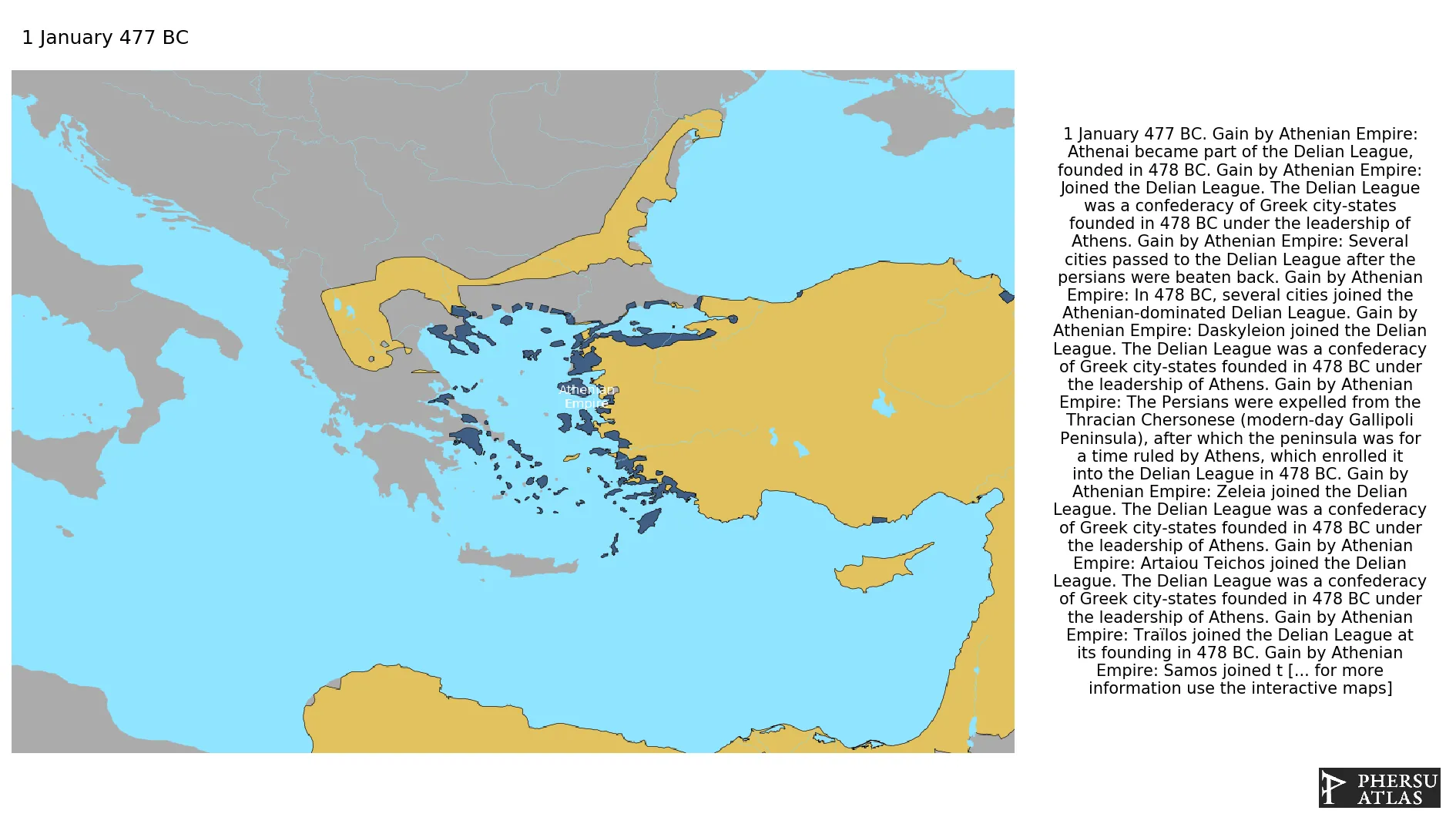
This article is about the specific polity Athenian Empire and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an association of Greek city-states under the leadership of Athens.
Establishment
January 477 BC: Arkesine became a member of the Delian League, an alliance led by Athens.
January 477 BC: Skabala became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Assera became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Boutheia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: In 478 BC, several cities joined the Athenian-dominated Delian League.
January 477 BC: Peparethos became part of the Delian League.
