This article is about the specific polity Stem Duchy of Saxony and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
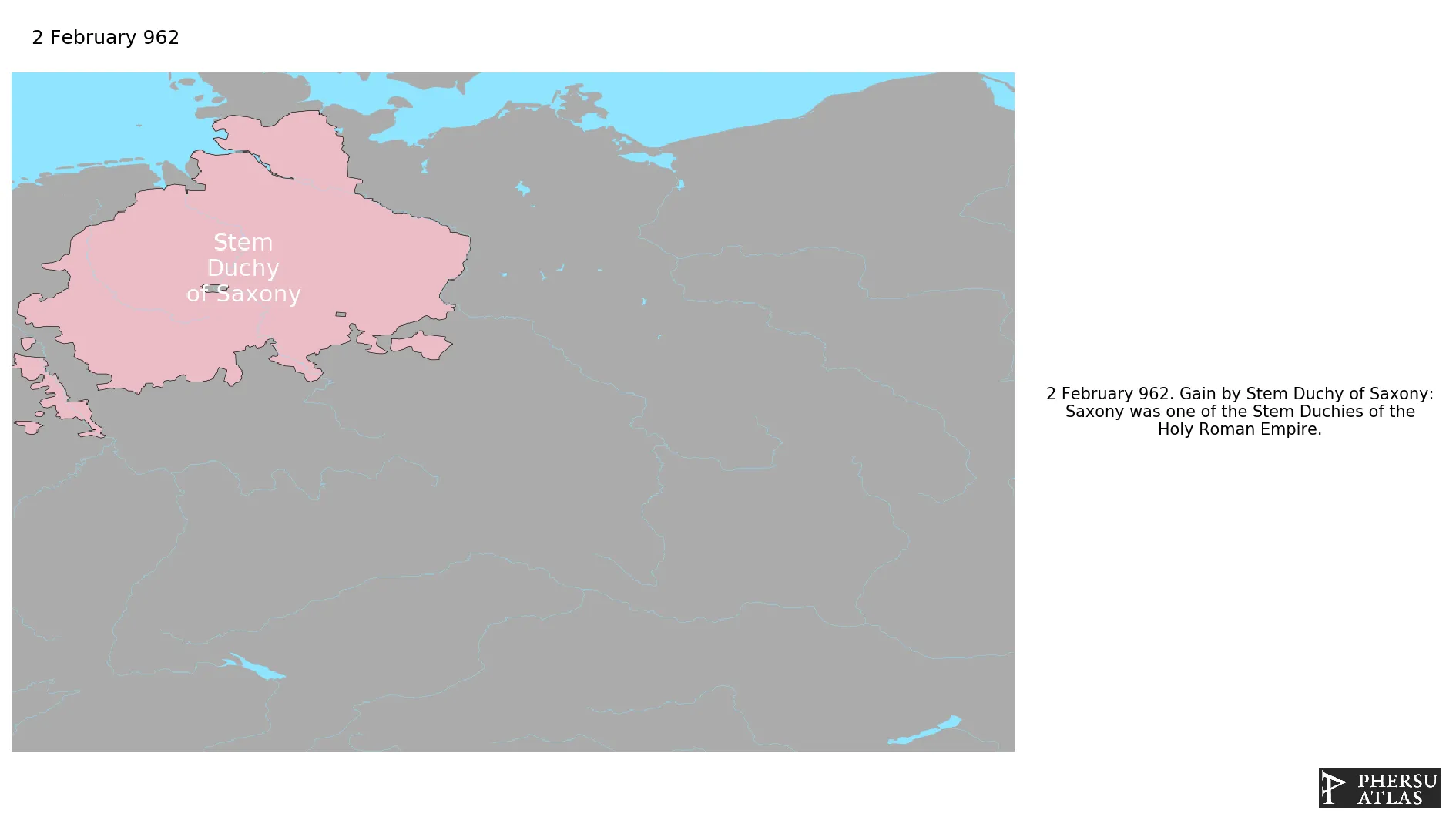
Was a medieval duchy located between the Lower Rhine and the Lower Elbe and Eider. It emerged from the settlement area of the Saxons, which was conquered in stages between 772 and 804 by Charlemagne and incorporated into the Frankish Empire.
Establishment
February 962: Saxony was one of the Stem Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Frankish Kingdom was partitioned and reuinited several times as the Frankish rulers used to divide their territories equally among their heirs. This lead also to a number of wars and revolts.
1.1.Incoronation of Otto I
East Frankish King Otto I was crowned first Holy Roman Emperor.
Was the invasion of northern Germany by king Canute VI of Denmark caused by disagreement with Adolf III, Count of Schauenburg and Holstein, over the possession of the island of Rügen.
