This article is about the specific polity Dutch Gold Coast and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch, beginning in 1612. On 6 April 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast was, in accordance with the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870-71, ceded to the United Kingdom.
Establishment
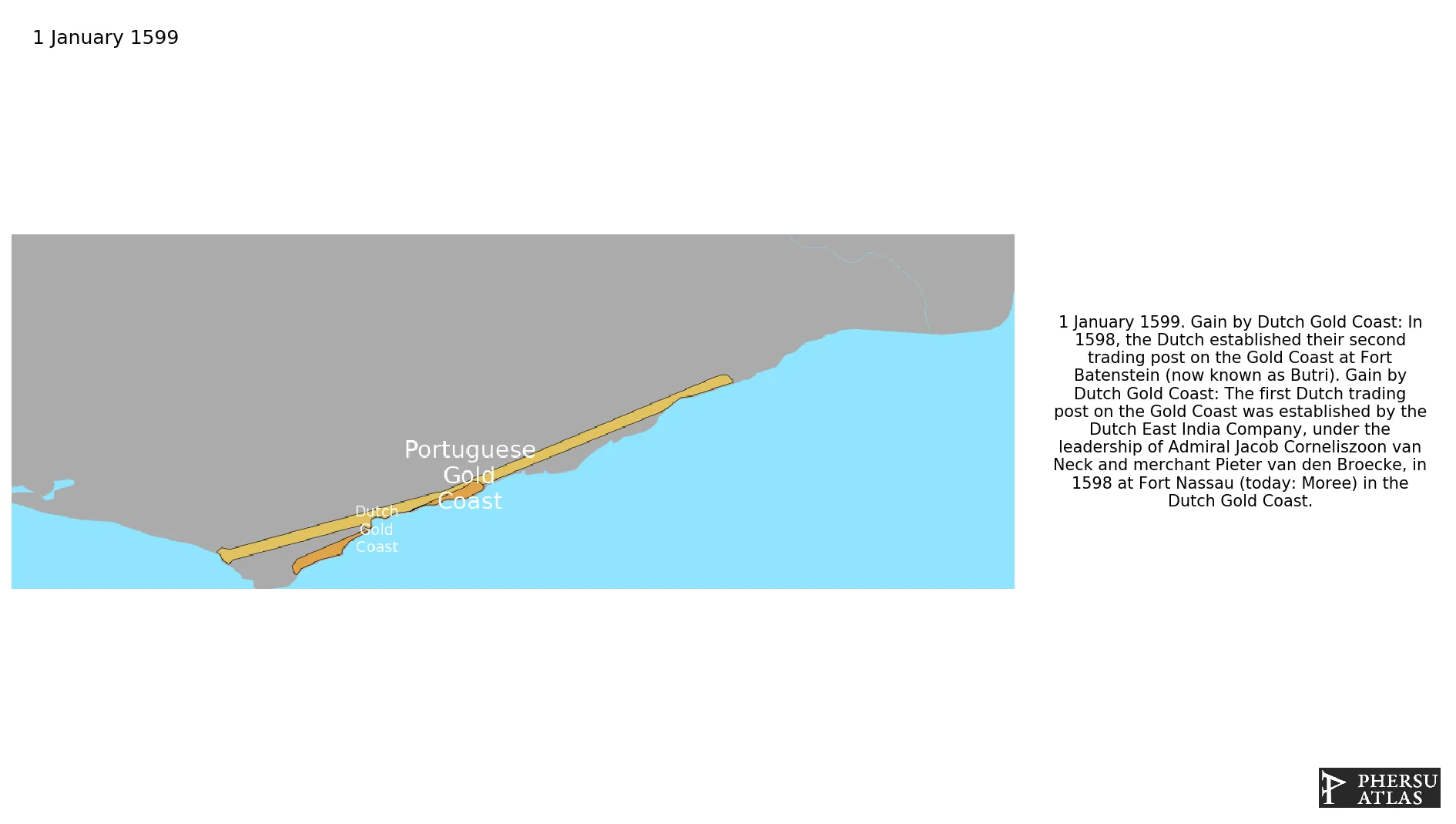
January 1599: In 1598, the Dutch established their second trading post on the Gold Coast at Fort Batenstein (now known as Butri).
January 1599: The first Dutch trading post on the Gold Coast was established by the Dutch East India Company, under the leadership of Admiral Jacob Corneliszoon van Neck and merchant Pieter van den Broecke, in 1598 at Fort Nassau (today: Moree) in the Dutch Gold Coast.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict between the Portuguese Empire and the Dutch Empire. The conflict primarily saw the Dutch companies invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies.
1.1.Dutch Invasion of the Portuguese Gold Coast
Was the Dutch invasion the Portuguese Gold Coast.
August 1637: The Dutch occupied São Jorge da Mina. .
