This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Romania and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
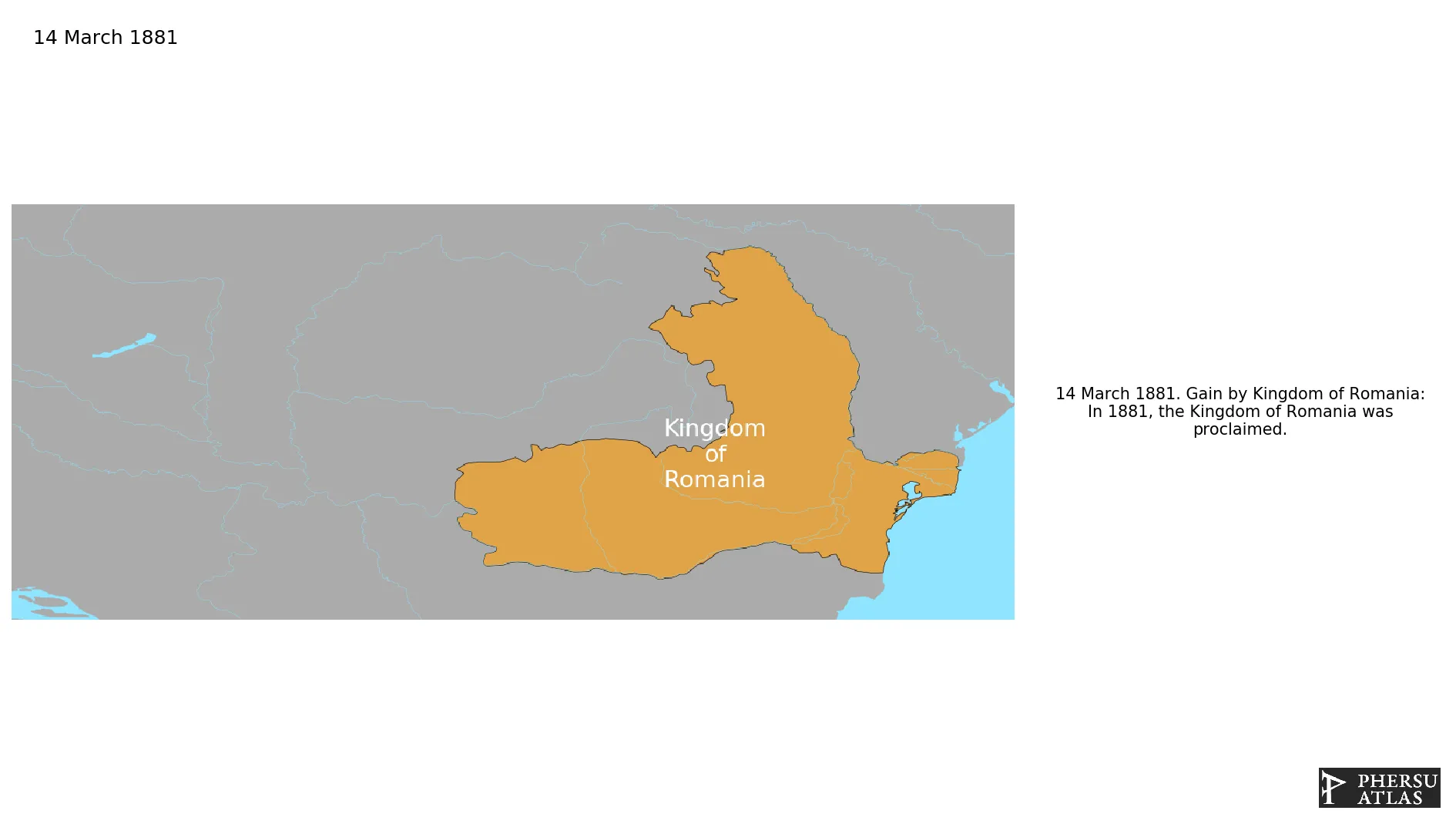
The Kingdom of Romania succeeded the Romanian United Principalities in 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I.
Summary
The proclamation of the Kingdom of Romania in 1881 was a significant milestone in the history of Romania. Under the reign of King Carol I, the new kingdom pursued a policy of cautious neutrality, seeking to balance its relationships with the Great Powers.
