If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Polity that includes all territories military occupied bythe Soviet Union that are not part of a specific military territory.
Establishment
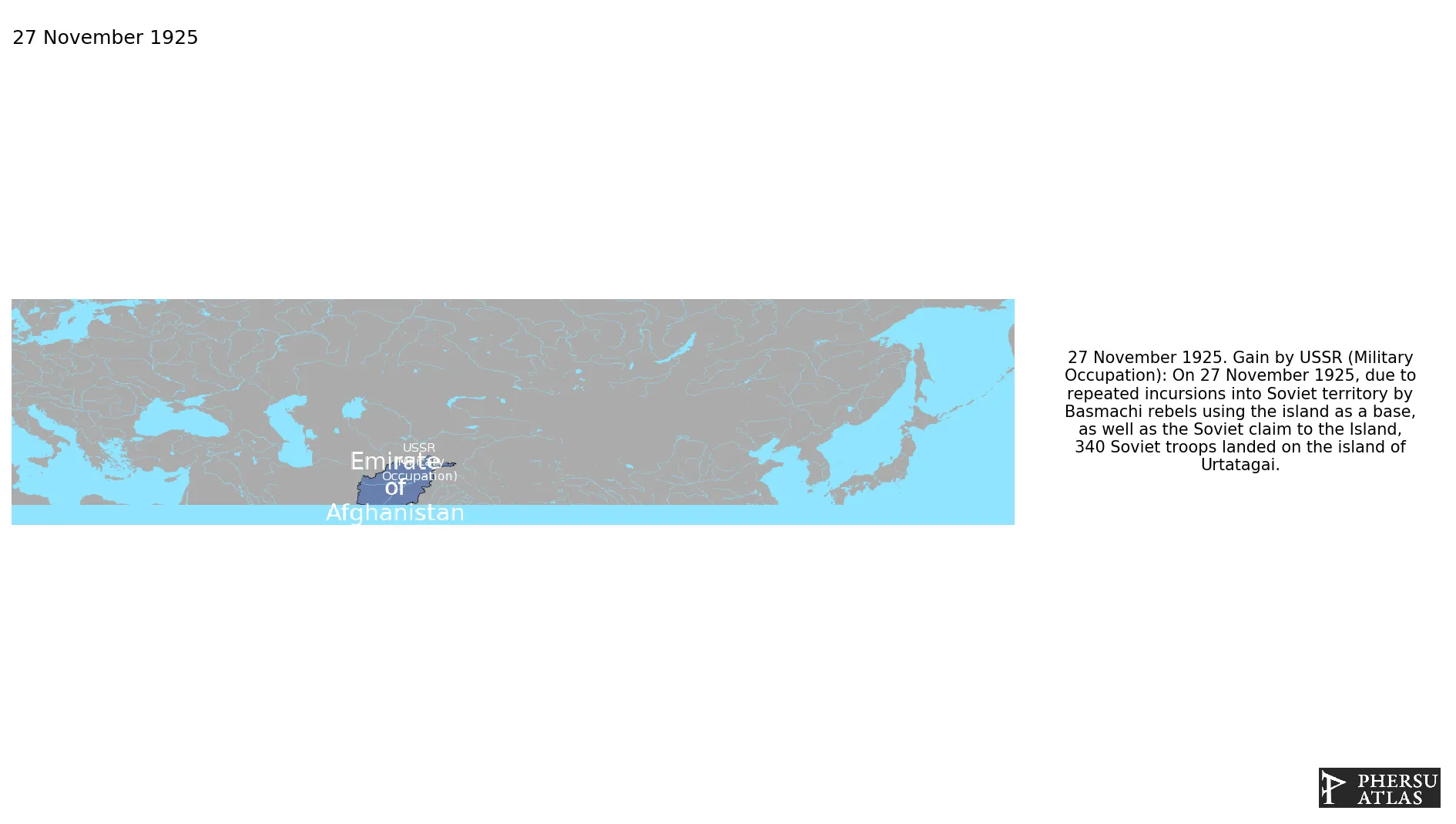
November 1925: On 27 November 1925, due to repeated incursions into Soviet territory by Basmachi rebels using the island as a base, as well as the Soviet claim to the Island, 340 Soviet troops landed on the island of Urtatagai.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a conflict between the Soviet Union and the Emirate of Afghanistan in the mid-1920s over the control of the island of Urtatagai.
February 1926: Western press took interest in the conflict, and supported the Afghan government. With potential war looming, the Soviet leadership decided to let a joint commission decide Urtatagai's fate, which ruled in favour of Afghanistan. On 28 February 1926, the Soviets transferred the island to Afghanistan in a ceremony.
Was a civil war in Afghanistan.
