If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
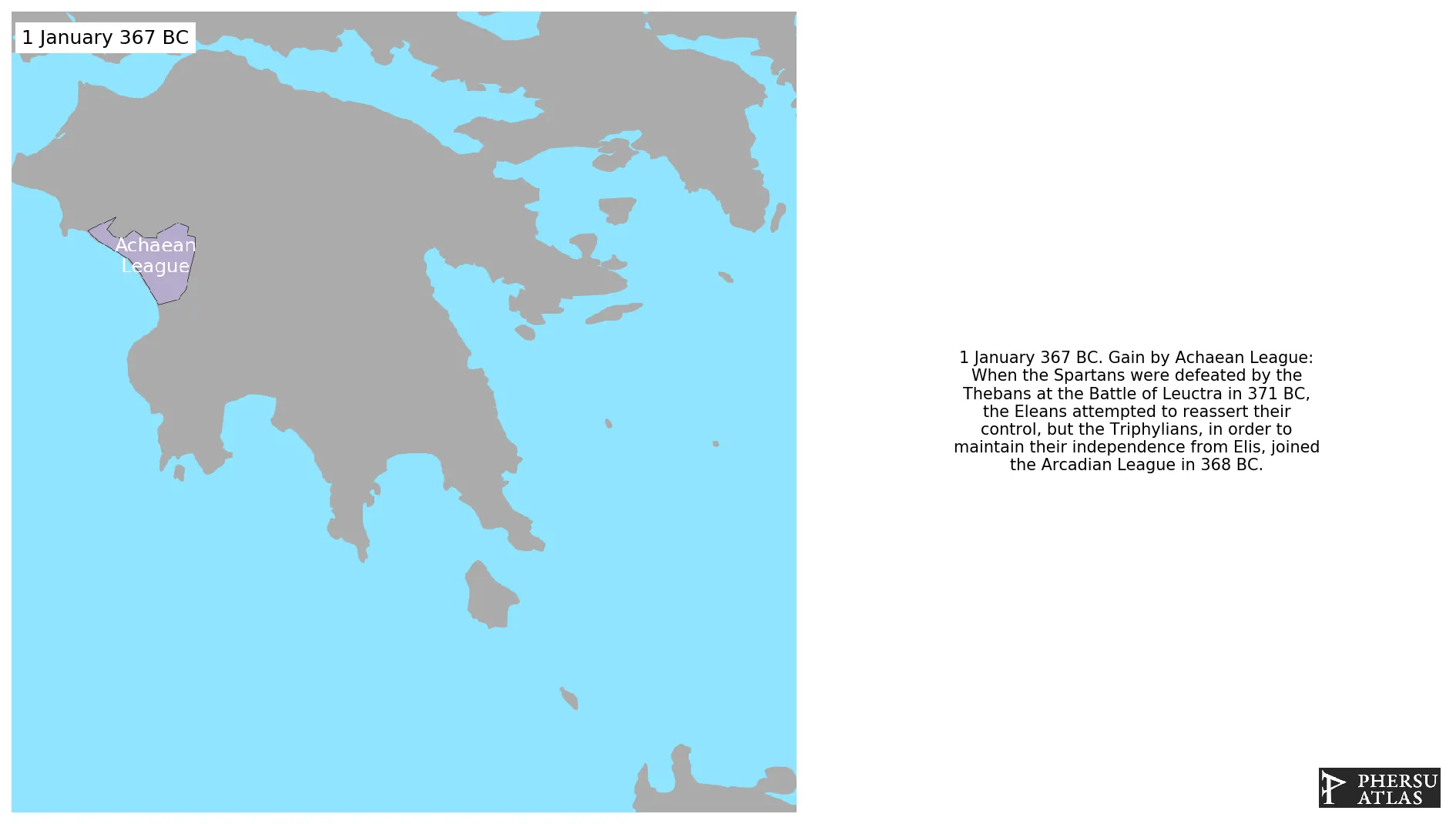
Was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese.
