If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
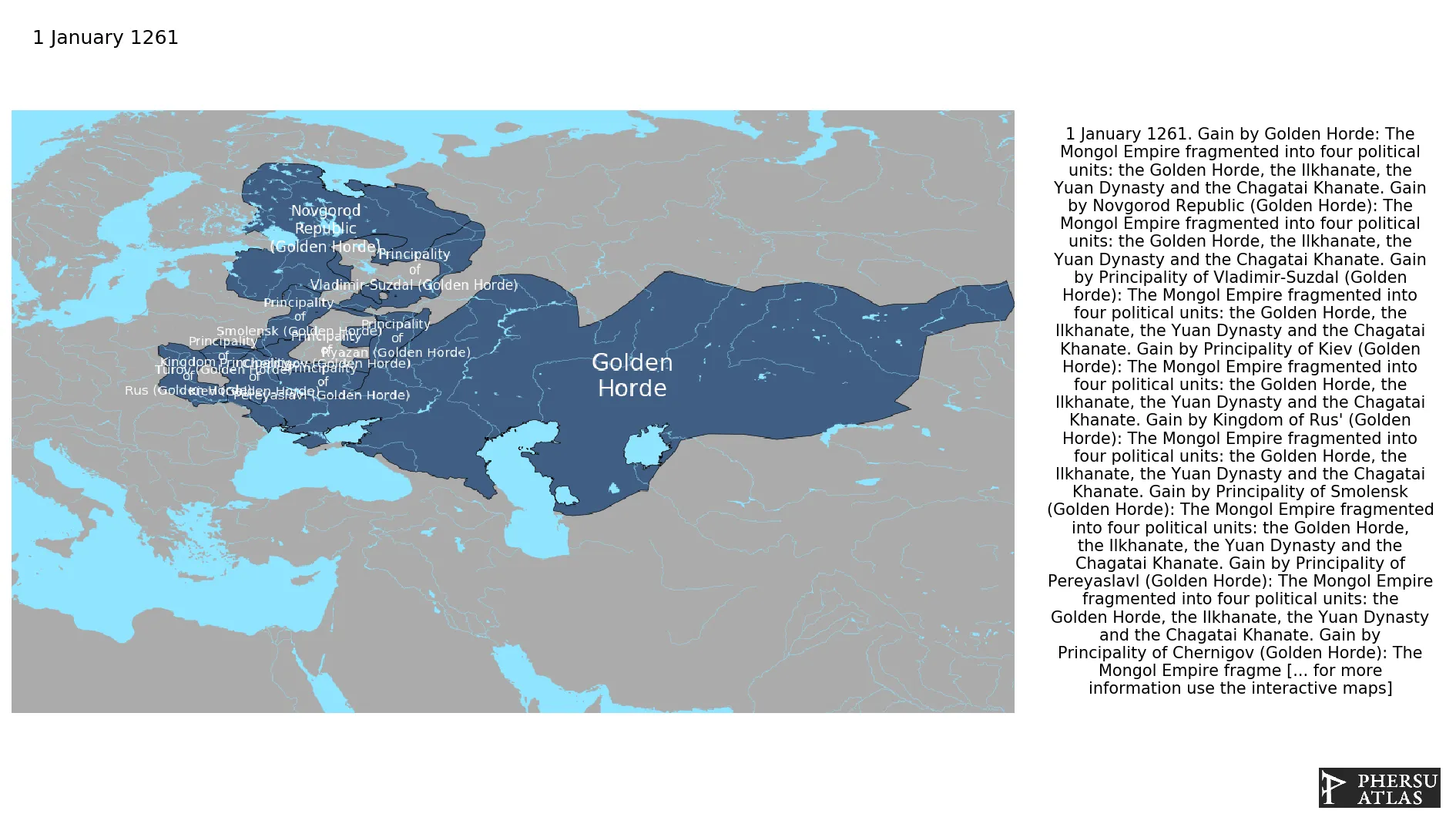
Golden Horde
Establishment
January 1261: The Mongol Empire fragmented into four political units: the Golden Horde, the Ilkhanate, the Yuan Dynasty and the Chagatai Khanate.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars between the successor states of the Mongol Empire.
1.1.Toluid Civil War
Was a war of succession over the Mongol Empire fought between Kublai Khan and his younger brother, Ariq Böke, from 1260 to 1264.
1.1.1.Division of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire fragmented into four successor states at the beginning of the Toluid Civil War.
1.2.Berke-Hulagu war
Was a war between two successor states of the Mongol Empire, the Ilkhanate and the Golden Horde, that took place mainly in the Caucasus, a border area between the two states.
January 1263: Ilkhan Hulegu marched northwards through the pass of Derbend. On the banks of the Terek, he was ambushed by an army of the Golden Horde under Nogai, and his army was defeated at the Battle of the Terek River.
