If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Principality of Wallachia
Principality of Wallachia (Ottoman Empire)
Principality of Wallachia (Russia Protectorate)
Principality of Wallachia (Russia)
Principality of Wallachia (Austria)
Principality of Wallachia (International Protectorate)
Establishment
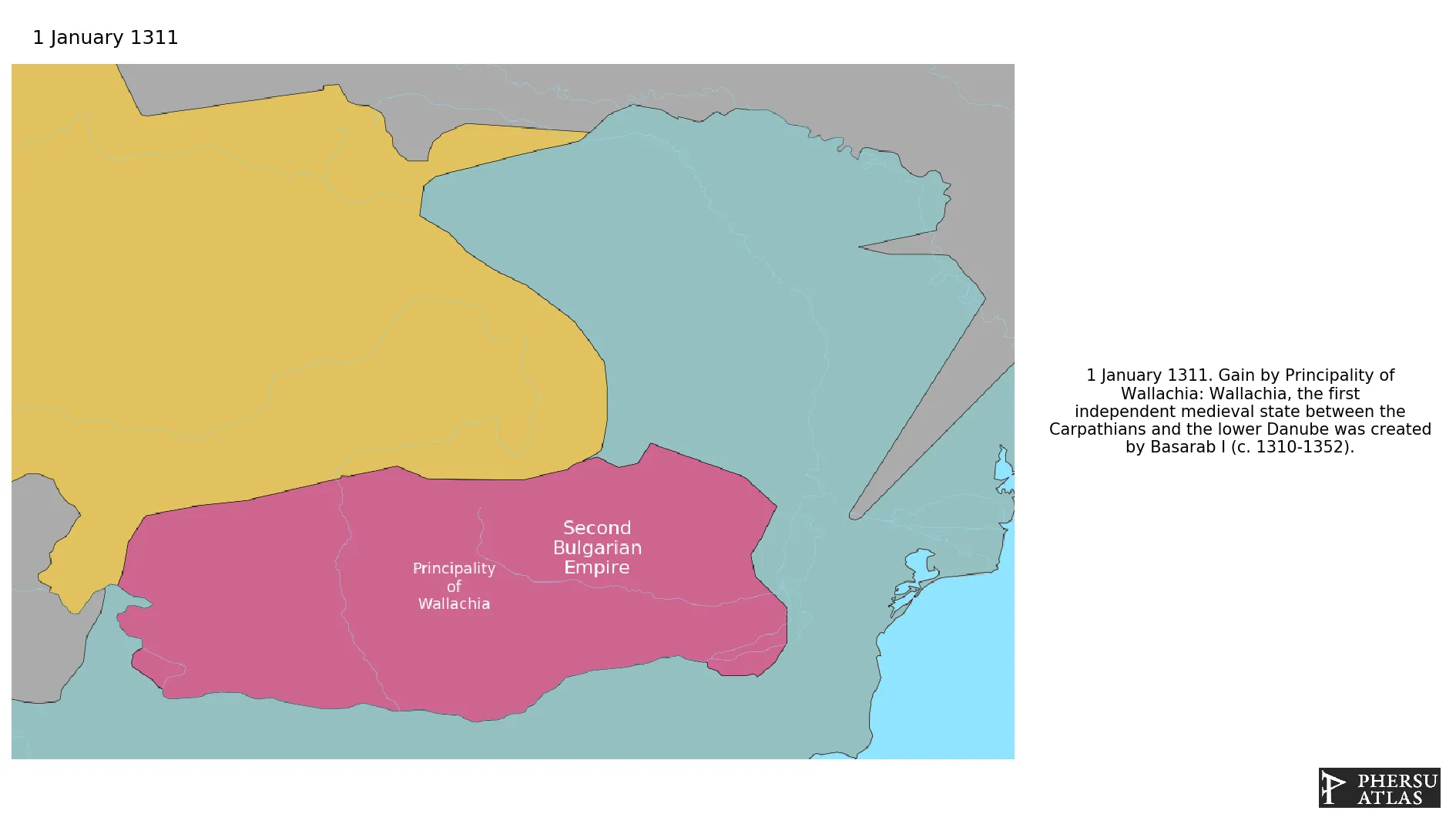
January 1311: Wallachia, the first independent medieval state between the Carpathians and the lower Danube was created by Basarab I (c. 1310-1352).
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Wars during the rule of Mehmed II in the Ottoman Sultanate.
January 1463: The Ottomans appointed Vlad's brother Radu as a vassal ruler of Wallachia.