Establishment
January 367 BC: When the Spartans were defeated by the Thebans at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, the Eleans attempted to reassert their control, but the Triphylians, in order to maintain their independence from Elis, joined the Arcadian League in 368 BC.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a series of military conflicts fought between Sparta and Thebes for hegemony over Greece. Sparta had emerged victorious from the Peloponnesian War against Athens (431-404 BC), and occupied an hegemonic position over Greece. However, the Spartans' violent interventionism upset their former allies, especially Thebes and Corinth.
1.1.Battle of Leuctra (Aftermath)
The aftermath of the Battle of Leuctra, a battle between the Boeotians and the Spartans.
1.1.1.Second invasion of the Peloponnese
Was a Theban military campaign in the territories of Sparta in the Peoloponnese that resulted in several cities controlled by Sparta becoming independent.
Was a war fought between Sparta and the Achaean League for the control of the Peloponnese.
January 221 BC: Antigonus III Doson of Macedon leaves Sparta having militarly occupied the city for a short time.
January 221 BC: After the Cleomenean War in -222, the whole territory of Sparta was taken over by Sparta. This war was fought between Sparta, led by King Cleomenes III, and the Achaean League. The conflict resulted in Sparta gaining control over its own territory once again.
2.1.Spartan Domination of the Peloponnese
Was a Spartan campaign in the Peloponnese.
January 228 BC: In 229 BC, Cleomenes took the important cities Tegea, Mantineia, Caphyae, and Orchomenus in Arcadia, who had by then allied themselves with the Aetolian League.
April 228 BC: Cleomenes advanced into Arcadia with 3,000 infantry and a few cavalry. However, he was called back by the ephors, and this retreat allowed Aratus to seize Caphyae as soon as Cleomenes returned to Laconia.
April 228 BC: The ephors sent Cleomenes out. He managed to capture the Megalopian city Methydrium.
January 226 BC: Cleomenese captured Heraea and Asea.
January 225 BC: Achaea was now in turmoil, and some cities were close to revolt; many residents were angered at Aratus' decision to invite the Macedonians into the Peloponnese. Some also hoped that Cleomenes would introduce constitutional changes in their cities. Encouraged by this development, Cleomenes invaded Achaea and seized the cities of Pellene, Pheneus, and Penteleium.
January 225 BC: Cleonae and Phlius were ancient Greek cities located in the Peloponnese region. Cleomenes III was a Spartan king who led a military campaign to seize control of various territories in the region. After capturing Argos, Cleomenes also gained control of Cleonae and Phlius in -226 BC.
January 225 BC: In -226, the Greek city-states of Hermione, Troezen, and Epidaurus surrendered to King Cleomenes III of Sparta during his military campaign to expand Spartan territory in the region. Cleomenes III was a prominent Spartan king known for his military reforms and aggressive expansionist policies.
January 225 BC: King Cleomenes III of Sparta seized the city of Argos.
January 225 BC: The Corinthians did surrender the city to Cleomenes of Sparta.
2.2.Macedonian intervention
Was a Macedonian military campaign against Sparta during the Cleomenean war.
January 222 BC: Cleomenes of Sparta conquers Megalopolis.
Were a seris of conflicts between the Roman Republic and Antigonid Macedonia over control of Greece and the eastern Mediterranean Basin. .
3.1.First Macedonian War
Was a war fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218-201 BC) against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
3.1.1.Campaign of Laevinus in Greece
Was a Roman military campaign in Greece led by Marcus Valerius Laevinus during the first Macedonian War.
January 210 BC: The region was conquered by the Aetolians.
3.2.Annexation of Macedonia
After the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled king of Macedonia in the Fourth Macedonian War, Macedonia became a Roman province.
January 145 BC: The Achaean League was dissolved by the Romans in 146 BC, making Kydonia independent.