February 1263: After Ilkhan Hulegu was defeated at the Battle of the Terek River, his army left the area.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
2.1.Mongol Invasions of Poland
Were a series of Mongol raids in Poland.
January 1287: In 1286, Talabuga, a Mongol general, and Nogai, a prominent Mongol leader, launched a devastating attack on Poland as part of the Golden Horde's expansionist campaigns. The invasion resulted in widespread destruction and plundering of the Polish territory.
February 1287: In 1286, Mongol generals Talabuga and Nogai led an attack on Poland, causing widespread devastation in the country. This event marked a period of conflict between the Mongol Empire and the Kingdom of Poland.
2.1.1.Third Mongol Invasion of Poland
The third Mongol invasion of Poland was carried out by Nogai Khan and Talabuga in 1287-1288. As in the second invasion, its purpose was to loot Lesser Poland.
December 1287: The third Mongol invasion of Poland was carried out by Nogai Khan and Talabuga in 1287.1288. Its purpose was to loot Lesser Poland.
January 1288: Mongol forces leave Poland after looting the region.
2.2.Mongol Invasions of Hungary
Were a series of Mongol raids in Hungary.
2.2.1.Second Mongol Invasion of Hungary
Was a Mongol raid in Hungary.
January 1286: Kingdom of Hungary raided by the Golden Horde.
February 1286: The Golden Horde leaves the Kingdom of Hungary.
2.3.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
2.3.1.Third Mongol Invasion of Germany
The Mongols raided the March of Brandenburg.
January 1341: In 1340, the Golden Horde, led by Khan Jani Beg, raided the March of Brandenburg.
February 1341: End of Mongol raid in Brandenburg.
2.4.Mongol Invasions of Lithuania
Was a Mongol raid in Lithuania.
January 1276: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
February 1276: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
January 1280: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
February 1280: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
January 1326: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
February 1326: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
2.5.Invasion of Thrace
Was a Mongol invasion of Byzantine Thrace.
January 1264: The Mongol invasion of Byzantine Thrace in 1263 was led by Berke Khan of the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate in Eastern Europe. The invasion was part of the wider Mongol conquests in the region, with the goal of expanding Mongol influence and control.
February 1264: The Mongol invasion of Byzantine Thrace in 1264 was led by the Mongol general Nogai Khan, who was a prominent military leader in the Golden Horde. The invasion resulted in the territory of Thrace falling under the control of the Byzantine Empire.
Were a series of conflicts in the 12th and 13th centuries between the Republic of Novgorod and Medieval Sweden over control of the Gulf of Finland.
June 1301: The Novgorod troops, led by Prince Yaroslav of Tver, retaliated by destroying Landskrona Fort in 1301. This was part of the ongoing conflict between the Novgorod Republic and the Golden Horde for control of the region.
July 1301: The Novgorod troops, led by Prince Yaroslav of Tver, retaliated by destroying Landskrona Fort in 1301. This was part of the ongoing conflict between Novgorod and the Kingdom of Sweden over control of the region.
January 1339: Novgorod besieged Viborg but an armistice was soon agreed upon.
3.1.Treaty of Nöteborg
The Treaty of Nöteborg of 1323 divided Karelia between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Republic of Novgorod.
August 1323: The Treaty of Nöteborg divided Karelia between Sweden and Novgorod. The Baltic Sea port city of Viborg (Finnish: Viipuri) became the capital of the new Swedish province, with the Fief of Viborg existing from 1320 to 1534. The Russians received East Karelia.
Expansion during the rule of Gediminas in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
January 1321: Expansion of Lithuania by 1320.
January 1322: In 1321, Gediminas of Lithuania captured Kiev, sending Stanislav, the last Rurikid to rule Kiev, into exile.
January 1327: Expansion of Lithuania by 1326.
January 1337: Expansion of Lithuania by 1336.
January 1341: Expansion of Lithuania by 1340.
January 1341: Incorporation of the Principality of Turov into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Were a series of Swedish military campaigns that led to the conquest of modern-day Finland.
August 1323: The Treaty of Nöteborg, made in 1323 between Sweden and Novgorod, was the first treaty that defined the eastern boundary of the Swedish realm and Finland at least for Karelia.
Were several wars fought in the years 1340-1392 over the succession in the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia.
August 1340: Casimir III of Poland invaded the Principality of Galicia-Volhynia. After four weeks he reached an agreement with local nobles and their leader Dmytro Dedko: in return for their services, local nobles would enjoy protection from the Polish king.
April 1341: During the winter of 1340-1341, the Golden Horde (probably with Lithuanian help) attacked Poland and reached Lublin as a result of diminished tribute from the principality to the Mongol khan. The raid weakened Polish influence in the principality.