January 1463: Vlad the Impaler who with Ottoman help had become the Ottoman vassal ruler of Wallachia, refused to pay tribute after some years and invaded Ottoman territory in northern Bulgaria. At that point Mehmed, with the main Ottoman army, was on the Trebizond campaign in Asia. When Mehmed returned from his Trebizond campaign he led a campaign against Wallachia. Vlad fled after some resistance to Hungary. Mehmed first made Wallachia an Ottoman eyalet.
Were a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg Domains. The conflicts started with the partition of Hungary between the Ottomans and the Habsburgs after the Battle of Mohács (1526).
2.1.Long Turkish War
Was a war between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburgs (along with their respective allies) over the control of Romanian and Hungarian territories.
October 1600: Wallachia was in personal union with Moldavia until September 1600.
January 1602: Wallachia was in personal union with Transylvania 1600.
2.2.Great Turkish War
Was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Poland-Lithuania, Venice, Russia, and Habsburg Hungary.
2.2.1.Treaty of Karlowitz
Was a treaty that concluded the Great Turkish War and the Morean War. The Ottoman Empire suffered major territorial losses.
January 1699: Following the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz, Transylvania was formally attached to the Habsburg-controlled Hungary.
2.3.Austro-Russian-Turkish War (1735-39)
Was a war mainly between Russia and the Ottoman Empire.
August 1737: A small army corps under the command of General George Olivier Wallis occupied a part of Wallachia.
2.3.1.Treaty of Belgrade
Was a peace treaty signed on September 18, 1739 in Belgrade, Habsburg Kingdom of Serbia (today Serbia), by the Ottoman Empire on one side and the Habsburg Monarchy on the other, that ended the Austro-Turkish War (1737-39).
September 1739: The Treaty of Belgrade, known as the Belgrade peace was the peace treaty signed on September 18, 1739 in Belgrade, Habsburg Kingdom of Serbia (today Serbia), by the Ottoman Empire on one side and the Habsburg Monarchy on the other, that ended the Austro-Turkish War (1737-39).
Was a war between the Habsburg Domains and the Ottoman Empire.
3.1.Treaty of Passarowitz
Was the treaty that ended the Austro-Turkish War (1716-1718).
July 1718: Part of Wallachia (an autonomous Ottoman vassal) known as the Lesser Wallachia (Oltenia) was also ceded to the Habsburg Monarchy.
Was a war between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire. The Russian Empire was victorious and ceded territories in Ukraine to Russia. The Crimean Khanate became a Russian protectorate.
4.1.Russian invasion (Russo-Turkish War of 1768-1774)
Was the Russian invasion of the Ottoman Empire during the Russo-Turkish War (1768-1774).
November 1769: The Russians continued the advance south into Wallachia, occupying its capital Bucharest.
4.2.Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
Was the treaty that ended the Russo-Turkish War (1768-1774). The Ottomans ceded territories in modern-day Ukraine to Russia, and the Crimean Khanate became a Russian protectorate.
July 1774: After the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca forced the Ottoman Empire to leave the Crimean Khanate, the Russian army left the other regions it had occupied.
Was an unsuccessful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to regain lands lost to the Russian Empire in the course of the previous Russo-Turkish War (1768-1774).
September 1789: Russian troops drove the Ottomans away from near the Râmnicul Sărat river
5.1.Treaty of Jassy
Was the treaty that ended the Russo-Turkish War (1787-1792).
January 1792: The Treaty of Jassy was signed on 9 January 1792 by the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, recognizing Russia's 1783 annexation of the Crimean Khanate. Yedisan (Odessa and Ochakov) was also ceded to Russia.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
6.1.War of the Fourth Coalition
Was a war between the French Empire and a coalition of European monarchies, mainly Prussia and Russia.
6.1.1.Polish, Russian and Swedish campaigns (War of the Fourth Coalition)
Was the theatre of war in Poland, Russia and Sweden during the War of the Fourth Coalition.
January 1807: In order to safeguard the Russian border against a possible French attack, a 40,000-strong Russian contingent advanced into Moldavia and Wallachia.
6.1.2.Peace of Tilsit
Were a series of treaties that ended the War of the Fourth Coalition.
July 1807: The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by Napoleon I of France in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Emperor Alexander I of Russia and Napoleon I of France. The Russian tsar agreed to evacuate Wallachia and Moldavia.
Was a war between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire.
May 1810: The garrison of Silistra, led by Ottoman military commander Ahmed Pasha, surrendered to the Russian forces in 1810 during the Russo-Turkish War. The occupation of Silistra by Russia marked a significant turning point in the conflict.
September 1810: The fortress of Rousse (or Rustchuk) fell to the Russians.
Was a war between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire. War broke out after the Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II closed the Dardanelles to Russian ships because Russia had supported the revolutionaries of the Greek War of Independency.