In the early 20th century, Romania experienced a period of economic growth and cultural flourishing. However, social tensions between the large peasant class and the landowning elite remained unresolved. The country's involvement in the Balkan Wars of 1912-1913 and World War I led to territorial gains, but also created new challenges.
After World War I, Greater Romania emerged, incorporating Transylvania, Bessarabia, and other regions. This expanded the country's size and population, but also introduced new ethnic and religious minorities. The interwar period was marked by political instability, the rise of authoritarian tendencies, and the growing influence of fascist and communist ideologies.
In 1940, Romania was forced to cede territories to Hungary, the Soviet Union, and Bulgaria, which fueled resentment and irredentist sentiments. During World War II, Romania initially aligned with the Axis powers, but later switched sides and joined the Allies. The postwar period saw the imposition of a communist regime and the transformation of Romania into a People's Republic.
Establishment
March 1881: In 1881, the Kingdom of Romania was proclaimed.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were two wars fought in southeastern Europe in 1912-1913 during which the states of the Balkan League (Bulgaria, Greece, Montenegro and Serbia) first conquered Macedonia and much of Thrace from the Ottomans and then clashed with each other over the division of the conquered lands.
1.1.Second Balkan War
Was a war fought by Bulgary against a coalition of Balkan states. During the First Balkan War the Balkan League had conquered most of the Ottoman Balkan territories. Bulgaria was dissatisfied by the territorial partition and invaded its former allies.
1.1.1.Treaty of Bucarest
Was the treaty that ended the Second Balkan War.
August 1913: In 1913, as a result of the Treaty of Bucharest, Bulgaria ceded southern Dobruja to Romania.
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
2.1.World War I eastern Front
Was the theatre of war in eastern Europe during World War I.
2.1.1.Romania during World War I
Romanian theatre of World War I.
May 1918: Romania signed a formal peace treaty with the Central Powers, the Treaty of Bucharest of 1918. Romania ceded the Carpathian mountain passes to Austria-Hungary. The central powers evacuated the remnant territories of Romania.
May 1918: Dobruja falls under the administration of the Central Powers.
May 1918: Everything below Constanța was annexed by Bulgaria.
November 1918: On November 10 Romania declared war once again to the Central Powers.
2.1.1.1.Battle of Transylvania
Was the first major operation of Romania against Austria-Hungary during World War I.
2.1.1.2.Counteroffensive of the Central Powers in Romania
Was a counteroffensive of the Central Powers in Romania.
2.1.1.3.Romanian military intervention in Bessarabia
Was a Romanian intervention in Bessarabia during the Russian Civl War.
April 1918: Bessarabia, which had declared itself as the Moldavian Democratic Republic in 15 December, united with Romania on 9 April 1918.
2.1.2.Kerensky Offensive
Was the last Russian offensive of World War I. Starting on July 1, 1917 the Russian troops attacked the Austro-Germans in Galicia, pushing toward Lviv.
July 1917: The Russians retreated about 240 kilometers in the territory of modern-day Ukraine.
2.2.Aftermath of World War I
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
June 1919: On June 21, 1919, the Banat region was divided between Romania, Serbia and Hungary.
June 1920: The Treaty of Trianon regulated the status of an independent Hungarian state and defined its borders. It left Hungary as a landlocked state that covered 93,073 square kilometres, only 28% of the 325,411 square kilometres that had constituted the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary.
2.2.1.Polish-Ukrainian War
Was a conflict between the Second Polish Republic and Ukrainian forces (both the West Ukrainian People's Republic and Ukrainian People's Republic).
November 1918: The Romanian Army occupied Chernivtsi.
2.2.2.Hungarian-Romanian War
Was a war between Romania and Hungary over territorial disputes after the dissolution of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I.
2.2.2.1.Romanian occupation of Transylvania
At the beginning of the Hungarian-Romanian War Romanian troops occupied Transylvania, a territory promised to Romania by the Entente in the Treaty of Bucharest (1916).
November 1918: The first Romanian troops enter Hungary and occupy the Gyergyótölgyes mountain pass accessing the Székely Land Region.
November 1918: The Romanian Army occupied Marosvásárhely (Târgu-Mureș).
December 1918: The Union of Transylvania with Romania was officiated by the elected representatives of the Romanian people of Transylvania, who proclaimed a union with Romania.