January 477 BC: Therambos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Priapos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Mekyberna became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Olophyxos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Stolos/Skolos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Neapolis (Chalkidike) became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Pteleon joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Polichnitai (Ionia) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Sane, Pallene became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Dios Hieron joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kolophon joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Akanthos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Sermylia became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Aige became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Aioleion became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Akrothooi became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Aphytis became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Dikaia (Chalkidike) became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Galepsos (Chalkidike) became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Gigonos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Haisa became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Kithas became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Kleonai (Chalkidike) became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Mende became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Olynthos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Piloros became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Pleume became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Poteidaia became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Sane (Akte): assumed to be conquered by Athens, similarly to the other city-states of the region.
January 477 BC: Sarte became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Sinos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Skithai became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Stagiros became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Torone (Chalkidike) became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Aigiale became a member of the Delian League, an alliance led by Athens.
January 477 BC: Minoa became a member of the Delian League, an alliance led by Athens.
January 477 BC: After the defeat of Xerxes the Thasians joined the Delian League.
January 477 BC: Ikos joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Panormos joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Seleinous joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Skiathos joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Bormiskos was mentioned in the Athenian tribute lists as a member of the Delian League in 422/1 BC.
January 477 BC: Argilos became part of the Delian League.
January 477 BC: Traïlos joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Galepsos became part of the Delian League.
January 477 BC: Abdera joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Ainos joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Dikaia joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Drys joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Maroneia joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Sale became part of the Delian League.
January 477 BC: The Persians were expelled from the Thracian Chersonese (modern-day Gallipoli Peninsula), after which the peninsula was for a time ruled by Athens, which enrolled it into the Delian League in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Several cities passed to the Delian League after the persians were beaten back.
January 477 BC: After the failed Persian invasion, Abydos became a member of the Athenian-led Delian League.
January 477 BC: Assos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Astyra Troika joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Birytis joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Dardanos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Gargara joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Gentinos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Gergis joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Ilion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kebren joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Lamponeia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Palaiperkote joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Perkote joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Sigeion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Skepsis joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kokylion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Tenedos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Artaiou Teichos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Artake joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Astakos (Propontic Coast of Asia Minor) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Bysbikos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Daskyleion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Didymon Teichos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Harpagion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kalchedon joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kolonai (Propontic Coast of Asia Minor) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Miletouteichos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Prokonnesos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Pythopolis joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Zeleia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kyzikos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Elaia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Gryneion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Karene joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Kyme (Aiolis) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Pitane joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Pordoselene joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Erythrai (Ionia) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Klazomenai joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Airai joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Ephesos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Lebedos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Marathesion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Myous joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Pygela joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Samos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: In the 5th century BC, Kelenderis was a member of the Attic-Delic Sea League.
January 477 BC: Athenai became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Arisbe joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Singos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Notion (Ionia) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Neandreia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Aineia became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Myrleia/Bryllion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Tinde became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Parion joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Strepsa became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Lampsakos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Priene joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Spartolos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: After the Persian Wars, Amphipolis became a member of the Attic Sea League.
January 477 BC: Sidousa joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Tereia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Astyra joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Dion (Chalkidike) became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Teos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Myrina (Aiolis) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Zone joined the Delian League at its founding in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Phokaia joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
January 477 BC: Thyssos became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Belbina became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Neapolis became part of the Delian League.
January 477 BC: Skione became part of the Delian League, founded in 478 BC.
January 477 BC: Larisa (Aiolis) joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states.
1.1.Wars of the Delian League
Were a series of campaigns fought between the Delian League of Athens and her allies (and later subjects), and the Achaemenid Empire of Persia.
January 475 BC: Both Kalchedon and Byzantium (from 476 to 405 BC) were members of the Attic-Delic Sea League.
January 474 BC: Eion is conquered by the Delian League in 475 BC.
January 474 BC: Eion is besieged by the Athenian Empire.
January 474 BC: In c. 475 BC, according to Thucydides (1.98), Cimon defeated the Dolopians (the original inhabitants) and conquered the entire island.
January 473 BC: After the fall of Eion, other coastal cities of the area surrendered to the Delian League, with the notable exception of Doriscus.
January 469 BC: According to Plutarch, Cimon sailed with these 200 triremes to the Greek city of Phaselis (in Lycia) but was refused admittance. He therefore began ravaging the lands of Phaselis, but with the mediation of the Chian contingent of his fleet, the people of Phaselis agreed to join the league.
January 467 BC: Cimon, in 468 BC, attacked the city and it was enrolled in the Delian Confederacy.
