chancellor Jia Sidao, while the Mongol envoy was likely a representative of Genghis Khan's grandson, Kublai Khan. The raid on Sichuan was part of the Mongol Empire's efforts to expand their territory and exert dominance over the region.
January 1236: In 1235, the Mongol Empire, led by Kublai Khan, launched an offensive against the Song dynasty. They successfully captured Siyang-yang, the Yangtze River, and Sichuan. However, they struggled to maintain control over these territories due to resistance from local forces.
February 1236: During the Mongol invasion in 1236, the Song Dynasty lost control of Siyang-yang, the Yangtze River, and Sichuan.
January 1237: Xiangyang was a strategic city in China defended by Song general Cao Youwen. The city fell to the Mongol Empire in 1236, marking a significant victory for the Mongols in their conquest of China.
January 1240: In 1239, General Meng defeated the Mongols and retook Xiangyang.
January 1242: In 1241, during the Mongol invasion of the Southern Song Dynasty, the Mongols under the command of Kublai Khan successfully captured Chengdu, a significant city in the Sichuan province of China.
January 1243: The Mongols captured Hangzhou and invaded Sichuan in 1242.
January 1244: In 1242 and 1243, Mongols led by Kublai Khan raided Sichuan, a region in southwestern China.
January 1245: In 1244, Mongols led by Kublai Khan raided Huainan, a city in southern China.
February 1245: Huainan is reconquered by the Song Dynasty.
January 1246: In 1245, the Mongols, led by the famous conqueror Genghis Khan's grandson Kublai Khan, successfully occupied Shouzhou.
January 1253: In 1252, the Mongol Empire, led by the Chinese general Wang Dechen, conquered Lizhou in Sichuan. This marked a significant expansion of Mongol territory in China during the reign of Kublai Khan.
October 1253: Mongol forces occupy Lizhou.
February 1259: Möngke Khan's forces take Yazhou.
January 1274: In 1273, Fancheng capitulated.
March 1276: When Bayan and Dong Wenbing camped outside Lin'an in February 1276, the Song Grand Empress Dowager Xie and Empress Dowager Quan surrendered.
5.3.Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus'
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered the Kievan Rus' in the mid-13th century.
January 1243: In 1242 and 1243, Mongols led by Kublai Khan raided Sichuan, a region in southwestern China.
January 964: In 963 the Wuping Circuit was seized by Song Dynasty.
January 964: Due to its size and location, Jingnan was the first of the kingdoms to succumb to the Song Dynasty, surrendering when armies from the north invaded in 963, ending the kingdom.
January 966: The Later Shu kingdom was invaded by and incorporated into the expanding Song empire in 965.
January 972: In 971, Liu Chang of the Southern Han Dynasty surrendered to the Song dynasty.
January 976: The Chiefdom of Shuidong was established by Song Jingyang during the Song dynasty. After he conquered the Manzhou Prefecture (centred on modern Kaiyang County) from the Yi people, Song Jingyang was recognized as the hereditary ruler of the region by the Song court in 975.
January 977: In 976, the Song dynasty annexed Southern Tang.
January 979: In 978, the last ruler of Wuyue, Qian Chu, surrendered to the Song dynasty.
January 979: In 978, with Song's determination to unify Chinese lands in full order, Chen decided that he could not stay de facto independent, and offered the control of the circuit to Song's Emperor Taizong, ending Qingyuan Circuit as a de facto independent entity.
September 979: In the summer of 979, Emperor Taizong of Song took Taiyuan and annexed Northern Han.
January 980: In 979, the Song dynasty annexed Northern Han.
January 1001: Extension of the Liao Dynasty by the year 1000.
January 1005: Khitan aggression towards the Song culminated in a full scale invasion in 1004 by Emperor Shengzong of Liao. Khitan forces penetrated as far as Chanzhou at the Yellow River.
January 1005: In January 1005, the Khitan general Xiao Dalin was killed by a giant crossbow, crippling the Khitan offensive. Peace negotiations commenced from 13 to 18 January. In the resulting peace treaty, known as the Chanyuan Treaty, the two sides agreed to delineate their territorial boundaries.
January 1074: In 1072 and 1073, the Song commander Wang Shao defeated the Tibetans of Tsongkha and conquered Xizhou and Hezhou.
December 1081: By November, the Xia had abandoned the middle of the Ordos plateau, losing Xiazhou.
October 1082: The Western Xia captured Yongle.
January 1104: In 1103, the Song annexed Tsongkha and spent the following year weeding out native resistance.
January 1171: In 1170, the Song occupied the Penghu Islands.
February 1232: The Mongol envoy killed by Song patrols was sent by Genghis Khan, the founder of the Mongol Empire. The raid on Sichuan was led by Subutai, one of Genghis Khan's most trusted generals. This event marked the beginning of the Mongol invasion of China.
February 1243: In 1242 and 1243, Mongols led by Kublai Khan raided Sichuan, a region in southwestern China.
February 1244: In 1242 and 1243, Mongols led by Kublai Khan raided Sichuan, a region in southwestern China.
January 1274: After strengthening his government in northern China, Kublai pursued an expansionist policy in line with the tradition of Mongol and Chinese imperialism. He renewed a massive drive against the Song dynasty to the south. Kublai besieged Xiangyang between 1268 and 1273, the last obstacle in his way to capture the rich Yangzi River basin.
April 1275: Bayan's Mongol forces crossed the Yangtze at Hankou and in March met Jia Sidao in battle at Dingjiaozhou, annihilating his force using artillery equipment, conquering the Hanshui region.
Disestablishment
March 1276: When Bayan and Dong Wenbing camped outside Lin'an in February 1276, the Song Grand Empress Dowager Xie and Empress Dowager Quan surrendered.
Selected Sources
Western_Xia_Expansion. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Datei:Western_Xia_expansion.png
 Song Dynasty
Song Dynasty