1.2.Operations in West Africa and Angola
Were the military operations of the Dutch in West Africa and Angola during the Dutch-Portuguese War.
January 1642: The Portoguese Gold Coast was ceded to the Dutch.
Were a series of wars from 1694 until 1700 largely between the Dutch West India Company and the English Royal African Company in present-day Ghana, over trade rights.
May 1700: At the end of the komenda wars, the british took de facto over the Eguafo kingdom. British-supported mercenary force moved upon Eguafo and on May 9, 1700, Takyi Kuma was named the new king of Eguafo.
Expansion during the rule of Opoku Ware I in the Ashanti Empire.
January 1751: It was during the reign of Opokou Ware I (1718-1750) that the Ashanti Empire reached its maximum expansion controlling most of the territory of present-day Ghana, but also spilling over into parts of present-day Togo and Ivory Coast.
Was the war of independence of the United States of America (at the time the Thirteen Colonies) against Great Britain.
4.1.Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
Was a conflict between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Dutch Republic during the American Revolutionary War.
January 1783: In 1782, during the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War, Britain seized Fort Nassau, Fort Amsterdam, Fort Lijdzaamheid, Fort Goede Hoop, and Fort Crêvecoeur from the Dutch. This was part of Britain's military occupation of the Dutch territories during the war.
January 1783: The Dutch Republic only managed to seize Fort Sekondi from the British.
May 1784: The Treaty of Paris of 1784 was signed between Great Britain and the Netherlands, ending the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War. As a result, Fort Sekondi in the British Gold Coast was returned to the Dutch, as stipulated in the treaty.
May 1784: The Treaty of Paris of 1784 returned Fort Nassau, Fort Amsterdam, Fort Lijdzaamheid, Fort Goede Hoop, and Fort Crêvecoeur to the Dutch, ending the hostilities between the Dutch and the British over control of the Dutch Gold Coast.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
5.1.French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars - Theatre of war in the overseas colonies
The theatre of war in the overseas colonies during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
January 1802: During the French occupation of the Netherlands between 1810 and 1814, the Dutch possessions on the Gold Coast held the rather unusual position—together with the island of Deshima in Japan—of being the only Dutch territories not occupied by either France or Great Britain.
Was a Convention between Great Britain and the Netherlands for an Interchange of Territory on the Gold Coast of Africa in which all Dutch forts to the east of Elmina were handed over to Britain.
March 1867: In 1867, the Convention between Great Britain and the Netherlands for an Interchange of Territory on the Gold Coast of Africa was signed, in which all Dutch forts to the east of Elmina were handed over to Britain.
March 1867: The British forts west of Elmina were handed over to the Netherlands.
January 1613: Jacob Clantius, who was to become the first General on the Coast, was sent to the Gold Coast in 1611. In 1612, after gaining permission of the local rulers through the Treaty of Asebu, he built Fort Nassau near Moree, on the site of an original Dutch trading post that had been burned down by the Portuguese.
January 1632: Fort Amsterdam, the first British fort on the Gold Coast, was captured in 1665 by Engel de Ruyter, a Dutch naval commander known for his successful military campaigns in West Africa. The territory then went to the British Gold Coast.
January 1641: Shama conquered by netherlands.
January 1641: In 1560 the Portuguese founded Fort São Francisco Xavier, in modern Osu, district of Accra.
January 1641: In 1640, the Dutch built Fort William.
January 1643: The Trading post of Port Orange established by the Dutch in 1642.
January 1647: English trading post of Fort Egya was built in 1647.
January 1648: Fort Egya (today: Egya) conquered by the Dutch.
April 1650: Fort Carlsborg was under Swedish administration by 22 April 1650.
January 1651: Fort Batenstein, located in present-day Butri near Sekondi-Takoradi in the Western region, was a fortification under Swedish administration from 1650 to 1656. It was an important trading post on the Swedish Gold Coast during this period.
January 1653: Fort Christiansborg, located in present-day Osu, Ghana, was under the administration of the Swedish Gold Coast from 1652 to 1658. The fort was a key trading post for the Swedish Empire during this period.
January 1654: In 1653, the Swedes captured Fort William.
January 1654: Fort Witsen, now Sekondi-Takoradi in the Western region, was under the control of the Swedish Gold Coast from 1653 to 1658. The fort was named after Dutch merchant Jacob Witsen, who played a significant role in the establishment of the trading post.
January 1656: Fort Apollonia was established by the Swedes in 1655 as part of the Swedish Gold Coast, a colony in present-day Ghana. The trading post was strategically located for the Swedish to engage in the lucrative trade of gold and other commodities in the region.