January 465 BC: The accession of further cities of Asia Minor to the Delian league, particularly from Caria, probably followed the battle of Eurymedon.
January 464 BC: At some point between 468 and 465 BC, the Athenians under Cimon fought the Persians at the Eurymedon, and won, thus adding Pamphylia to their "Delian League" empire.
January 464 BC: At this point, some Persian forces were holding (or had re-taken) some part of the Chersonesos with the help of native Thracians. Cimon sailed to the Chersonesos with just 4 triremes, but managed to capture the 13 ships of the Persians, and then proceeded to drive them out of the peninsula.
January 464 BC: Thasos rebelled against Athens in 465 BC.
January 464 BC: At some point between 468 and 465 BC, the Athenians under Cimon fought the Persians at the Eurymedon, and won; thus adding Pamphylia to their "Delian League" empire.
January 462 BC: Thasos surrenders to the Delian League and is reduced to tributary status.
January 459 BC: Megara defected from the Spartan-dominated Peloponnesian League (c. 460 BC) to the Delian league.
January 457 BC: From 458 to 446 BC BC Troizen was occupied by Athens.
1.1.1.Expedition in Achaemenid Egypt
Was a Greek military campaign in the Achaemenid satrapy of Egypt.
January 459 BC: Inaros appealed to the Delian League for assistance in their fight against the Persians.
January 454 BC: Siege of Prosopitis.
Was a war fought between Sparta as leader of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, against the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos.
January 456 BC: The Athenians sent an army under Myronides to attack Boeotia. The Boeotian army gave battle to the Athenians at Oenophyta. The Athenians scored a crushing victory which led to the Athenians conquering all of Boeotia except for Thebes, as well as Phocis and Locris.
January 456 BC: Aegina surrendered to Athens and was forced to become part of the Delian League.
January 456 BC: During the Peloponnesian War, the Athenians, led by their general Alcibiades, launched a naval expedition in -457 to attack the Spartan stronghold of Gythium. This strategic move weakened the Spartan naval power and expanded Athenian control in the region.
January 456 BC: The Athenians followed up this success by capturing the city of Chalcis on the Corinthian Gulf and then landing in the territory of Sicyon and defeating the Sicyonians in battle.
February 456 BC: During the Peloponnesian War, the Athenians, led by Admiral Tolmides, launched a naval expedition in -456 to attack the Spartan dockyards in Gythium. This strategic move aimed to weaken Sparta's naval power and control over the region.
January 455 BC: Athens occupied the territory of Naupactus
January 446 BC: In 447 BC a revolt against the Athenians broke out in Boeotia causing the end of the continental part of the Athenian Empire on the Greek mainland. The Athenians were defeated at the Battle of Coronea. Athens abandoned Boeotia, Phocis, and Locris.
2.1.Thirty Years' Peace
Was a treaty signed between the ancient Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta that brought an end to the First Peloponnesian War.
April 445 BC: Aegina was to be a tributary to Athens but autonomous.
April 445 BC: Troezen and Achaea became independent from Athens.
April 445 BC: The arrangement between Sparta and Athens was ratified by the "Thirty Years' Peace" (winter of 446-445 BC). According to this treaty, Megara was returned to the Peloponnesian League.
January 444 BC: With the peace treaty between Athens and Sparta, Paghe came under the influence of Megara.
Were a series of wars in ancient Greece over the control of the sacred city of Delphi.
3.1.Second Sacred War
Was a Spartan expedition against Phocis, that had occupied the sacred city of Delphi.
January 448 BC: The Spartans launched an expedition against Phocis, seized the Delphic sanctuary and handed it over to the Delphs. As a result, the Phocians lost control of the sanctuary; Delphi became independent again.
January 447 BC: As early as 448 BC, soon after the departure of the Spartans, an Attic army led by Pericles rushed to Phocis, conquered Delphi and restituted the Phocians in possession of the temple.
Was an Ancient Greek military conflict between Athens and Samos. The war was initiated by Athens's intervention in a dispute between Samos and Miletus.
January 439 BC: A group of oligarchs opposing Athenian influence, collaborating with allies in the city, invaded Samos with 700 mercenaries of Pissuthnes, and defeated the democrats. Samos left the Athenian sphere of influence.
January 438 BC: Athenian siege of Samos, at the end of which the Samians surrendered and were forced to become a member of the Athenian Empire.
Conquests by Spartokos I, ruler of Bosporan Kingdom.
January 437 BC: Kimmerikon is annexed to the Bosporan Kingdom.