May 1341: During the winter of 1340-1341, the Golden Horde (probably with Lithuanian help) attacked Poland and reached Lublin as a result of diminished tribute from the principality to the Mongol khan. The raid weakened Polish influence in the principality.
Expansion during the rule of Algirdas in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
January 1356: Expansion of Lithuania by 1355.
January 1357: Expansion of Lithuania by 1356.
January 1358: Briansk was taken in 1356 by the Grand Duke of Lithuania, Olgierd, and the principality lost its autonomy.
January 1360: Expansion of Lithuania by 1359.
December 1363: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led by Grand Duke Algirdas and his brother Kęstutis, launched a successful campaign against the Golden Horde in 1363. The Battle of Blue Waters resulted in the capture of Kiev and Podolia, expanding the territory of the Grand Duchy.
January 1364: In 1363 after the Battle of Blue Waters, the Pereyaslavl principality became part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania .
Were a series of wars between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (later the Tsardom of Russia).
8.1.Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-1372)
Were a series of military invasions of the the Grand Duchy of Moscow by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
8.1.1.Invasion of Russia by Algirdas
Was a military campaign launched by Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas in Russia.
November 1368: The Lithuanians defeated the Russian defense forces on the Trosna River.
December 1368: The Lithuanians surrounded the Kremlin of Moscow, burned and looted it.
January 1369: In 1368, Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania gathered a large army, which included his brother Kęstutis and forces from Tver and Smolensk. The army was assembled in secret and marched quietly so that not to give an advance warning to the Russians. After crossing the Lithuania-Russia border, Lithuanians began pillaging and burning various villages.
June 1372: Prince of Moscow Dmitry Donskoy marched with his army to meet the invading Lithuanian army, which was stopped near Lyubutsk.
8.1.2.Russian counterattack against Algirdas
Was the Russian counterattack to the Lithuanian invasion started in 1368.
December 1368: The Lithuanian army retreated from all Russian territories without a serious attempt at taking the Moscow Kremlin.
November 1370: On November 26, the Lithuanian army besieged Volokolamsk. The battle continued for two days. Lithuanians killed Prince Vasily Ivanovich Berezuysky, commander of the city's defenses, but did not succeed in capturing the city.
December 1370: The Lithuanian army led by Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, besieged Moscow on December 6. Algirdas' forces burned and pillaged, but did not succeed in taking the city's Kremlin where the Prince of Moscow, Dmitry Donskoy, had retreated.
December 1370: A truce between Russia and Lithuania was concluded. Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas retreated from the occupied territories.
8.1.3.Kęstutis' raid
Was a military campaign launched by Kęstutis, the brother of Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas, in Russia.
June 1372: In spring 1372, Lithuanians raided Russian lands again. This time Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, did not participate. The Lithuanian Army was commanded by Kęstutis (Algirdas' brother) and his son Vytautas and Algirdas' son Andrei of Polotsk. They attacked Pereslavl-Zalessky, burned the posad and churches, looted and extracted a ransom.
June 1372: Mikhail II prince of Tver (allied with Lirhuania) attacked the city of Dmitrov.
June 1372: The armies of Lithuania and Tver attacked Kashin and its duke acknowledged Tver's suzerainty.
8.1.4.Truce - Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-1372)
Was a treaty that ended the Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-72).
September 1372: The Treaty of Lyubutsk was a peace treaty signed in summer of 1372 between Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, and Dmitri Donskoi, Prince of Moscow. The treaty ended the Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-72) and resulted in a seven-year peace period. Lithuanian forces left the occupied territories.
8.2.Lithuanian annexion of Smolensk
Was a war between Moscow and Lithuania that included figths on the Ugra river and the Lithuanian annexion of Smolensk.
January 1403: Vasily hesitated until Vytautas advanced on Pskov. Alarmed by Lithuania's continuing expansion, Vasily sent an army to aid the Pskovians against his father-in-law. The Russian and Lithuanian armies met near the Ugra River.
February 1403: The commander didn't ventured to commit his troops to battle. A peace ensued, whereby Vytautas kept Smolensk.
Military campaigns of Timur (or Tamerlane), a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia.
January 1382: Tamerlan ruled over much of Persian Khorasan by 1381.
9.1.Tokhtamysh-Timur war
Was a war between the Golden Horde and the Timurid Empire.
9.1.1.Timur's invasions of Georgia
Was the military invasion of Georgia by the Timurid Empire.
January 1386: After having overrun Azerbaijan and Kars, Timur marched into Georgia.
November 1386: Tamerlan occupied Tbilisi and captured the Georgian king Bagrat V.
June 1387: When Timur was informed that Tokhtamysh, Khan of the Golden Horde, was approaching Iran, he temporarily withdrew from the territories he had occupied in Georgia.
Was a series of wars fought between the Grand Duchy of Moscow and the Khanate of Kazan from 1439, until Kazan was finally conquered by the Tsardom of Russia under Ivan the Terrible in 1552.
