This article is about the specific polity Novgorod Republic (Golden Horde) and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an East Slavic polity that ruled over the northern regions of European Russia. Following the death of Mstislav I of Kiev in 1132, it became independent from the Kievan Rus'. From 1243 it fell to the Vassalage of the Mongol Empire (and then its successor in Eastern Europe, the Golden Horde).
Establishment
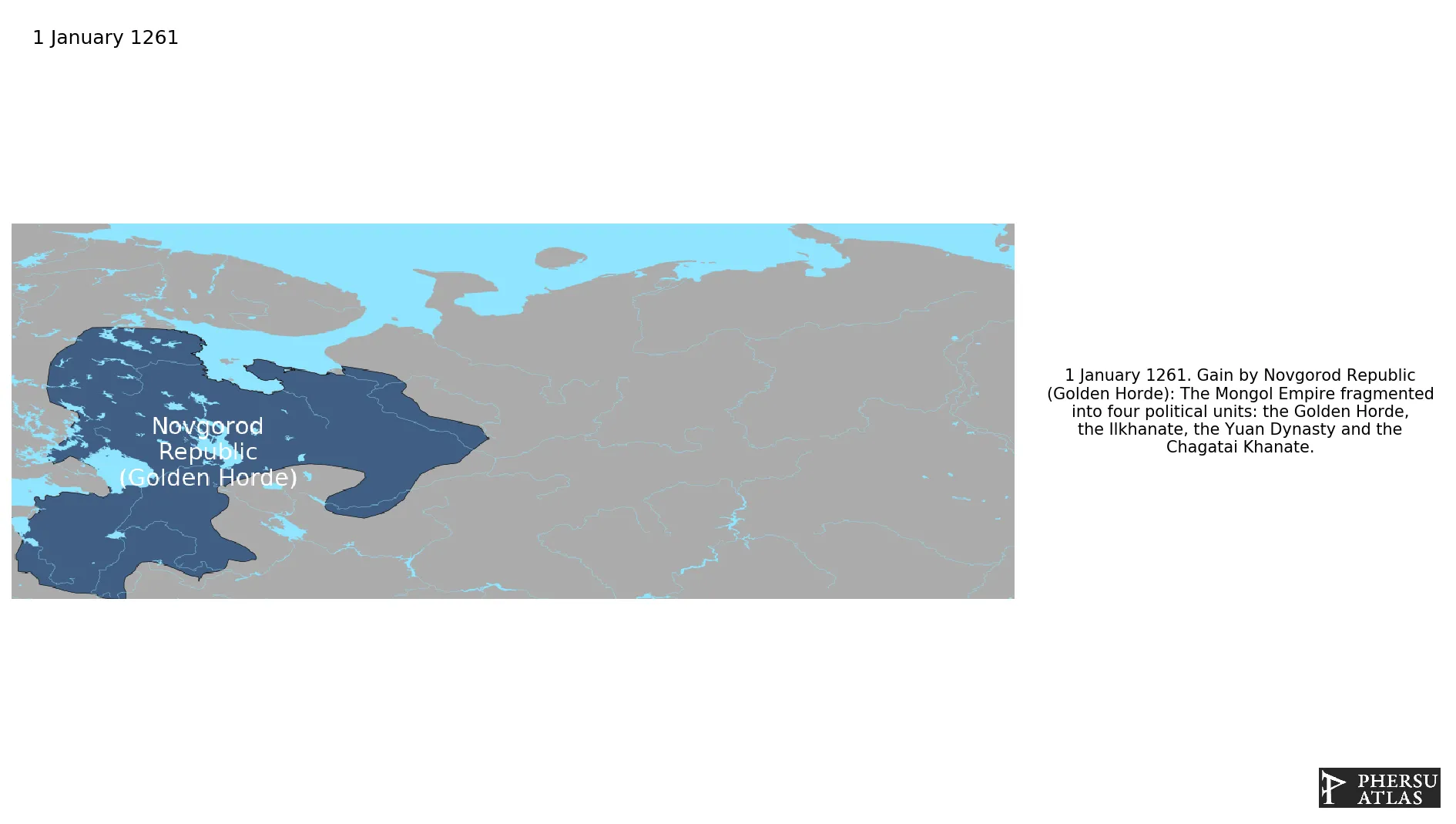
January 1261: The Mongol Empire fragmented into four political units: the Golden Horde, the Ilkhanate, the Yuan Dynasty and the Chagatai Khanate.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars between the successor states of the Mongol Empire.
1.1.Toluid Civil War
Was a war of succession over the Mongol Empire fought between Kublai Khan and his younger brother, Ariq Böke, from 1260 to 1264.
1.1.1.Division of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire fragmented into four successor states at the beginning of the Toluid Civil War.
Were a series of conflicts in the 12th and 13th centuries between the Republic of Novgorod and Medieval Sweden over control of the Gulf of Finland.
June 1301: The Novgorod troops, led by Prince Yaroslav of Tver, retaliated by destroying Landskrona Fort in 1301. This was part of the ongoing conflict between the Novgorod Republic and the Golden Horde for control of the region.
July 1301: The Novgorod troops, led by Prince Yaroslav of Tver, retaliated by destroying Landskrona Fort in 1301. This was part of the ongoing conflict between Novgorod and the Kingdom of Sweden over control of the region.