January 1228: In 1203, King Valdemar II of Denmark conquered the area later comprising Saxe-Lauenburg, but it reverted to Albert I, Duke of Saxony in 1227.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
3.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
3.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1241: The Mongols invaded the Holy Roman Empire without major clash of arms.The army invaded eastern Germany, and crossed the March of Moravia in April-May 1241.
June 1241: The Mongols left eastern Germany and Moravia.
January 995: Establishment of the Quedlinburg Abbey.
January 999: The North March is conquered by Saxony.
January 1001: In the 11th century, the Counts of the Niederlahngau region assumed the name Isenburg.
January 1031: The first written mention of the nobles Haus an der Aa dates from around 1030.
January 1051: Mansfeld County is mentioned for the first time in 1050.
January 1081: The roots of the dynasty of the noble lords von Wassel, and thus the roots of Deipenau, go back to the year 1080 with the birth of a noble lord Bernhard I.
January 1096: Before 1195, when the city was founded, Büren was already a farming settlement for 300 years. Büren (Buranon) was first mentioned in 1095. The noble lords of Büren applied for the founding of the city.
January 1097: The county of Geldern emerged about 1096, when Gerard III of Wassenberg was first documented as "Count of Guelders".
January 1098: Höckelheim Lordship is mentioned for the first time in 1097.
January 1101: The county of Dassel came into existence shortly after the turn of the 11th and 12th centuries, when after the male line of the Billungers died out, their property in the Suilbergau north of the Solling was divided into the lordships of Einbeck and Dassel, and Reinold von Dassel was able to secure lordship rights similar to that of a count.
January 1101: Tecklenburg County is mentioned for the first time in 1100.
January 1103: The construction (of Arnsberg Castle) was first mentioned in 1102.
January 1111: Schauenburg Lordshi originated from Saxony in 1110.
January 1112: Establishment of the Holstein County.
January 1117: Since 1116, the noble lords and counts of Everstein (also Eberstein) have been named after the castles on the Großer and Kleiner Everstein (Everstein Castle) on the Burgberg in the Holzminden district, Lower Saxony.
January 1122: Wernigerode County is mentioned for the first time in 1121.
January 1124: Lippe Lordship is mentioned for the first time in 1123.
January 1124: Blankenburg County is mentioned for the first time in 1123.
January 1130: Steinfurt Lordship is mentioned for the first time in 1129.
January 1132: A branch of Steußlingen established a line at Arnstein.
January 1135: In 1134 Emperor Lothair of Supplinburg bestowed the Northern March on the Ascanian count Albert the Bear.
January 1141: The first known Wölper was Egilbert I, probably first attested in an undated document by Bishop Sigward von Minden (1124-1140).
January 1145: Siegfried IV. von Boyneburg (death: 1144) from the house of Northeim had the castle of Homburg built to protect the Amelungsborn monastery.
January 1148: The Wendish Crusade of 1147, concurrent to the Second Crusade, was largely unsuccessful, resulting in devastation to the Liutizi lands and forced baptisms. The campaign did secure Saxon control of Wagria and Polabia, however.
January 1151: Corvey Abbey gains imperial immediacy.
January 1153: In 1152, the castle of Schöneberg was acquired by the Mainz Archbishopric.
January 1154: Dannenberg County is mentioned for the first time in 1153.
January 1155: Ratzeburg Prince-Bishopric was reestablished.
January 1157: Henry the Lion (* around 1129/30 or 1133/35; † August 6, 1195 in Braunschweig) from the House of Guelph was Duke of Saxony (Henry III) from 1142 to 1180 and also Duke of Bavaria from 1156 to 1180 (Henry XII.).
January 1158: For further one-and-a-half centuries, the lands east of the Elbe defied German control, until in 1134 Emperor Lothair of Supplinburg bestowed the Northern March on the Ascanian count Albert the Bear. Albert signed an inheritance contract with the Slavic Hevelli prince Pribislav and in 1150 succeeded him in his eastern territory around the fortress of Brandenburg an der Havel, which became the nucleus of his newly established Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1157.
January 1160: The Lords of Bederkesa are first mentioned in an archbishop's document. In 1159, Marcward de Bederkesa appeared as a witness under a document issued by Archbishop Hartwig I of Stade (1148-1168).
January 1161: Leuchtenburg County is established.
January 1161: Diepholz County is mentioned for the first time in 1160.
January 1161: Schaumberg County is mentioned for the first time in 1160.
January 1163: Establishment of the Schwerin Prince-Bishopric.
January 1165: The 1164 Battle of Verchen, the Pomeranian dukes became vassals of Henry the Lion of Saxony.