10.1.Wars of Vasily II
Russian military campaign against the Khanate of Kazan by Vasily II.
January 1440: In 1439, a year after the khanate's foundation, the very first khan of Kazan, Ulugh Muhammad, advanced on Moscow with a large army. Vasily II of Moscow fled from his capital across the Volga River.
January 1440: Tatars devastated the outskirts of Moscow for 10 days and on their way back to Kazan burned Kolomna. They also took many captives.
January 1446: Vasily II of Moscow mustered an army and defeated the Tatars near Murom and Gorokhovets.
January 1446: Khan Maxmut took the strategic fortress of Nizhny Novgorod and invaded Muscovy.
10.2.Wars of Ivan III
Russian military campaign against the Khanate of Kazan by Ivan III.
January 1468: When frosty winter came, the Russian generals launched an invasion of the northern Vyatka Region.
January 1468: In 1467, the campaign led by Ivan III of Russia against the Khanate of Kazan fell apart due to the lack of unity and military capability among the Russian forces.
January 1470: In 1469, under the terms of the peace settlement, the Khanate of Kazan set free all the ethnic Christian Russians they had enslaved in the forty previous years. The Russian and Kazan forces left the territories they had occupied during the war.
November 1480: The Great Stand on the Ugra River was a standoff between the forces of Akhmat Khan of the Great Horde, and the Grand Prince Ivan III of Muscovy in 1480 on the banks of the Ugra River, which ended when the Tatars departed without conflict. It is seen in Russian historiography as the end of Tatar/Mongol rule over Moscow.
January 1264: The Moscow principality was allocated in 1226 3 as an inheritance to the youngest son of Alexander Nevsky.
January 1265: In 1264, the territory shown on the map was incorporated into the Gorodets Principality, which existed from 1264 to 1403. The principality was ruled by Prince Yaroslav of Tver and later by his descendants, playing a significant role in the political landscape of medieval Russia.
January 1267: The Curonian resistance in Southern Courland was led by the Semigallian chief, Dabrelis. In 1266, the Teutonic Order successfully subdued the resistance, leading to the partition of Courland between the Livonian Order and the Archbishop of Riga.
January 1271: The Principality of Obolensk was established around 1270.
January 1277: From 1274 to 1276 Leo of Galicia fought a war with the new Lithuanian ruler Traidenis but was defeated, and Lithuania annexed the territory of Black Ruthenia with its city Navahrudak.
January 1278: The Kostroma principality returned to the Vladimir principality.
January 1278: The Mozhaisk Principality separated from the Smolensk principality no later than 1277.
January 1281: In 1280, Prince Lev of Galicia-Volhynia defeated Hungary and annexed part of Transcarpathia, including the city of Munkács. This territory was then incorporated into the Kingdom of Rus' under the rule of the Golden Horde.
January 1281: The Dmitrov Principality was an independent state entity between 1280 and 1334.
January 1285: In 1284, Saqchi, a town in Bulgaria, was conquered by the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate. As a result of the invasion, coins were minted in the name of the ruling Khan, marking the town's submission to Mongol rule.
January 1293: Lublin conquered by the Kingdom of Rus.
January 1294: In 1293 the Grand Duke of Vladimir Dmitry Alexandrovich ceded the lands of the Kostroma principality to his brother Andrei.
January 1296: In 1295, Butigeidis, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, transferred Vaŭkavysk to Galicia-Volhynia in exchange for peace with the Kingdom of Rus' (Golden Horde). This decision was part of the complex political dynamics and power struggles in the region during that time.
January 1300: Chaka reigned as tsar of Bulgaria from 1299 to 1300. Chaka was the son of the Mongol leader Nogai Khan.
January 1301: Volosts, from Ryazan , located on the river of the same name.
January 1301: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1300.
January 1301: The 14th century newly established Avar Khanate managed maintain independence from the Mongols.
January 1301: In 1300, Theodore Svetoslav of Bulgaria took advantage of a civil war in the Golden Horde, overthrew Chaka (the son of the Mongol leader Nogai Khan), and presented his head to the Mongol khan Toqta (who was at war with Chaka). This brought an end to Mongol interference in Bulgarian domestic affairs and secured Southern Bessarabia as far as Bolgrad to Bulgaria.
January 1301: In the 12th-15th centuries, the Novgorodian Republic expanded east and northeast. The Novgorodians explored the areas around Lake Onega, along the Northern Dvina, and coastlines of the White Sea. At the beginning of the 14th century, the Novgorodians explored the Arctic Ocean, the Barents Sea, the Kara Sea, and the West-Siberian river Ob. The Ugrian tribes that inhabited the Northern Urals had to pay tribute to Novgorod.
January 1301: Establishment of Zichia.
