This article is about the specific polity Principality of Isenburg and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
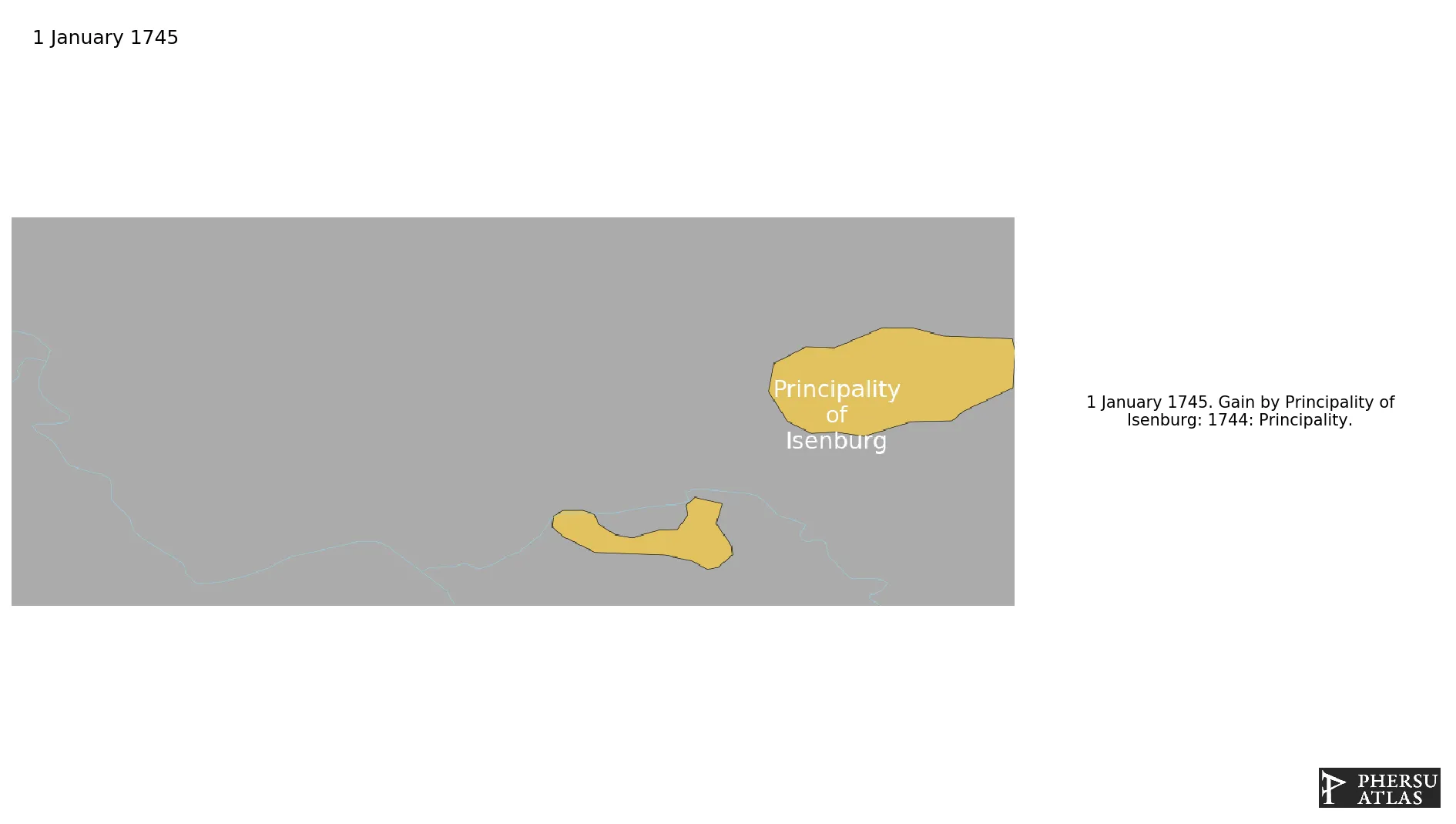
Was a county, and a later a principality, of the Holy Roman Empire located in Hesse.
Establishment
January 1745: 1744: Principality.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
1.1.Central German Theatre
Was the theatre of war in central Germany of the Seven Years' War.
1.1.1.Rhineland Theatre (Seven Years' War)
Was the theatre of War in the Rhineland during the Seven Years' War.
April 1759: The French under General Victor-François de Broglie obtained a victory against British, Hanoverian, Hessian, and Brunswick forces in the Battle of Bergen.
August 1759: On 1 August 1759, the Anglo-German army of Ferdinand Prince of Brunswick-Lüneburg, routed the French during the Battle of Minden.
July 1760: French general de Broglie launched an offensive in the direction of Hesse, defeating Duke Ferdinand of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel's forces on July 10 at the Battle of Korbach.
July 1760: The Battle of Warburg was fought on 31 July 1760 during the Seven Years' War. The battle was a victory for the Hanoverians and the British against the French army.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
August 1806: The Duchy of Nassau, named for its historical core city, Nassau, was founded in 1806.
2.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
2.1.1.Rhine campaign of 1796
Were a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
June 1796: French General Kléber defeated the Duke of Württemberg in the Battle of Altenkirchen.
2.1.2.Rhine campaign of 1798
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
September 1796: On 16-18 September Charles of Brunswick defeated the French Army of Sambre & Meuse in the Battle of Limburg.
2.1.3.Treaty of Campo Formio
Was a treaty between France and Austria that ended the War of the First Coalition.
January 1798: The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI). The treaty transferred the Austrian Netherlands to France. The territories of Venice were partitioned, most were acquired by Austria. Austria recognized the Cisalpine Republic and the newly created Ligurian Republic. Extension of the borders of France up to the Rhine, the Nette, and the Roer.
2.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
2.2.1.Suvorov Swiss campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Switzlerand.
October 1799: The Russian troops were forced by the French to abandon their hold on the left bank of the Rhine.
2.2.2.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
2.3.Congress of Vienna
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
June 1815: This decision was confirmed at the Congress of Vienna. The lands of the principality were divided between the Grand Duchy of Hesse-Darmstadt and the Electorate of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel).
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
June 1815: This decision was confirmed at the Congress of Vienna. The lands of the principality were divided between the Grand Duchy of Hesse-Darmstadt and the Electorate of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel).
Selected Sources
Articles secrets et convention additionelle du traité de Campo Formio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2024 on https://books.google.de/books?id=SStJAAAAcAAJ&dq=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&hl=de&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&f=false
Battle of Warburg. BritishBattles.com. Retrieved on 30 march 2024 on https://www.britishbattles.com/frederick-the-great-wars/seven-years-war/battle-of-warburg/
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 48
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Exshaw, A. (1763): A Compleat History of the Late War, pp. 282-283
Frieden von Campoformio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2014 on https://books.google.de/books?id=UbGMtENHaBIC&pg=PA9#v=onepage&q&f=false
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Swiss campaign of Suvorov and his wonder-heroes. Top War. 30 September 2011. https://en.topwar.ru/7227-shveycarskiy-pohod-suvorova-i-ego-chudo-bogatyrey.html

 Principality of Isenburg
Principality of Isenburg