Was a war between Athens and the Kingdom of Macedonia that preceded the Peloponnesian War of 431-404 BC.
January 432 BC: The Athenian Empire captured the Macedonian cities Therma and Beroea.
January 432 BC: King Perdiccas II retaliated against Athens by supporting the rebellion of their allies in Chalcidice. As a result, he was able to gain control of the strategic city of Potidaea in -433.
June 432 BC: In the spring of 432 BC, during the first phase of the Peloponnesian War, several cities of Chalcidice broke away from the Athenian-dominated Delian League.
January 430 BC: Sitalces was a Thracian king who brokered a peace treaty in -431 between Athens and Potidaea, a city in Chalcidice. As a result of the treaty, much of Chalcidice's territory was ceded to the Athenian Empire.
January 430 BC: Therma was returned to Macedonia.
Was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world.
January 430 BC: In 429 BC, Athens sent an expedition against Lycia to try to force it to rejoin the League. This failed when Lycia's leader Gergis/Kheriga of Xanthos defeated Athenian General Melesander.
January 429 BC: Herakleion passed into Athenian control in the years 430/29, 425/4.
January 428 BC: Herakleion conquered by Macedon.
January 427 BC: Antissa left the Delean League.
January 427 BC: In -428, the city-state of Pyrrha left the Delian League.
January 427 BC: In -428, the city of Methymna left the Delian League, which was led by Athens at the time. The Delian League was an alliance of Greek city-states formed to defend against the Persian Empire, but Athens eventually turned it into an empire of its own.
January 427 BC: In -428, the city-state of Eresos left the Delian League, which was led by Athens at the time.
January 427 BC: Caria returned to Achaemenid rule for about one century, from around 428 BC.
January 427 BC: In -428, the city of Mytilene left the Delian League led by Athens. This decision was made during the Peloponnesian War, a conflict between Athens and Sparta.
January 426 BC: Athens took over all the so-called Actaean cities in the Troad.
January 426 BC: Eresos fell to the Athenian general Paches.
January 426 BC: Antissa fell to the Athenian general Paches.
January 426 BC: Pyrrha fell to the Athenian general Paches.
January 426 BC: Mytilene fell to the Athenian general Paches and, along with the other cities of the island except for Methymna, had an Athenian cleruchy imposed on it.
January 426 BC: Methymna fell to the Athenian general Paches.
January 425 BC: During the Peloponnesian War, the city of Naxos revolted against the Delian League led by Athens in -426. The rebellion lasted until -410, when the Athenian Empire regained control of the territory.
January 424 BC: Odessos was included in the assessment of the Delian league of 425 BC.
January 424 BC: Platamon passed into Athenian control.
January 423 BC: Phersu Atlas Assumption: Assumed border corrections due to military occupations and reorganization (based on maps).
January 423 BC: Argilo left the Delian League.
January 423 BC: Platamon conquered by Macedonia.
January 423 BC: The place where this event occurred was Amphipolis, a strategic city in ancient Macedonia. Brasidas was a Spartan general known for his military prowess, while Cleon was an Athenian general and politician. The territory of Amphipolis was eventually regained by Cleon after it was briefly occupied by Brasidas.
January 423 BC: Mesambria (Pontos: West Coast) joined the Delian League, under the leadership of Athens.
January 423 BC: In 425/4 BC Mesambria (Thrace) joined the Delian League, under the leadership of Athens.
January 422 BC: The territory of Amphipolis was occupied by the Spartan general Brasidas in 424 BC during the Peloponnesian War. However, it was later recovered by the Athenian general Cleon in the following year, -423 BC.
January 412 BC: After Athenian alliance with Perdiccas II in 413 BC it became again a city of Macedon.
January 409 BC: The region of -410 that fell under Spartan control was the city of Athens. This transfer of power occurred during the Peloponnesian War, a conflict between Athens and Sparta. The war lasted from 431 to 404 BC and resulted in Sparta emerging as the dominant power in Greece.
7.1.The Archidamian War (first phase of the Peloponnesian War)
Was the first phase of the Peloponnesian War and consisted in Sparta's invasion of the territories of Athens. The phase is known as the Archidamian War (431-421 BC) after Sparta's king Archidamus II.
January 430 BC: The Spartan strategy during the first war, known as the Archidamian War, was to invade the land surrounding Athens. The Spartans also occupied Attica for periods of only three weeks at a time.Iin the tradition of earlier hoplite warfare the soldiers were expected to go home to participate in the harvest. Moreover, Spartan slaves, known as helots, needed to be kept under control, and could not be left unsupervised for long periods of time. The longest Spartan invasion, in 430 BC, lasted just forty days. We assume, however, that Sparta controlled Attica.