January 1302: Annexation of Kolomna to the Moscow principality in 1301 .
January 1303: Yuri I lost Lublin to the Poles in 1302.
January 1303: In 1302, the last Pereyaslavl-Zalessky prince Ivan Dmitrievich died, with no direct heirs, and the principality, according to his will, passed to his uncle, Daniel Alexandrovich, the first prince of Moscow.
January 1304: In 1303, the Mozhaisk Principality was captured by the Moscow prince Yuri Danilovich.
January 1309: In 1308, Caffa was plundered by the Mongols.
January 1311: Vosporo (today's Kerč) was a Genoese colony since 1310.
January 1316: Expansion of Lithuania by 1315.
January 1319: The Golden Horde, led by Uzbeg Khan, invaded the Ilkhanate under Abu Sa'id in 1318. The Ilkhanate was a Mongol khanate established in Persia, while the Golden Horde was a Mongol khanate in Russia and Eastern Europe. Abu Sa'id was the last ruler of the Ilkhanate.
February 1319: The Golden Horde, led by Uzbeg Khan, invaded the Ilkhanate under Abu Sa'id in 1318. The Ilkhanate was a Mongol khanate established in Persia, while the Golden Horde was a Mongol khanate in Russia. Abu Sa'id was the last ruler of the Ilkhanate, facing internal strife and external threats during his reign.
January 1320: Öz Beg was the ruler of the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate in Eastern Europe. Thrace was a region in southeastern Europe. Bulgaria was engaged in wars against Byzantium and Serbia during this time, and Öz Beg supported them with his massive army, which exceeded 300,000 soldiers.
January 1320: Establishment of the Zubtsovsky principality (1318-1460).
February 1320: Öz Beg was the khan of the Golden Horde, a Mongol state in Eastern Europe. The Byzantine Empire was facing threats from both Bulgaria and Serbia, and Öz Beg's massive army supported Bulgaria in their conflicts with Byzantium and Serbia in Thrace in 1319.
January 1321: After the death of prince Boris, Kostroma passed under the control of the Moscow princes.
January 1322: After the death of Prince David of Yaroslavl in 1321, his sons, Vasily and Mikhail, divided the Yaroslavl principality. The Principality of Molozh was established. It encompassed the Mologa River basin, and its capital was the city of Mologa
January 1324: In 1323, the territory of Great Perm was transferred to the Principality of Great Perm. This marked the emergence of a separate Komi-Permyak feudal entity in the 14th-15th centuries, facilitated by the weakening of the Novgorod Republic.
January 1325: In 1324, the Ilkhanate territory was raided by the Golden Horde, led by their ruler Ozbeg Khan. This military raid was part of the ongoing power struggles and conflicts between the Mongol successor states in the aftermath of the Mongol Empire's fragmentation.
January 1325: Öz Beg was the khan of the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate in Eastern Europe. In 1324, his armies invaded Thrace, a region in southeastern Europe, and pillaged it for 40 days.
February 1325: In 1325, the Ilkhanate territory was raided by the Golden Horde, led by the Mongol ruler Ozbeg Khan. After the raid the Golden Horde left the territory.
February 1325: Öz Beg's armies left Thrace.
January 1326: In 1325, the territory of Pokuttya was conquered by the Kingdom of Poland.
January 1332: The Moscovites absorbed the Duchy of Vladimir-Suzdal by the 1320s.
January 1333: Venetian Tanais (Tana), 13C-1332.
January 1336: In the year 1335 Ilkhanate was annexed by the Golden Horde.
February 1336: End of the brieft control of the Ilkhanate by the Golden Horde.
January 1338: For 15 days in 1337, the territory of Thrace was under the control of the Golden Horde, a Mongol and Turkic khanate founded by Batu Khan, a grandson of Genghis Khan. This event marked a period of influence and power for the Golden Horde in the region.
February 1338: For 15 days in 1337, the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos besieged the city of Adrianople in Thrace, as part of his campaign to reclaim territories lost to the Bulgarian Empire. The siege ended in 1338 when the city surrendered to the Byzantine Empire.
January 1340: Separated from the Belozersk principality during the period of feudal fragmentation in Russia, the territory of Sugorye - along the Kema and Soga rivers - went to the Sugorsk Principality in 1339. This transfer of land was a result of the political and territorial divisions that occurred during this period in Russian history.
January 1341: In 1340, the territory of Volost, located on the banks of the Berega River, was purchased from the principality of Novosilsky by the Grand Duchy of Moscow, which was under the rule of Ivan Kalita at the time. This acquisition helped expand Moscow's territory and influence in the region.
January 1341: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1340.
January 1341: Acquisition of Volosts from the Ryazan principality in the middle reaches of the Protva river.
January 1341: Around 1340 the Yurievsky principality was annexed to the Moscow principality.