2.1.Afghan campaign of the Red Army (1929)
Was a special operation aimed at supporting the ousted king of Afghanistan, Amanullah Khan, against the Saqqawists and Basmachi.
April 1929: On the morning of 22 April, Primakov’s detachment began shelling Mazar-i-Sharif. Machine guns hit the defenders on the walls. Two hours after the start of the battle, the gunners brought the guns to the entrance to the citadel and, having launched a volley, broke the gate.
May 1929: After airstrikes and shelling, the garrison of Dehdadi left the fortress to the Red Army.
May 1929: On 12 May, Soviet leader Primakov’s detachment occupied Balkh.
May 1929: Not meeting any resistance, the Red Army entered the city of Tashkurgan.
May 1929: The Red Army left Afghanistan after the flight of King Amanullah Khan abroad.
Was a Soviet military intervention in Afghanistan to destroy the economic bases of the Basmachi Movement.
June 1930: At the end of June 1930, the combined cavalry brigade of the Red Army under the command of the brigade commander Yakov Melkumov, crossed the Amu Darya, entering Afghanistan. Not meeting on its way opposition from the local authorities and the regular Afghan army, the Soviet detachment advanced 50-70 km inland.
July 1930: The Soviet forces left the territories they had occupied in northern Afghanistan.
Was a civil war fought in China between the Kuomintang and the Chinese Communist Party. The war continued intermittently for more than twenty years, and overlappes with the Second Sino-Japanese War that started in 1937 with the Japanese occupation of Manchuria. The Communists gained control of mainland China and established the People's Republic of China in 1949, forcing the leadership of the Kuomintang-led Republic of China to retreat to the island of Taiwan.
4.1.War in Xinjiang
Was the theatre of war of the Chinese Civil war in Xinjiang, where the First and Second East Turkestan Republic were founded.
November 1944: Rebels established the Provisional Government of the Second East Turkestan Republic in 1944.
4.2.Second Phase (Chinese Civil War)
Was the second phase of the Chinese Civil War. The war had been interrupted by the Japanese invasion of China in 1937. After the defeat of Japan in World War II, the Chinese Civil War resumed in 1945.
January 1946: On January 8, 1946, Liu Handong, the commander of the Nationalist 107th Division, arrived at Siping with over a hundred associates to discuss the city's transfer from the Soviet Red Army to the Chinese administration. The Red Army still occupied the city at the time. Subsequently, on January 10, the Nationalists created the Liaobei Province, with Liu Handong named the chairman of the province.
April 1946: The USSR left Manchuria to the communists.
Was a series of withdrawals from territories occupied by the Allies during World War II in the aftermath of the war.
5.1.Division of Korea between USA and URSS
Was the occupation and subsequent partition of Japanese-held Korea by the USSR and the USA.
August 1945: USSR declares war on Japan on 8 August. Some days after the declaration, Soviet troops move into Korea.
5.2.Creation of North and South Korea
The two occupation zones of Korea, by the USSR and the USA, became independent countries.
February 1947: Establishment of the People's Committee of North Korea in Northern Korea up to the 38th Parallel.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
6.1.World War II (Asia & Pacific)
Was the East Asian, South Asian and Pacific theatre of World War II.
September 1945: A congress of "People's Representatives" was held in what is now the Sonid Right Banner.
6.1.1.Soviet-Japanese War
Was a conflict during World War II that started when Soviet forces invaded the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo.
6.1.1.1.Invasion of South Sakhalin
Was the Soviet invasion of the Japanese portion of Sakhalin Island during World War II.
August 1945: Keton conquered by russia.
August 1945: Toro conquered by russia.
August 1945: Maoka conquered by russia.
August 1945: Tayohara conquered by russia.
6.1.1.2.Soviet invasion of Manchuria
Was the Soviet invasion of the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo.
August 1945: The Red Army forces were able to break through the hastily organized Japanese defenses and capture the city of Mutanchiang.
August 1945: The Mengjiang area was conquered by the Red Army and its Mongol allies, and Hohhot was quickly taken.
August 1945: The Red Army took Mukden, Xinjing and Qiqihar on August 20.
6.1.1.3.Seishin Operation
Was an amphibious assault on northern Korea between 13-17 August 1945, carried out by the forces of the Soviet Union.
August 1945: The Soviet 13th Naval Infantry brigade (in total 181 men under command of Colonel A. Z. Denisin) entered the city of Chongjin.
6.1.1.4.Invasion of the Kuril Islands
Was the World War II Soviet military operation to capture the Kuril Islands from Japan in 1945.
August 1945: Shimushu conquered by russia.
August 1945: Paramushiru conquered by russia.
August 1945: Matsuwa conquered by russia.
August 1945: Etorufu conquered by russia.
August 1945: Uruppu conquered by russia.