January 429 BC: In 430 BC an outbreak of a plague hit Athens. The fear of plague was so widespread that the Spartan invasion of Attica was abandoned, their troops being unwilling to risk contact with the diseased enemy.
7.2.Sicilian Expedition (Peloponnesian War)
Was an Athenian military expedition in Sicily against the poleis of Syracuse, an ally of Sparta. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces.
November 415 BC: During the Peloponnesian War, the Athenians, led by general Alcibiades, conquered Hykkara, an ally of Segesta in -415. They enslaved the population and razed the city to the ground before moving towards Segesta and Catania.
December 415 BC: During the Sicilian Expedition, the Athenians, led by Alcibiades, conquered Hykkara in -415, a city allied with Segesta. They enslaved the population and destroyed the city. After the conquest, the Athenian troops split, with one group heading towards Catania and the other towards Segesta.
June 414 BC: In the spring of 414 BC the Athenians took the initiative again (for the last time) and began the siege of Syrakousai. With a coup d'état they managed to take the strategically important Epipolai (high field) north of the city.
June 414 BC: The Athenian fleet took the portof Syrakousai.
September 413 BC: After having finished their resources they Athenians tried to escape by sea and land but were unsuccesfull and were captured by the syracusans.
7.3.Second Phase - Deceleian War
Was the second phase of the Peloponnesian War, where Sparta allied with Persia against Athens, which capitulated and lost its empire.
January 412 BC: If the Sicilian defeat had already been a terrible blow, this was followed by a new invasion of Attica by Spartan troops, the outcome of which was even worse than any other military campaign in Attica. In fact, on the advice of Alcibiades, King Agide II decided to militarily occupy the fortress of Decelea.
January 411 BC: The Spartans consolidated their control over Miletus and the mainland.
January 411 BC: Late in the Peloponnesian War (412 BC), the city of Chios revolted again. This rebellion was part of the ongoing power struggles between Athens and Sparta during the final years of the war.
January 411 BC: Late in the Peloponnesian War (412 BC), the city of Miletus revolted again along with Chios and Klazomenai. This rebellion was part of the ongoing power struggles between Athens and Sparta during the final years of the war.
January 411 BC: Late in the Peloponnesian War (412 BC), the city of Erythrai in Ionia revolted again with Chios and Clazomenae. This rebellion was part of the ongoing power struggles between Athens and Sparta, with Erythrai seeking to assert its independence from Athenian control.
October 411 BC: After the Battle of Eretria all of Euboea went over to the Spartans
January 410 BC: During the oligarchical revolution in Athens in -411 BC, Thasos revolted from Athens and was placed under the control of Sparta. This period marked a time of political upheaval in ancient Greece, with power struggles between different city-states and factions.
January 410 BC: In 411 BC Andros proclaimed its freedom.
January 410 BC: During the Second Peloponnesian War, a Spartan expedition led by Dercylidas arrived at Abydos in early May 411 BC and successfully convinced the city to defect from the Delian League.
January 410 BC: Byzantium was besieged by Greek forces during the Peloponnesian War. As part of Sparta's strategy for cutting off grain supplies to Athens during their siege of Athens, Sparta took control of the city in 411 BC, to bring the Athenians into submission.
January 410 BC: Shortly after the Battle of Syme Rhodes also joined the Spartan alliance.
January 407 BC: Siege of Byzantium (408 BC). The Athenians conquer Byzantium.
January 406 BC: In 407 BC the partisans of Lacedaemon were expelled, and the Athenians under Thrasybulus were admitted.
September 405 BC: Sparta ended the siege of Athens after almost a year.
January 404 BC: After the Battle of Aegospotami (405 BC), Thasos again fell into the hands of the Lacedaemonians.
April 404 BC: The Battle of Aegospotami was the Spartan naval victory that ended the Peloponnesian War: in the battle the Spartan fleet, commanded by Lysander, completely destroyed the Athenian one, ending the war. Fearing retaliation from the victorious Spartans, the Athenians decided to resist the siege, led by Nicias' brother Eucrates, but they had no hope: with no fleet to import grain from the Black Sea, Athens was on the verge of starvation, so it surrendered.
January 403 BC: The Delian League was dissolved upon the conclusion of the Peloponnesian War with the defeat of Athens (404 BC).