December 1918: The Romanian Army enters Brașov, in southeastern Transylvania.
December 1918: Romanian troops enter Nagyszeben (Sibiu) in southern Transylvania.
December 1918: Romanian troops enter Cluj (Kolozsvár).
January 1919: Romanian troops reached Baia Mare.
January 1919: The Romanian Army enters Sighetu Marmației.
January 1919: Romanian troops now control the entire territory up to the new demarcation line indicated by the Entente powers. Inner Transylvania and Maramureș are under Romanian control, leaving Banat under Serbian, and Crișana under Hungarian control.
April 1919: Romanian troops enter Carei (Nagykároly) and Satu Mare (Szatmárnémeti).
April 1919: The Romanian Army entered Oradea (Nagyvárad) and Salonta (Nagyszalonta).
2.2.2.2.Romanian invasion of Hungary to conquer further territories
Was a Romanian military invasion of Hungary after Romania had already occupied Transylvania.
May 1919: The Romanian Army reaches the river Tisza.
May 1919: Romanian army units enter Arad.
August 1919: French-supported Romanian forces entered Budapest. The Communist government of Hungary collapsed and its leaders flee.
August 1919: Romania occupied all of Hungary with the exception of an area around Lake Balaton.
January 1920: In early 1920, Romanian troops departed Hungary. All of Hungary but a region around Lake Balaton was evacuated.
2.2.2.3.Hungarian Offensive (Hungarian-Romanian War)
Was the Hungarian counteroffensive against Romanian troops that had invaded the country during the Hungarian-Romanian War.
July 1919: Hungary invaded Romanian border regions after the Tisza river.
July 1919: Mindszent and Törökszentmiklós reconquered by Romania.
2.2.2.4.Hungarian-Romanian War Aftermath
The border between Romania and Hungary after World War I was decided in the The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919).
September 1919: The Treaty of St. Germain established the borders of the Czechoslovak Republic.
September 1919: The Treaty of St. Germain established the borders of the Kingdom of Romania with Poland.
2.2.3.Aftermath of World War I in Pokuttya
Events that happened shortly after the end of World War I in the Pokuttya region.
May 1919: During the interwar period, Romania was Poland's main ally in Eastern Europe. To actively cooperate, governments in Bucharest and Warsaw emphasized the necessity of a shared border. The proposal was accepted by the Polish leader, Marshal Józef Piłsudski and on May 24, 1919 by the Romanian Army. Infantry Division, led by General Iacob Zadik, entered Pokuttya. After three days, the Romanians met the Poles in the area of Kalusz. As the Polish Army was involved in other conflicts (chiefly with the Soviets), the Romanians stayed in Pokuttya until late August 1919.
August 1919: In late summer of 1919 Polish troops entered Pokuttya (see Polish-Ukrainian War) and the Romanians withdrew to their country.
2.2.4.Treaty of St Germain
Was a treaty that settled the dissolution of Austria-Hungary after World War I.
Was a Civil War in Russia that involved varios factions but mainly the Bolsheviks and the conservative White Army in the core Russian territories, as well as a multitude of local secessionist states. At the end of war the Bolsheviks were victorious and established the Soviet Union.
3.1.Ukrainian-Soviet War
Was a conflict between Ukrainian nationalist forces and the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War. It also included a multitude of ethnical and local factions.
November 1918: The West Ukrainian People's Republic was proclaimed.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
4.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
April 1944: Frontline of the eastern front of World War II in that date.
June 1944: Restoration of the 1940 Romanian-Soviet border. Northern Bukovina and Bessarabia are annexed to the USSR.
December 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the eastern front of World War II in that date.
4.1.1.Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and northern Bukovina
The Soviet Union had planned to accomplish the annexation of Bessarabia and northern Bukovina with a full-scale invasion, but the Romanian government, responding to the Soviet ultimatum delivered on June 26, 1940, agreed to withdraw from the territories in order to avoid a military conflict.
July 1940: The Soviet Union had planned to accomplish the annexation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina with a full-scale invasion, but the Romanian government, responding to the Soviet ultimatum delivered on June 26, agreed to withdraw from the territories in order to avoid a military conflict.
4.1.2.Hungarian Expansion from the Second Vienna Award
Refers to the second Vienna Award, the second of two territorial disputes arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It took place on 30 August 1940 and assigned Northern Transylvania from Romania to Hungary.
