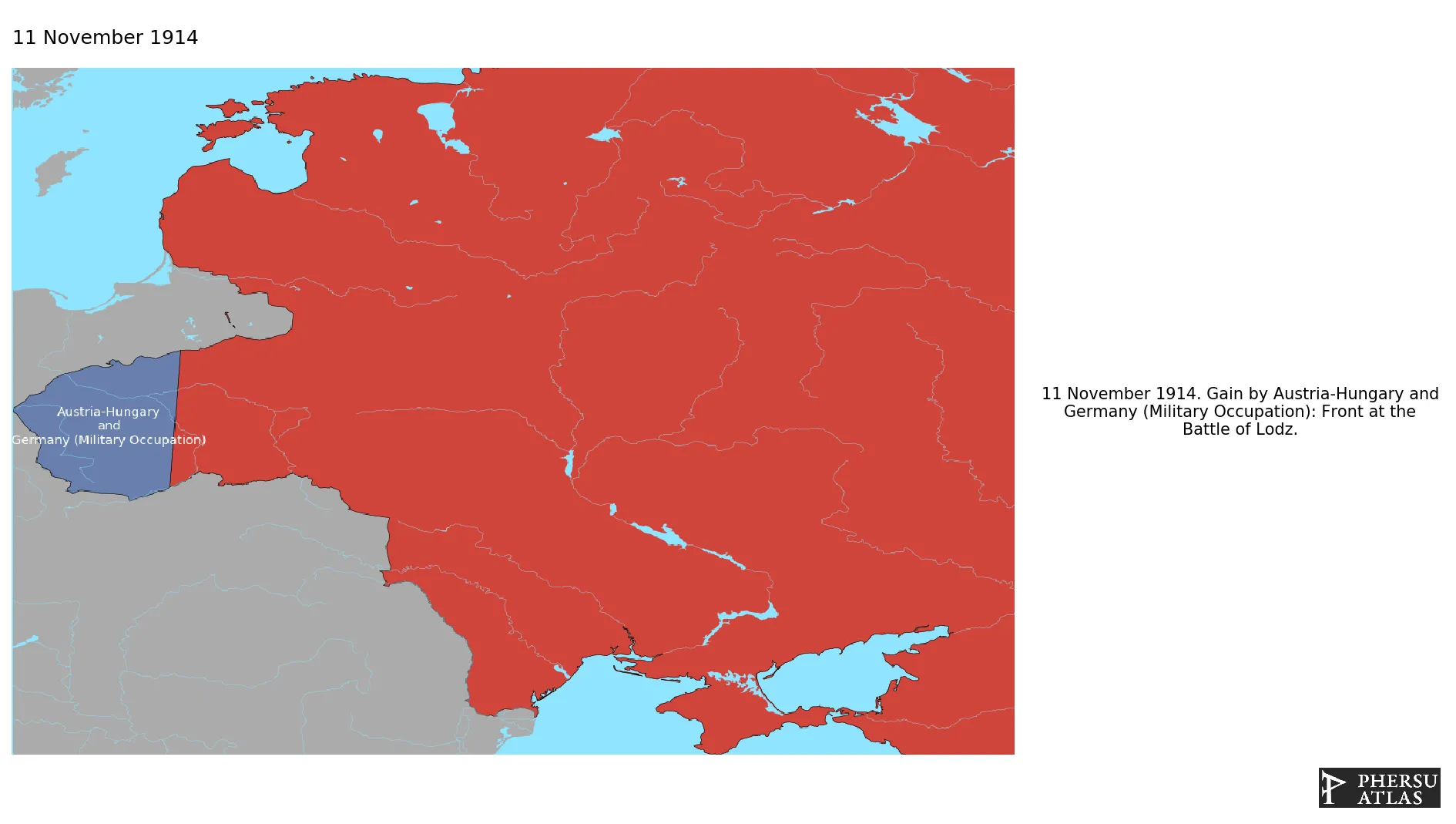
.png.webp)
Data
Name: Austria-Hungary and Germany (Military Occupation)
Type: Polity
Start: 1914 AD
End: 1919 AD
Parent:
austria,germanyStatistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Austria-Hungary and Germany (Military Occupation)
Austria-Hungary and Germany (Military Occupation)
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Polity that includes all territories military occupied by Austria-Hungary and Germany that are not part of a specific military territory.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. World War I
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
Was the theatre of war in eastern Europe during World War I.
Was a major battle between Russia and Austria-Hungary during the early stages of World War I. The Austro-Hungarian armies were severely defeated and forced out of Galicia.
1.1.2.Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive
The Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive during World War I was initially conceived as a minor German offensive to relieve Russian pressure on the Austro-Hungarians to their south on the Eastern Front, but resulted in the Central Powers' chief offensive effort of 1915, causing the total collapse of the Russian lines and their retreat far into Russia.
Was a major Russian offensive against the Central Powers during World War I.
Was a Central Powers offensive in World War I. It was the last major action on the Eastern Front. The northern force, consisting of 16 divisions, captured the key Daugavpils junction on the first day.
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Brest Peace in Russia) was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, between the new Bolshevik government of Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's participation in World War I.
1.1.5.1.Consequences of Brest-Litovsk Treaty in Latvia
Was the reorganization of Latvia after the Brest-Litovsk Treaty.
1.1.6.White Russia administrative changes
Where the administrative changes of Belarus during World War I and the Russian Civil War.
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
1.2.1.Aftermath of World War I in Poland
Events that happened shortly after the end of World War I in Poland.
Was a conflict between the Second Polish Republic and Ukrainian forces (both the West Ukrainian People's Republic and Ukrainian People's Republic).
1.2.2.Creation of Estonia after the retreat of the German Army
After their defeat in World War I, the Germans handed over the power in Estonia to a Provisional Government.
1.2.3.Estonian War of Independence
Was the Estonian War of independence from Bolshevik Russia and German troops.
1.2.3.1.Soviet Offensive (Estonian War of Independence)
Was the Bolshevik invasion of Estonia, a former region of the Russian Empire that had declared independence.
2. Russian Civil War
Was a Civil War in Russia that involved varios factions but mainly the Bolsheviks and the conservative White Army in the core Russian territories, as well as a multitude of local secessionist states. At the end of war the Bolsheviks were victorious and established the Soviet Union.
2.1.Soviet westward offensive of 1918-25
Was a military campaign by the Russian SFSR into regions that had been evacuated by the German forces in eastern Europe after World War I.
2.1.1.Soviet westward offensive in Poland
Was a military offensive by the Russian SFSR in Poland after the German army left the area.