8.1.Balkan front of the Russo-Turkish War (1828-29)
Was the Balkan theatre of the Russo-Turkish War (1828-1829).
June 1828: In April and May 1828, the Russian commander-in-chief, Prince Peter Wittgenstein, led Russian forces into the Romanian Principates of Wallachia and Moldavia as part of the Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829. The territories were placed under Russian military occupation.
8.2.Treaty of Adrianople (1829)
Was the treaty that ended the Russo-Turkish War (1828-1829).
September 1829: The treaty also fixed the border between the Ottoman Empire and Wallachia on the thalweg of the Danube, transferring to Wallachia the rule of the rayas of Turnu, Giurgiu and Brăila.
Was a war between Russia and an alliance comprising the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Sardinia.
9.1.Danube campaign (Crimean War)
Was the Danubian theatre of the Crimean War.
June 1853: The Danube campaign opened when the Russians occupied the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia in May 1853, bringing their forces to the north bank of the River Danube.
November 1853: Following the Ottoman ultimatum in September 1853, forces under the Ottoman general Omar Pasha, a prominent military leader in the Ottoman Empire, crossed the Danube at Vidin and captured Calafat in October 1853. This event marked the beginning of the military occupation of Calafat by Turkey.
July 1854: During the Crimean War, the Ottoman forces led by Omar Pasha crossed the Danube River and defeated the Russian troops in Giurgiu, a city in Wallachia. This victory resulted in the territory of Giurgiu being placed under Turkish military occupation in 1854.
July 1854: On 26 July 1854, Tsar Nicholas I, responding to an Austrian ultimatum, ordered the withdrawal of Russian troops from the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. Their place in the Principalities was taken by the Austrians, as a neutral peacekeeping force.
March 1856: Moldavia and Walachia (Romania) were recognized as quasi-independent states under Ottoman suzerainty. They gained the left bank of the mouth of the Danube and part of Bessarabia from Russia.
9.2.Black Sea theatre
Was the Black Sea theatre of the Crimean War.
January 1324: The Despotate of Vidin, under Mihail Shishman, returned to the suzerainty of Bulgaria.
January 1331: Basarab refused to grant Hungary the lands of Făgăraș, Almaș and the Banate of Severin, defeated Charles in the Battle of Posada (1330).
January 1392: Prince Petru of Moldavia expanded his rule southwards to the Danube Delta.
January 1401: Mircea the Elder (the Voivode of Wallachia) defeated the Ottomans in several battles, including the Battle of Rovine in 1394, driving them away from Dobruja and briefly extending his rule to the Danube Delta, Dobruja and Silistra (c. 1400-1404).
January 1405: Mircea the Elder (the Voivode of Wallachia) defeated the Ottomans in several battles, including the Battle of Rovine in 1394, driving them away from Dobruja and briefly extending his rule to the Danube Delta, Dobruja and Silistra (c. 1400-1404).
January 1416: In 1415, Mehmed I, the Ottoman Sultan, conquered Wallachia and made it a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire.
January 1418: Ottoman sultan Mehmed I took control of Turnu Măgurele and Giurgiu.
January 1463: Vlad the Impaler who with Ottoman help had become the Ottoman vassal ruler of Wallachia, refused to pay tribute after some years and invaded Ottoman territory in northern Bulgaria. At that point Mehmed, with the main Ottoman army, was on the Trebizond campaign in Asia. When Mehmed returned from his Trebizond campaign he led a campaign against Wallachia. Vlad fled after some resistance to Hungary. Mehmed first made Wallachia an Ottoman eyalet.
January 1600: The Principality of Transylvania fell under the authority of Wallachia.
June 1600: Wallachian rule was extended to Moldavia.
February 1859: The United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia was the personal union of the Principality of Moldavia and the Principality of Wallachia, formed on 5 February 1859.
Disestablishment
February 1859: The United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia was the personal union of the Principality of Moldavia and the Principality of Wallachia, formed on 5 February 1859.
Selected Sources
Tucker, S. C. (2011): A Global Chronology Of Conflict, London (UK), p. 963
Tucker, S. C. (2011): A Global Chronology Of Conflict, London (UK), p. 965

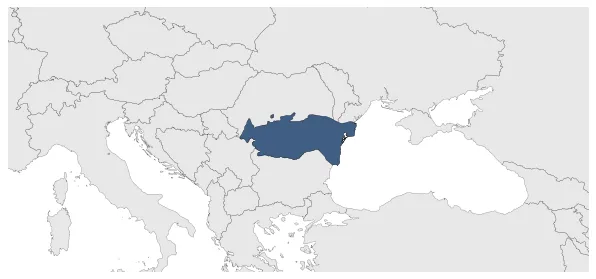
 wallachia
wallachia