November 1341: The Nizhny Novgorod-Suzdal principality was formed in October 1341, when the Khan of the Golden Horde, Uzbek Khan, divided the Vladimir Grand Duchy, transferring Nizhny Novgorod and Gorodets to the Suzdal Prince Konstantin Vasilyevich.
January 1344: The Dorogobuzh Principality was a small feudal possession that separated from the Smolensk principality in the 13th century.
January 1347: In the 14th century, King Charles I of Hungary attempted to expand his realm and the influence of the Catholic Church eastwards after the fall of Cuman rule, and ordered a campaign under the command of Phynta de Mende (1324). In 1342 and 1345, the Hungarians were victorious in a battle against Tatar-Mongols and founded the Moldavian mark in 1346.
January 1349: The Novgorod boyars formally recognized Pskov's independence in the Treaty of Bolotovo (1348).
January 1351: In the 50s of the XIV century, the Tarusa Principality fell into dependence on the Moscow prince.
January 1351: The first known conflict in the Obdorsk Principality occurred in 1364 between Prince Ivan III and the Novgorod Republic. Ivan III was the ruler of the Principality, while the Novgorod Republic was a powerful city-state in the region. The conflict was likely over territorial disputes or political power.
January 1351: Establishment of the Koninskoe Principality.
January 1351: Establishment of the Mosalsk Principality.
January 1354: In 1353, Lopasnya was incorporated into the Principality of Ryazan, which was under the rule of the Golden Horde at the time. This transfer of territory was a result of political and military agreements between the rulers of Ryazan and the Golden Horde.
January 1357: Khan Jani Beg asserted Jochid dominance over the Chagatai Khanate and conquered Tabriz, ending Chobanid rule there in 1356.
January 1358: Following the assassination of Jani Beg, the Golden Horde quickly lost Azerbaijan to the Jalayir king Shaikh Uvais in 1357.
January 1360: Bogdan of Cuhea, voivode fof the Wallachians, who had fallen out with the Hungarian king, crossed the Carpathians in 1359, took control of Moldavia, and succeeded in becoming thre first independent ruler of Moldavia.
January 1361: The Moscovites purchase the Galich-Mer principality.
January 1361: The Dmitrov Principality is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow (Mongol Empire).
January 1361: In 1360, Meshchovsk became part of the Principality of Mezets.
February 1361: In 1360 the Galich-Mer Principality was recreated by decision of the Horde.
January 1362: The Sufid dynasty gained independence in Khwarazm in 1361 but their rule only lasted until 1379. The Sufids were a prominent Persian dynasty known for their contributions to art, culture, and literature in the region.
January 1364: The Galich-Mer Principality is annexed to the Moscow domain.
January 1364: The Starodub principality is acquired by Moscow.
January 1365: Uglitsky principality (1216-1605).
January 1365: It separated from the Rostov principality in 1364. The principality was located between the Bohtyuga and Glushitsa rivers.
January 1365: The Ustyug principality was created in 1364.
July 1365: On 19 July 1365, a Genoese force from Kaffa seized the city of Sudak.
January 1378: Conquest of Lithuanian territories by the Grand Duchy of Moscow (based on maps).
January 1381: Establishment of the Przemysl Principality.
January 1382: In 1381, the territory of Meshchera (Мещёрская) was purchased by the Grand Duchy of Moscow from local princes.
January 1382: Tula (Тула, Russia) was conquered by Ryazan from the Mongols but at some point reconquered back by the Mosvoites.
January 1386: The Principality of Andozh was established around 1385, with the territory including the Andoma river.
January 1386: Beloselsky was a principality (c. 1385-1470) located in Beloe Selo in Poshekhonsky district.
January 1388: Vassalage of the Principality of Smolensk to Lithuania since 1348.
January 1390: In 1389, the Principality of Beloozero was subjugated by Muscovy.
January 1393: The Grand Duchy of Moscow purchases the principalities of Murom and of Suzdal-Nizhny Novgorod from the khan of the Golden Horde.
January 1398: In 1397, the cavalry of the voivode of Moldavia Stephen, allied with the governor of Lithuania Vitold, reached without resistance23 the western bank of the lower Dnieper and the Pontic shores.
January 1398: The Vologda principality was taken by Moscow from Novgorod by military force.
August 1399: In 1399, Grand Duke Vytautas of Lithuania and Tokhtamysh, former khan of the Golden Horde, attacked Temür Qutlugh and Edigu at the Battle of the Vorskla River. The Golden Horde emerged victorious, securing control over Kiev, Podolia, and some land in the lower Bug River basin.
January 1400: Athe lliance of the Four Oirat Tribes or Oirat Confederacy, which lasted from 1399 to 1634, was a confederation of the Oirat tribes, which marked the rise of the Western Mongols in Mongolian history.