January 1339: Novgorod besieged Viborg but an armistice was soon agreed upon.
2.1.Treaty of Nöteborg
The Treaty of Nöteborg of 1323 divided Karelia between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Republic of Novgorod.
August 1323: The Treaty of Nöteborg divided Karelia between Sweden and Novgorod. The Baltic Sea port city of Viborg (Finnish: Viipuri) became the capital of the new Swedish province, with the Fief of Viborg existing from 1320 to 1534. The Russians received East Karelia.
Expansion during the rule of Gediminas in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
January 1321: Expansion of Lithuania by 1320.
Were a series of Swedish military campaigns that led to the conquest of modern-day Finland.
August 1323: The Treaty of Nöteborg, made in 1323 between Sweden and Novgorod, was the first treaty that defined the eastern boundary of the Swedish realm and Finland at least for Karelia.
Expansion during the rule of Algirdas in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
January 1356: Expansion of Lithuania by 1355.
Were a series of wars between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (later the Tsardom of Russia).
6.1.Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-1372)
Were a series of military invasions of the the Grand Duchy of Moscow by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
6.1.1.Russian counterattack against Algirdas
Was the Russian counterattack to the Lithuanian invasion started in 1368.
November 1370: On November 26, the Lithuanian army besieged Volokolamsk. The battle continued for two days. Lithuanians killed Prince Vasily Ivanovich Berezuysky, commander of the city's defenses, but did not succeed in capturing the city.
December 1370: A truce between Russia and Lithuania was concluded. Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas retreated from the occupied territories.
January 1267: The Curonian resistance in Southern Courland was led by the Semigallian chief, Dabrelis. In 1266, the Teutonic Order successfully subdued the resistance, leading to the partition of Courland between the Livonian Order and the Archbishop of Riga.
January 1301: In the 12th-15th centuries, the Novgorodian Republic expanded east and northeast. The Novgorodians explored the areas around Lake Onega, along the Northern Dvina, and coastlines of the White Sea. At the beginning of the 14th century, the Novgorodians explored the Arctic Ocean, the Barents Sea, the Kara Sea, and the West-Siberian river Ob. The Ugrian tribes that inhabited the Northern Urals had to pay tribute to Novgorod.
January 1320: Establishment of the Zubtsovsky principality (1318-1460).
January 1322: After the death of Prince David of Yaroslavl in 1321, his sons, Vasily and Mikhail, divided the Yaroslavl principality. The Principality of Molozh was established. It encompassed the Mologa River basin, and its capital was the city of Mologa
January 1324: In 1323, the territory of Great Perm was transferred to the Principality of Great Perm. This marked the emergence of a separate Komi-Permyak feudal entity in the 14th-15th centuries, facilitated by the weakening of the Novgorod Republic.
January 1349: The Novgorod boyars formally recognized Pskov's independence in the Treaty of Bolotovo (1348).
January 1351: The first known conflict in the Obdorsk Principality occurred in 1364 between Prince Ivan III and the Novgorod Republic. Ivan III was the ruler of the Principality, while the Novgorod Republic was a powerful city-state in the region. The conflict was likely over territorial disputes or political power.
January 1365: It separated from the Rostov principality in 1364. The principality was located between the Bohtyuga and Glushitsa rivers.
January 1386: The Principality of Andozh was established around 1385, with the territory including the Andoma river.
January 1398: The Vologda principality was taken by Moscow from Novgorod by military force.
January 1401: The Zaozersk Principality emerged from an inheritance division of the Yaroslavl Principality.
January 1406: The Khanate of Sibir was ruled by a dynasty originating with Taibuga in 1405 at Chimgi-Tura. Taibuga was a prominent leader of the Siberian Khanate and played a key role in expanding its territory and influence in the region.
January 1426: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1425.
January 1451: The Pelym Principality was an union of the Mansi tribes that existed from the middle of the 15th century.
January 1451: Lyapin Principality (Куноватско-Ляпинское княжество) was a medieval Mansi principality that existed from 1450.
January 1451: A union of the Mansi tribes existed from the middle of the 15th to the end of the 16th century .
January 1463: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1462.
January 1472: Varzuzhskaya Volost was seized in the XIV-XV centuries from Novgorod and Rostov by the Grand Duchy of Moscow, which was under the rule of Ivan III at the time. This marked a significant expansion of Moscow's territory and influence in the region.
January 1473: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1473.
Disestablishment
January 1478: The Grand Duchy of Moscow annexed the Novgorod Republic in 1477.
Selected Sources
Batūra, R. (2013): Algirdo žygiai į Maskvą 1368 1370, 1372in Zikaras, K.: Žymiausi Lietuvos mūšiai ir karinės operacijos (2nd ed.). Vilnius (Lithuania), pp. 46-49
Kopalyan, N. (2017): World Political Systems after Polarity, Taylor & Francis, p. 164
VKL-1462-ru. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A4%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BB:VKL-1462-ru.png
Атлас. 6 класс. История России с древнейших времен до XVI века (Atlas. 6th grade. History of Russia from ancient times to the 16th century.) , Дрофа Publisher (2015), Moscow (Russia), p. 23
.svg.png.webp)
.png.webp)
 Novgorod Republic (Golden Horde)
Novgorod Republic (Golden Horde)