The Laconian War of 195 BC was fought between the Greek city-state of Sparta and a coalition composed of Rome, the Achaean League, Pergamon, Rhodes, and Macedon.
January 194 BC: Roman general Flamininus advanced on Caryae.
January 194 BC: The allied army marched on Tegea, in Arcadia.
January 194 BC: Roman general Flamininus led his force of 50,000 against Sparta and, after defeating the Spartans in a battle outside the city walls, began the siege of the city.
February 194 BC: The Romans leave Tegea.
February 194 BC: The Roman army leaves Caryae.
February 194 BC: The coastal Laconian cities become independentfrom Sparta under Achaean protection as the Union of Free Laconians.
February 194 BC: Roman general Flamininus led his force of 50,000 against Sparta and, after defeating the Spartans in a battle outside the city walls, began the siege of the city.
The Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League. The war marked the beginning of direct Roman control of Greece, and the end of Greek independence.
January 145 BC: The Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League. The war marked the beginning of direct Roman control of Greece, and the end of Greek independence.
January 279 BC: The second Achaean League was established in 280 BC.
January 250 BC: Sikyon joined the Achean League.
January 242 BC: The site of Aigosthena was under the control of the Achaean League in 243-224 BC.
January 242 BC: Epidauros (Argolis) joins the Achean League.
January 242 BC: Troizen joins the Achean League.
January 242 BC: Megara enters the Achaean League.
January 242 BC: Corinth joined the Achean League (243 BC).
January 234 BC: Kleonai (Argolis) joins the Achean League.
January 229 BC: The date of its final disappearance is uncertain, but at the latest it had vanished by the 230s BC, as the Arcadian cities joined the Achaean League.
January 228 BC: The Achaean League, a confederation of ancient Greek city-states, gained control of Halieis.
January 228 BC: Argos (Argolis) joins the Achean League.
January 228 BC: The Achaean League, a confederation of ancient Greek city-states, gained control of Phleious.
January 228 BC: Aigina entered the Achaean League.
January 228 BC: Hermion joins the Achean League.
January 224 BC: Corinth joined the Achean League.
January 223 BC: Corinth left the Achean League (224 BC).
January 223 BC: In 224 - 146 BC it joined the Boeotian League.
January 222 BC: In 223 BC, Megara in Attica deserted the Achaean League and joined the Boeotian Confederacy.
January 218 BC: Kydonia became part of the Achaean League in 219 BC.
January 196 BC: Corinth joined again the Achean League (197 BC).
January 192 BC: Not more than thirty years later, however, the Megarians grew tired of the Boeotian decline and returned their allegiance to Achaea. The Achaean strategos Philopoemen fought off the Boeotian intervention force and secured Megara's return, either in 203 or in 193 BC.
January 191 BC: Later Hypana in Elis, Corone, Messene, Sparta and Pagae in Attica were joined by conquest.
January 191 BC: Under Machanidas or Nabis, the tyrants of Sparta, the Belminatis was again annexed to Laconia.
January 190 BC: Elis was conquered by the Achean League.
January 181 BC: In -182 BC, the Achaean League, led by Philopoemen, expanded its territory by conquering Hypana in Elis, Corone, Messene, Sparta, and Pagae in Attica. This marked a significant military achievement for the league under Philopoemen's leadership.
January 181 BC: Hypana in Elis, Corone, Messene, Sparta and Pagae in Attica joined the Achaean League.
January 166 BC: Pleuron is acquired by the Achaean League.
Disestablishment
January 145 BC: The Achaean League was dissolved by the Romans in 146 BC, making Kydonia independent.
January 145 BC: The Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League. The war marked the beginning of direct Roman control of Greece, and the end of Greek independence.
Selected Sources
Bastini, A. (1987): Der achäische Bund als hellenische Mittelmacht: Geschichte des achäischen Koinon in der Symmachie mit Rom, Peter Lang , p. 17

 Achaean League
Achaean League