September 1945: Shikotan conquered by russia.
September 1945: Kunashiri conquered by russia.
September 1945: Habomai conquered by USSR.
6.1.2.Japanese Surrender (World War II)
Were the evacuation of the Japanese forces from occupied territories after the formal surrender of the Empire of Japan.
August 1945: The Kwantung Leased Territory was occupied by the Soviet Union.
February 1946: After World War II, the Soviet Union gained control of the southern part of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands from Japan. This territorial transfer was confirmed in the Treaty of San Francisco in 1951.
6.2.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
6.2.1.Invasion of Poland
Was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union. It marked the beginning of World War II.
September 1939: The Red Army invades eastern Poland.
September 1939: Soviet forces capture Wilno.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 19 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 20 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 21 September.
September 1939: The Red Army occupies Lviv.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 23 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 24 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 25 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 26 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 27 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 28 September.
September 1939: Advance of the Russian Invasion of Poland until 29 September.
October 1939: In 1939, Poland was divided between the Soviet Union and Germany as part of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact.
November 1939: Western Ukraine and Belarus are annexed by the Soviet Union.
6.2.2.Winter War
The Winter War, also known as the First Soviet-Finnish War, was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. The war began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peace Treaty on 13 March 1940.
November 1939: Soviet forces invaded Finland.
December 1939: The Finnish Democratic Republic was a short-lived puppet state of the Soviet Union in Finland from December 1939.
6.3.World War II (Middle Eastern Theatre)
Was the Middle Eastern theatre of World War II.
6.3.1.Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran
Was the joint invasion of the neutral Imperial State of Iran by the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union in August 1941.
August 1941: The British and Soviet forces met at Sanandaj.
August 1941: Qazvin conquered by russia.
6.3.1.1.Soviet invasion of Northwestern Iran
Soviet operations in Northwestern Iran during the Anglo-Sovieto invasion of Iran.
August 1941: The Soviet attack against Gilan Province began.
August 1941: The garrison of Bandar Pahlavi was forced to surrender to Soviet forces.
August 1941: Soviet forces captured the city of Mianeh, East Azerbaijan.
August 1941: The Red Army took Qazvin on the 29th.
August 1941: Saveh and Qom conquered by russia.
August 1941: The Soviet forces had reached the city of Chalus.
August 1941: The Iranians accepted the Soviet ceasefire on 29 August, and the Soviets entered the now "open city" of Tehran on 30 August.
August 1941: The Soviet Union's 53rd Army captured the city of Hamadan in Iran,
6.3.1.2.Soviet invasion of Northeastern Iran
Soviet operations in Northeastern Iran during the Anglo-Sovieto invasion of Iran.
August 1941: There was heavy fighting for three days, and by 28 August, the Iranians had been driven back after taking heavy casualties. Mashhad fell to the Soviets the same day.
6.3.1.3.Partition of Iran
Iran was partitioned between Britain and the Soviet Union after the the Anglo-Soviet invasion, with the Soviets stationed in northern Iran and the British south of Hamadan and Qazvin.
October 1941: The Allies withdrew from Tehran on 17 October and Iran was partitioned between Britain and the Soviet Union, with the Soviets stationed in northern Iran and the British south of Hamadan and Qazvin.
6.3.1.4.Allied withdrawal from Iran after World War II
Was the withdrawal from Iran by Great Britain and the USSR, that had occupied the country during World War II.
June 1946: Soviet troops did not withdraw from Iran proper until May 1946.
6.4.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
October 1949: The German Democratic Republic (or Deutsche Demokratische Republik, DDR), with East Berlin as its capital, was established in the Soviet Zone.
6.4.1.Austrian State Treaty
The Austrian State Treaty re-established Austria as a sovereign state after World War II.
May 1945: In the immediate aftermath of World War II, Austria was divided into four occupation zones and jointly occupied by the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France.
July 1955: The Austrian State Treaty was signed on May 15, 1955, in Vienna, Austria. The treaty was signed by the foreign ministers of the United States, Soviet Union, United Kingdom, and France, officially ending the Allied occupation of Austria and re-establishing the country as a sovereign state.
6.4.2.Allied occupation of Germany
The Allies occupied Germany, but the Western allies and Soviet Union formed separate governments covering specific parts of Germany (West Germany, as well as West Berlin, and East Germany).
August 1945: The Allies divided Germany into four occupation zones.
A period (1839-1949) of foregin interventions in China resulting in the occupation, conquest or lease of large territories by foregin countries.
7.1.Concessions in China
During the XIX and XX century China was forced into treaties with foreign powers that established concessions (factually enclaves) in its territory.
January 1946: With the unconditional surrender of Japan in August 1945, Dairen was passed to the Soviets, whose Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation had liberated the city.