January 1401: The Zaozersk Principality emerged from an inheritance division of the Yaroslavl Principality.
January 1401: The Romanov Principality fell to the Moscovites at the beginning of the 15th century.
January 1401: The Shamkhalate of Tarki originated "no later than XIV-XV centuries".
January 1401: By the 14th century the newly established Avar Khanate managed to maintain independence from the Mongols.
January 1404: Semyon Dmitrievich dies in 1401 and Vasily Kirdyapa in 1403. After their death, Vasily I annexed the Vyatka land to the Moscow principality.
January 1404: Expansion of Poland-Lithuania in 1403 (based on maps).
January 1405: In 1404, the Verkhovskoe principality in Kozelsk was seized by the Grand Duchy of Moscow from the Mongol Empire, possibly as a strategic move against Lithuania. This event marked a shift in power dynamics in the region.
January 1406: The Khanate of Sibir was ruled by a dynasty originating with Taibuga in 1405 at Chimgi-Tura. Taibuga was a prominent leader of the Siberian Khanate and played a key role in expanding its territory and influence in the region.
January 1407: In 1406 Kozelsk was conquered by Lithuania.
January 1407: Timur died in 1405 and Khan Edigu took advantage to seize Khwarezm.
January 1409: The Kozelsk Principality was acquired by the Moscow prince Vasily I Dmitrievich.
January 1411: At the end of the 15th century, the Sheleshpalsky princes were already vassal princes of the Grand Duke of Moscow.
January 1411: Establishment of the Vadbolsk Principality.
January 1411: Establishment of the Romodanovskoe Principality in village of Romodanovo , located east of Starodub.
January 1413: The armies of the Grand Duke of Lithuania, Vitold, and his vassal, the Voivode of Moldavia, Alexander the Good, reached the Black Sea, making Yedisan a Lithuanian land.
January 1415: In 1414, Shah Rukh of the Timurids conquered Khwarezm.
January 1420: In 1419, the Republic of Genoa gained control of Tmutarakan, a strategic trading outpost on the Black Sea. The Genoese presence in the region lasted until 1482, when the territory was eventually lost to the expanding Russian Empire.
January 1421: Tabarinskoe Principality is established on the lands at the mouth of the Tabara River (modern Iska River) including Tabaryn town.
January 1425: The Nizhny Novgorod-Suzdal Grand Duchy was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1426: Around 1425 the Bohtyug Principality was annexed to the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1426: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1425.
January 1426: At the beginning of the 15th century, the Shumorovskoe principality became part of the Moscow principality.
January 1426: The Ustyug Principality is annexed by Moscow.
January 1429: Abu'l-Khayr Khan founded the Uzbek Khanate.
January 1431: Kargolom principality (c. 1375-1430).
January 1431: The Kemsky Principality is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1431: The Principality of Andozh is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1435: Modern-day Penza region and Republic of Mordovia are annexed by Russia.
January 1441: The Romodanovskoe Principality was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1441: The Ryapolovskoe Principality was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Moscow under the rule of Grand Prince Vasily II of Moscow.
January 1446: In 1445, Ulugh Muhammad, the ruler of the Golden Horde, was murdered by his son, Mäxmüd of Kazan. Mäxmüd fled to the middle Volga region and established the Khanate of Kazan. This event marked the beginning of the Khanate of Kazan's independence from the Golden Horde.
January 1446: The Lithuanians again took possession of Kozelsk and annexed it to their possessions.
January 1448: Before 1447, the Zaozersk principality was annexed to Moscow.
January 1449: End of the independent Shuisky principality, which is nnexed by Moscow.
January 1450: In 1449, Hacı I Giray seized Crimea from Sayid Ahmad I, and founded the Crimean Khanate.
January 1451: By the 1440s, a descendant of Edigu by the name of Musa bin Waqqas was ruling at Saray-Jük as an independent khan of the Nogai Horde.
January 1451: Lyapin Principality (Куноватско-Ляпинское княжество) was a medieval Mansi principality that existed from 1450.
January 1451: A union of the Mansi tribes existed from the middle of the 15th to the end of the 16th century .
January 1451: Vadbolsk principality (c. 1410-50).
January 1451: The Ukhtomsk Principality is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1451: The Principality of Molozh is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1451: The Pelym Principality was an union of the Mansi tribes that existed from the middle of the 15th century.
January 1451: The exact time of foundation of the Ruza Principality is unknown, but it is mentioned in the chronicle for the first time in the 15th century.
January 1451: The territory of the Koninskoe Principality was included in the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1453: Ulugh Muhammad was a prominent ruler of the Golden Horde. His son, Qasim Khan, sought refuge in Moscow and was granted land by Vasily II, establishing the Qasim Khanate in 1452. This territory was located in the modern-day Republic of Tatarstan, Russia.