January 1167: The Codex Falkensteinensis, compiled in 1166, offers an unusually detailed snapshot of the rule and possessions of the count family. At that time, the Count's house under Siboto IV owned the four castles Falkenstein above the Inn, Neuburg an der Mangfall, Hartmannsberg near Hemhof am Chiemsee and Hernstein near Baden in Lower Austria.
January 1169: Defeat of the Principality of Rugia in 1168. The Rugian princes became vassals of Valdemar I of Denmark.
January 1171: From 1170 to 1200, the Counts of Grögling and Dollnstein built an extensive castle complex on the Hirschberg and named themselves “Counts of Hirschberg” after their new seat from 1205.
January 1171: Rheda Lordship is mentioned for the first time in 1170.
February 1171: At the end of January 1171, the nobles of Moosburg became counts. A county was formed around Moosburg for them.
January 1172: Henry the Lion founded the five counties of Holstein, Ratzeburg, Schwerin, Dannenberg and Lüchow to protect his country's new territories and borders. Ulrich III. and Hermann I. (1144-1171) moved the count seat to Lüchow and referred to themselves from then on as the Counts of Lüchow.
January 1173: The castle fo Greiffenstein is mentioned for the first time.
January 1175: The Woldenberg Lordship takes its name from Castle Wohldenberg, mentioned since 1174.
January 1180: Establishment of the Brixen Prince-Bishopric.
January 1181: Hohnstein County gains imperial immediacy.
January 1181: Halberstadt Prince-Bishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1181: The Verden Prince-Bishopric emerged from the old Duchy of Saxony in 1180.
January 1181: Especially after Henry the Lion was overthrown and the tribal duchy of Saxony was crushed in 1180, the Schwalenberger developed into the most powerful family in the area between Herford and Höxter. They occupied an almost imperial position.
January 1181: The Archbishopric of Cologne acquired Westphalia and Angria.
January 1181: Osnabrück fief of Tecklenburg.
January 1181: Establishment of the Cammin Bishopric.
January 1181: Establishment of the Archbishopric of Bremen.
January 1181: Lübeck Prince-Bishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1181: Magdeburg Archbishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1181: Ravensberg County gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1181: Minden Prince-Bishopric gains imperial immediacy.
January 1181: Münster Prince-Bishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1182: The Hohenstaufen dynasty succeeded in isolating Henry the Lion and eventually deprived him of his duchies of Bavaria and Saxony. Bavaria fell to Otto I, the first Bavarian ruler from the House of Wittelsbach, a dynasty which reigned until the abdication of King Ludwig III of Bavaria in the German Revolution of 1918.
January 1182: Bogislaw I received the Duchy of Pomerania from emperor Frederick Barbarossa.
January 1182: County of Oldenburg gains imperial immediacy.
January 1183: Bentheim County gains imperial immediacy.
January 1193: Nassau Domains gain imperial immediacy.
January 1199: Querfurt was the ancestral seat of the noble lords of Querfurt. 974 is given as the year of birth of St. Brun von Querfurt as the first documented representative of this noble family. The inner city wall is mentioned in a document from 1198, which means that Querfurt already had city rights at that time.
January 1199: Foundation of the Mark County.
January 1203: Establishment of the Hoya County.
January 1204: In 1203, King Valdemar II of Denmark conquered the area later comprising Saxe-Lauenburg from Albert I, Duke of Saxony.
January 1215: Establishment of the Ruppin Lordship by Gebhard of Arnstein.
January 1215: In 1214, Gebhard of Arnstein acquired Ruppin, establishing a line that eventually led to the territory going to Lindow Lordship. Gebhard of Arnstein was a nobleman and landowner in the region during the medieval period.
January 1221: Dortmund is declared a Free Imperial City.
January 1221: Reign of the Lords of Bilstein (from around 1220 to 1365).
January 1236: From 1235 to 1802 the bishop of Hildesheim was also imperial prince.
January 1236: At the Imperial Diet of 1235 in Mainz, as part of the reconciliation between the Hohenstaufen and Welf families, Henry's grandson, Otto the Child, transferred his estates to Emperor Frederick II and was enfeoffed in return with the newly created Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg, which was formed from the estates transferred to the Emperor as well as other large areas of the imperial fisc.
January 1236: A Count of Wunstorf was first mentioned in a document in 1235.
Disestablishment
January 1297: Several years after the death of Albert I, Duke of Saxony, the territory of Saxony was definitively partitioned, with Saxe-Lauenburg going to the brothers Albert III, Eric I and John II (grandchildern of Albert) and Saxe-Wittenberg going to Albert II (son of Albert).
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 26-49
Strakosh-Grassmann, G. (1893): Der Einfall der Mongolen in Mitteleuropa in den Jahren 1241 und 1242, Innsbruck (Austria), pp. 53-67
.svg.png.webp)
 Stem Duchy of Saxony
Stem Duchy of Saxony