7.2.Soviet invasion of Xinjiang
Was a military campaign of the Soviet Union in the Chinese northwestern region of Xinjiang in 1934.
March 1934: The Torgut and Russian army marched into Korla.
May 1934: Conclusion of a ceasefire between the Kuomintang and the USSR. Xinjiang is divided into two.
January 1935: Battle of Tutung.
Was a civil war in Afghanistan between the end of the 1970's and 2022 that included a series of related conflicts. The first phase of the civil war were two coups d'état that resulted in the establishment of the Socialist Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. In order to support the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, the USSR invaded the country. Two years after the Soviet withdrawal, in 1992, the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan was ended by the Mujahideen, an Islamic rebel group. This was followed by a conflict mainly between the Mujahideen and the Taliban forces (another Islamic militia). Until 1996 Taliban took control of Kabul and most of Afghanistan, and established of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. The civil war continued between the Islamic State of Afghanistan and the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, two governments recognized by different international actors. This phase was ended by the US-led invasion of Afghanistan in 2001. The invasion's goals were to capture or kill Osama bin Laden and al-Qaeda militants, as well as replace the Taliban with a U.S.-friendly government. With support of the US the Talibans were initially defeated and the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was established. However, the Talibans started a counteroffensive and in 2021 recaptured whole Afghanistan and established again the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan.
8.1.Soviet-Afghan War
Was a Soviet intervention in Afghanistan in support of the socialist Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, and is also considered the first phase of the wider Afghan Civil War. After nearly ten years of fighting with the Afghan mujahideen, the Soviet troops left Afghanistan in 1989 and the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan collapsed in 1992.
8.1.1.Soviet Intervention in Afghanistan
Was the Soviet military invasion at the beginning of the Soviet-Afghan War.
December 1979: The units of the 108th Motorized Division of the Soviet Union, under the command of General Boris Gromov, first crossed the Amu Darya river on the evening of 24 December 1979. They then proceeded to occupy the cities of Baghlan, Kunduz, and Pol-e Khomri in northern Afghanistan by the afternoon of 27 December.
December 1979: The 5th Motorized Division, part of the Soviet Union's armed forces, entered western Afghanistan in 1979. Led by General Gromov, they quickly captured the cities of Herat and Shindand as part of the USSR's military occupation of the region.
December 1979: A large numbers of Soviet Airborne Forces joined stationed ground troops and began to land in Kabul on December 25. On December 27, 1979, 700 Soviet troops dressed in Afghan uniforms, including KGB and GRU special forces officers from the Alpha Group and Zenith Group, occupied major governmental, military and media buildings in Kabul. The operation was fully complete by the morning of December 28, 1979.
January 1980: The Soviet Union expanded his area of control in Afghanistan up to Farah and Kandahar.
January 1980: By mid-January 1980 the main centers of Afghanistan were in Soviet hands. Red Army troops never attempted to occupy the entire Afghan territory, but concentrated their attention on areas deemed most important such as major urban areas, airports and main roads, ignoring rural areas altogether; at least 80% of Afghan territory remained effectively outside the control of the Kabul government and its Soviet allies.
8.1.2.Soviet Withdrawal from Afghanistan
Was the withdrawal of Soviet forces from Afghanistan that ended the Soviet-Afghan War. The final troop withdrawal started on May 15, 1988, and ended on February 15, 1989.
February 1989: The final troop withdrawal started on May 15, 1988, and ended on February 15, 1989.
December 1945: The Azerbaijan People's Government was a short-lived unrecognized secessionist state in northern Iran from November 1945 to December 1946.
January 1946: The Republic of Mahabad was established in 1946 in present-day Iran, led by Kurdish nationalist leader Qazi Muhammad and supported by the Soviet Union. It aimed to create an independent Kurdish state.
Disestablishment
February 1989: The final troop withdrawal started on May 15, 1988, and ended on February 15, 1989.
Selected Sources
Campaign In Poland, 15-22 September 1939. United States Military Academy of Westpoint. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope07.jpg
Cook, C. / Stevenson, J. (2006): The Routledge Companion to World History since 1914, Routledge, p.20
Kamp wrzesn9-17. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-17.png
Kamp wrzesn9-19. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-19.png
Kamp wrzesn9-21. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-21.png
Kamp wrzesn9-23. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-23.png
Kamp wrzesn9-24. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-24.png
Kamp wrzesn9-25. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-25.png
Kamp wrzesn9-26. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-26.png
Kamp wrzesn9-27. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-27.png
Kamp wrzesn9-28. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-28.png
Kamp wrzesn9-29. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kamp_wrzesn9-29.png
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.551
.png.webp)
 USSR (Military Occupation)
USSR (Military Occupation)