August 1656: After the Dutch managed to dislodge the Swedes from Butre and began building Fort Batenstein at that site, the leaders of the Dutch West India Company thought it beneficial to negotiate a treaty with the local political leadership in order to establish a peaceful long-term relationship in the area. The local Ahanta leaders found it equally beneficial to enter into such an agreement, and thus on 27 August 1656, the Treaty of Butre was signed. This treaty established a Dutch protectorate in the area.
January 1659: In 1658, Fort Christiansborg in present-day Osu, Ghana, was transferred from Swedish to Dutch control.
February 1659: Fort Christiansborg was lost to Denmark-Norway.
January 1661: In 1659 or 1660, the Dutch recaptured Fort William (today: Anomabu).
January 1665: Fort Egya was demolished in 1665 by the British after they had recaptured it in the year before.
January 1666: Fort Amsterdam, on the Gold Coast, was captured in 1665 by Engel de Ruyter.
July 1667: When the second Anglo-Dutch war ended in 1667 with the Treaty of Breda, the English gained a foothold in Anomabo.
January 1668: Fort Goede Hoop (today: Senya Beraku) conquered by netherlands.
January 1671: Ashanti political organization was originally centered on clans headed by a paramount chief or Amanhene.One particular clan, the Oyoko, settled in the Ashanti's sub-tropical forest region, establishing a center at Kumasi. The Ashanti became tributaries of another Akan state, Denkyira.
June 1682: In May 1682 the newly founded Brandenburg African Company, which had been granted a charter by Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg (core of the later Prussian kingdom), established a small West African colony.
January 1683: Fort Sekondi, also Fort George, was an English fort on the Gold Coast, built in 1682 at Sekondi.
January 1684: The British began building Fort Metl Cross (today: Dixcove, Ghana) in 1683.
May 1684: Fort Dorothea, also called Accada (now Akwid), was established by Brandenburg in modern-day Ghana.
January 1686: Between 1683 and 1685, the Brandenburgers, led by Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, expanded their settlements and fortifications in the area. Despite this, Fort Groß Friedrichsburg remained the key stronghold on the Brandenburger Gold Coast.
January 1688: The Dutch, led by Governor Hendrik Hertog, occupied Fort Dorothea (Akwida) in 1687 as part of their control over the Dutch Gold Coast. The fort was later abandoned in 1698 due to conflicts with the local tribes.
January 1698: Fort Lijdzaamheid (today: Apam) conquered by netherlands.
January 1699: The Dutch, led by Admiral Willem de la Palma, occupied Fort Dorothea (Akwida) in 1687. However, in 1698, the territory was transferred to the Brandenburger Gold Coast, a trading company established by the Electorate of Brandenburg.
January 1699: Fort Komenda was established between 1695 and 1698 at Komenda, in contemporary Ghana.
January 1709: Before 1708 the chiefdom of Anomabu was established in Ghana, possibly by Nana Eno who became its first king.
January 1721: Sefwi-Wiawso is established.
January 1722: In 1721 the rights to the colony were sold to the Dutch, who renamed it Hollandia, as part of their larger Dutch Gold Coast colony.
January 1725: Only in 1724 was it possible to expel Jan Conny.
January 1730: Nana Brempong Codjo becomes the first king of the chiefdom of Oguaa.
January 1735: Fort Singelenburgh (today: Keta) conquered by netherlands.
January 1738: Destroyed by the Dutch in 1737 after it was attacked by the local population.
January 1741: The Kingdom of Sanwi was established in about 1740 by Anyi migrants from Ghana. It was located in the present district of Sud-Comoé in Ivory Coast. The kingdom was known for its strong cultural traditions and political organization.
January 1788: By 1787 Denmark established Fort Augustaborg (today: Teshie) in the Gold Coast (modern-day Ghana).
January 1801: Establishment of Ahanta Kingdom in Ghana.
January 1815: During the French occupation of the Netherlands between 1810 and 1814, the Dutch possessions on the Gold Coast were not occupied by either France or Great Britain. The colony reverted to the Netherlands in 1814.
January 1817: The Dutch Gold Coast regained control of Fort Goede Hoop in 1816, marking the end of Akim occupation.
January 1833: In 1832, Nana Kwaku Ackah gained control of nr 5 on the map, which belonged to Western Nzima. Nana Kwaku Ackah was a prominent leader in the region during this time period, exerting influence over the territory until 1848.
April 1872: In February of that year, a treaty had been signed with the United Kingdom, under which terms the whole colony was to be ceded for a sum of 46,939.62 Dutch guilders. On 6 April 1872, after ratification of the treaty by parliament, Elmina was formally handed over to Britain.
Disestablishment
April 1872: In February of that year, a treaty had been signed with the United Kingdom, under which terms the whole colony was to be ceded for a sum of 46,939.62 Dutch guilders. On 6 April 1872, after ratification of the treaty by parliament, Elmina was formally handed over to Britain.

 Dutch Gold Coast
Dutch Gold Coast