January 403 BC: Toward the end of the Peloponnesian War, the Athenians were weakened enough that the Persians were able to retake Pamphylia.
January 403 BC: In -404, the city of Athens was a member of the Attic-Delic Sea League, an alliance of city-states in ancient Greece. The league was led by Athens and played a significant role in the politics and military affairs of the region during that time.
January 403 BC: In the 5th century BC, Athenai was a member of the Attic-Delic Sea League, led by the powerful Athenian Empire. This league was formed to protect against Persian invasions and maintain Athenian dominance in the region.
January 403 BC: Heraclea Cybistra taken back by Persia.
January 403 BC: After a prolonged siege by Sparta, Athens surrendered. As a consequence Athens had to form an alliance with Sparta, the Long Walls of the city were demolished, its territory was reduced to just Attica and Salamis and the Delian-Attic league was dissolved.
January 403 BC: Despites being defeated by Sparta in 404 BC, Athens soon recovered and re-established her hegemony over Euboea.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Bisanthe left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: The decisive battle of Aegospotami in -404 BC was fought between the Athenian navy, led by Admiral Conon, and the Spartan navy, led by Lysander. The Spartans emerged victorious.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Perinthos left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Selymbria left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Serrion Teichos left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Byzantion left the Delian League.
January 454 BC: In 455 B.C. Paghe was occupied by the Athenians.
January 454 BC: Neupactus reconquered by Sparta.
January 453 BC: Olynthus became a Greek polis, but it remained insignificant.
January 443 BC: Phersu Atlas Assumption: Assumed border corrections due to military occupations and reorganization (based on maps).
January 443 BC: Athens chose it as its principal military base in the region ca. 444 BC.
January 436 BC: Foundation of Amphipolis in 437 BC by Athens.
January 433 BC: Methone was not ruled by Macedonia but was an ally of Athens and since 434 BC, a member of the Athenian League.
January 420 BC: Heracleium passed under Athenian control.
January 415 BC: Athens besieges Melos, which surrenders. The Athenians massacre the adult male Melians and sell the rest of the inhabitants into slavery.
Disestablishment
January 403 BC: Heraclea Cybistra taken back by Persia.
January 403 BC: The Delian League was dissolved upon the conclusion of the Peloponnesian War with the defeat of Athens (404 BC).
January 403 BC: After a prolonged siege by Sparta, Athens surrendered. As a consequence Athens had to form an alliance with Sparta, the Long Walls of the city were demolished, its territory was reduced to just Attica and Salamis and the Delian-Attic league was dissolved.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Bisanthe left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: Despites being defeated by Sparta in 404 BC, Athens soon recovered and re-established her hegemony over Euboea.
January 403 BC: The decisive battle of Aegospotami in -404 BC was fought between the Athenian navy, led by Admiral Conon, and the Spartan navy, led by Lysander. The Spartans emerged victorious.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Perinthos left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Selymbria left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Serrion Teichos left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: After the decisive battle of Aegospotami in 404 BC where Sparta defeated Athens, Byzantion left the Delian League.
January 403 BC: Toward the end of the Peloponnesian War, the Athenians were weakened enough that the Persians were able to retake Pamphylia.
January 403 BC: In -404, the city of Athens was a member of the Attic-Delic Sea League, an alliance of city-states in ancient Greece. The league was led by Athens and played a significant role in the politics and military affairs of the region during that time.
January 403 BC: In the 5th century BC, Athenai was a member of the Attic-Delic Sea League, led by the powerful Athenian Empire. This league was formed to protect against Persian invasions and maintain Athenian dominance in the region.
Selected Sources
Bleckmann, B. (2016): Der Peloponnesische Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 107-113
Boardman, J. / Griffin, J. / Murray, O. (2001): The Oxford Illustrated History of Greece and the Hellenistic World, Oxford (UK), p. 417
Hansen, M. G. / Nielsen, T. H. (2004): An inventory of archaic and classic polities, Oxford University Press, p. 1356-1359, p. 111-113
Malczynski, R (2009): Die griechische Welt im Zeitalter des Aristoteles, Düsseldorf (Germany), pp. 5-6
Plutarch: Parallel Lives, Pericles: 26.1
Roisman, J. / Yardley, J. C. (2011): Ancient Greece From Homer to Alexander: The Evidence, Hoboken (USA), pp. 96, 105–106
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXIV
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXIX
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXV
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXVII
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXVIII
Thucydides, History of the Peloponnesian War, 1.108
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.25-29

 Athenian Empire
Athenian Empire