January 1454: In 1453, the territory of Kabardia, located in the North Caucasus region, gained better political organization under the leadership of the Kabardian princes. The society had a feudal social structure and had been a political entity since at least the 15th century.
January 1454: The Circassian Confederation was established between 1427 and 1453 in the region of Circassia, located in the North Caucasus. It was a union of various Circassian tribes led by local princes and nobles.
January 1456: Kurbsk principality (c. 1425-1455).
January 1457: Vassalage of Ryazan to Moscow since 1456.
January 1461: The Prozorov Principality is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1461: In 1460, the territory of Tutaev was bought by Maria of Borovsk, the wife of Grand Prince Vasily II of Moscow. This acquisition was part of the expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow under the rule of the Mongol Empire.
January 1461: Sitsky principality (c. 1408-1460).
January 1463: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1462.
January 1464: Yaroslavl prince Alexander was forced to sell the rights to the principality to the next Grand Duke of Moscow, Ivan III, and a governor from Moscow was appointed to rule.
January 1467: After 1466, Mahmud bin Küchük's descendants continued to rule in Astrakhan as the khans of the Astrakhan Khanate.
January 1467: The Great Horde was a Tatar-Mongol khanate that existed from about 1466 to 1502. It was the steppe remnant of the Golden Horde.
January 1467: The Khanate of Astrakhan is said to have been founded 1466.
January 1471: Around 1470, the Volkonskoe principality was annexed to the Grand Duchy of Moscow and ceased to exist.
January 1471: The Principality of Novlenskoe was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1471: Beloselsky was a principality (c. 1385-1470) located in Beloe Selo in Poshekhonsky district.
January 1471: Palekh principality conquered by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1472: Varzuzhskaya Volost was seized in the XIV-XV centuries from Novgorod and Rostov by the Grand Duchy of Moscow, which was under the rule of Ivan III at the time. This marked a significant expansion of Moscow's territory and influence in the region.
January 1473: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1473.
January 1473: Great Perm principality.
January 1475: In 1474, the Grand Duke Ivan III, bought the remaining half of the Rostov principality from the last Rostov princes.
January 1476: An attack by Akhmat Khan (Khan of the Golden Horde 1465-81) forced Crimean Khan Meñli to flee to the Ottoman Empire.
January 1478: The Grand Duchy of Moscow annexed the Novgorod Republic in 1477.
January 1479: In 1478 the Crimean Khanate recognized Ottoman suzerainty.
January 1501: In 1500, the lower reaches of the Terek River in modern Northern Dagestan belonged to the Principality of the Kumyks. This period marked the state formation in the North Caucasus during the 15th and 16th centuries, with various local rulers and princes playing significant roles in shaping the region's political landscape.
January 1503: Independence of Astrakhan Khanate.
Disestablishment
January 1510: Nogays move into lands vacated by Great Horde.
Selected Sources
Batūra, R. (2013): Algirdo žygiai į Maskvą 1368 1370, 1372in Zikaras, K.: Žymiausi Lietuvos mūšiai ir karinės operacijos (2nd ed.). Vilnius (Lithuania), pp. 46-49
Kopalyan, N. (2017): World Political Systems after Polarity, Taylor & Francis, p. 164
Robert, A. / Obolensky, D. (1981): A Companion to Russian Studies: An Introduction to Russian History, Cambridge (UK), p. 86
VKL-1462-ru. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A4%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BB:VKL-1462-ru.png
Атлас. 6 класс. История России с древнейших времен до XVI века (Atlas. 6th grade. History of Russia from ancient times to the 16th century.) , Дрофа Publisher (2015), Moscow (Russia), p. 23
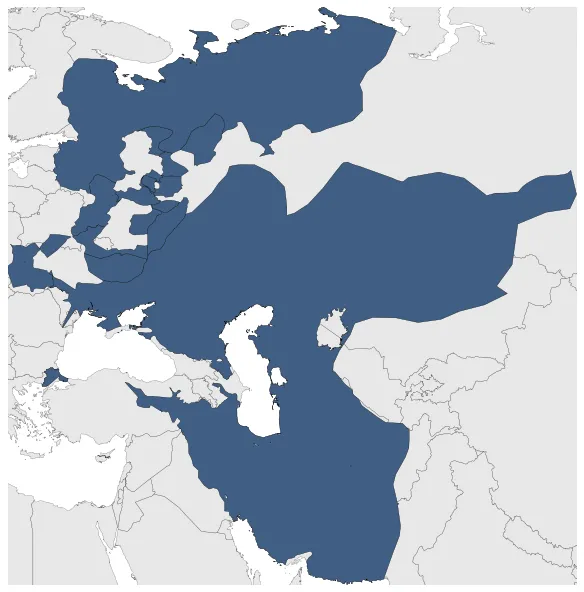
 golden horde
golden horde