August 1940: The Second Vienna Award was the second of two territorial disputes arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. Rendered on 30 August 1940, it assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania (including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana) from Romania to Hungary. Hungarian annexation of Northern Transylvania occured until 13 september 1940.
September 1940: The Second Vienna Award was the second of two territorial disputes arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. Rendered on 30 August 1940, it assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania (including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana) from Romania to Hungary. Hungarian annexation of Northern Transylvania occured until 13 september 1940.
4.1.3.Operation Barbarossa
Was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies.
4.1.3.1.Operation München (Bessarabia)
A joint German-Romanian offensive during the German invasion of the Soviet Union in World War II, with the primary objective of recapturing Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina and the Hertsa region, ceded by Romania to the Soviet Union a year before.
August 1941: On August 17, Bessarabia and northern Bukovina were officially reintegrated into the Romanian state.
4.1.4.Dnieper-Carpathian Offensive
Was a Soviet strategic offensive whose goal was to clear the German-Romanian-Hungarian forces from most of the Ukrainian and Moldavian territories.
March 1944: Mogilov-Podolsky was taken by Soviet forces on March 19th.
March 1944: Cernauti (Bessarabia) falls to Soviet forces of First Ukrainian Front.
April 1944: Tiraspol is liberated by the Red Army.
April 1944: The Soviet 40 Army captured Botoșani.
4.1.5.Operation Bagration
Was the Soviet offensive against German-occupied Belarus during World War II.
4.1.5.1.Šiauliai Offensive
Was an operation of the Soviet forces of the 1st Baltic Front, commanded by General Hovhannes Bagramyan, conducted from 5 July to 29 August 1944. It drove German troops from much of Lithuania, with the main tactical objective being the city of Šiauliai.
August 1944: Soviet advances during Operation Bagraton and Šiauliai Offensive.
4.1.6.Battle of Romania
The Soviet Operations to drive out the Axis powers from Romania during World War II.
September 1944: Soviet advance in Romania on 8 September 1944.
September 1944: By 24 September 1944, nearly all of Romania was under Allied control.
4.1.6.1.Jassy-Kishinev Offensive
Was a Soviet offensive against Axis forces in Eastern Romania during World War II.
August 1944: Troops of the USSR 7th Guards Army stormed Bacău and the 40th Army took Târgu Neamț.
August 1944: Focsani falls to troops of Second Ukrainian Front. Galati, third largest city in Rumania and chief port on the Danube, to those of Third Ukrainian Front.
August 1944: Tolbukhin's troops took the port cities of Brăila and Sulina on August 28.
August 1944: Troops of Second Ukrainian Front overrun Bucharest, capital of Rumania
4.1.7.Battle of Debrecen
Was a battle taking place 6-29 October 1944 on the Eastern Front in Hungary during World War II.
4.1.8.Soviet Invasion of Hungary
Was the Soviet invasion of German-occupied Hungary during World War II.
4.2.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
February 1947: Romania was restored to its borders of 1 January 1941, but with Hungary giving Northern Transylvania back to Romania. The loss of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina to the Soviet Union was confirmed.
December 1947: King Michael I of Romania was forced to abdicate, and afterwards, the Romanian People's Republic was proclaimed.
Disestablishment
February 1947: Romania was restored to its borders of 1 January 1941, but with Hungary giving Northern Transylvania back to Romania. The loss of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina to the Soviet Union was confirmed.
December 1947: King Michael I of Romania was forced to abdicate, and afterwards, the Romanian People's Republic was proclaimed.
Selected Sources
Ian Kershaw (trad. de l'anglais), La Fin : Allemagne, 1944-1945, Paris, Seuil, 2012, p.137
Operation Bagration, 22 June-19 August 1944. United States Military Academy of West Point. Retrieved on 6 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope30.jpg
Russian Balkan And Baltic Campaigns, 19 August-31 December 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope31.jpg
Russian Leningrad And Ukraine Offensives, 2 December 1943-30 April 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope29.jpg
Treaty of Bucharest (1918), https://web.archive.org/web/20130223024635/http://www.mtholyoke.edu/acad/intrel/routreat.html
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.182
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.184
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.257
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.260
.webp)
 Kingdom of Romania
Kingdom of Romania