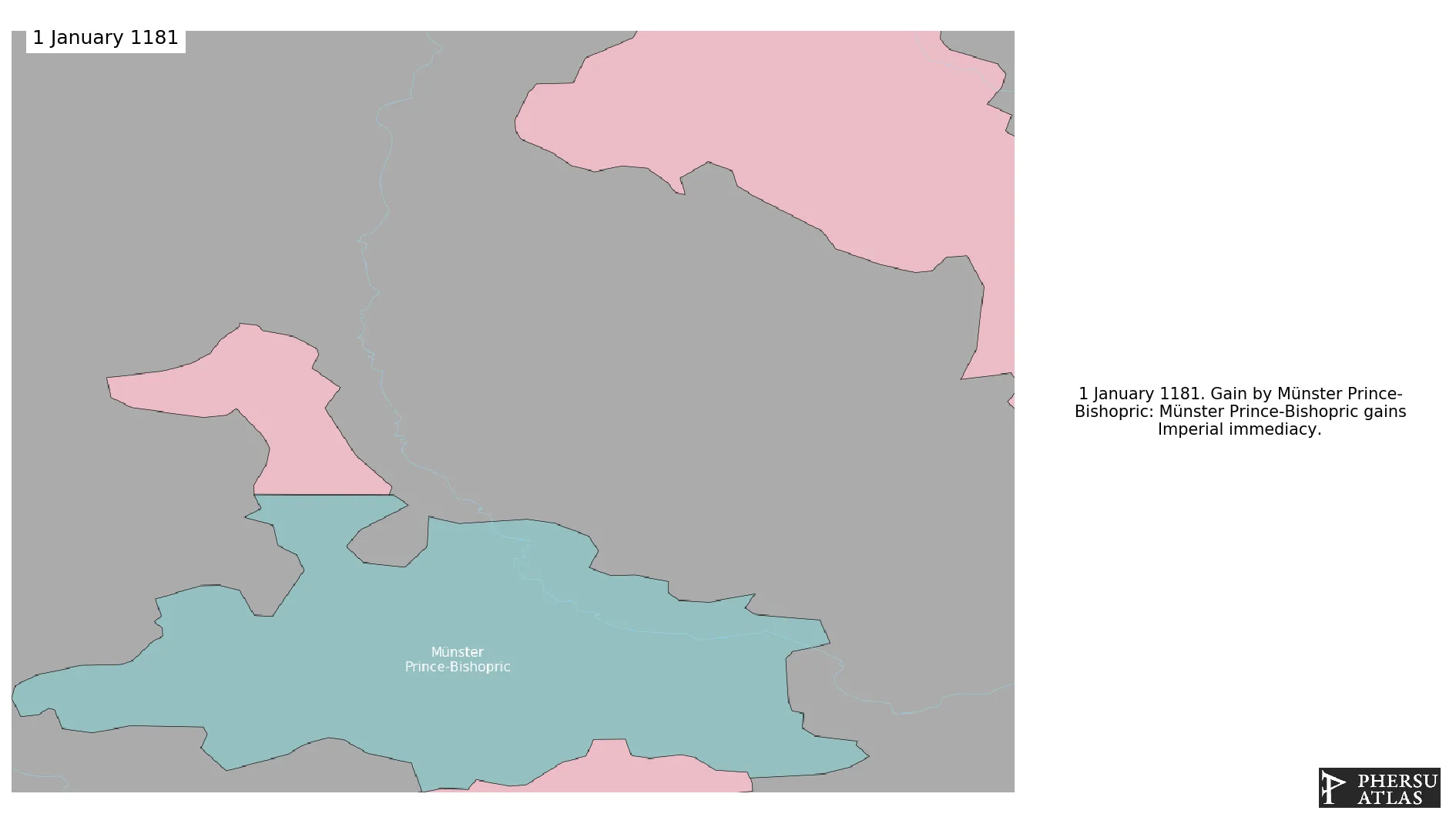
This article is about the specific polity Münster Prince-Bishopric and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a large ecclesiastical principality in the Holy Roman Empire, located in the northern part of today's North Rhine-Westphalia and western Lower Saxony.
Establishment
January 1181: Münster Prince-Bishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
1.1.Münster rebellion
Was an attempt by radical Anabaptists to establish a communal sectarian government in the German city of Münster, then part of the Prince-Bishopric of Münster in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1534: The city was under Anabaptist rule from February 1534, when the city hall was seized and Bernhard Knipperdolling installed as mayor, until its fall in June 1535.
June 1535: Münster was retaken by the Prince Bishop.
1.2.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
1.2.1.Bohemian-Palatine period
Was the first period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with a protestant revolt in Bohemia, at the time a territory of the Habsburg Domains.
1.2.1.1.War in Palatinate
Was the theatre of war in Palatinate during the first phase of the Thirty Years' War.
January 1622: German Protestant military leader Christian of Brunswick captures Lippstadt.
January 1622: Christian of Brunswick captures Soest.
September 1622: From the summer of 1622, the territories of the Palatinate on the right bank of the Rhine were occupied by the troops of the Catholc League. Frederick V of the Palatinate eventually lost his electoral dignity on February 23, 1623, which was transferred to Maximilian of Bavaria.
1.2.2.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
January 1649: The Münster Prince-Bishopric fell to Sweden.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1803: Salm was created in 1802 as a state of the Holy Roman Empire in order to compensate the princes of Salm-Kyrburg and Salm-Salm, who had lost their states to France in 1793-1795. The new territory was not near most of the old territories of the princes, but instead extended the County of Anholt, which had been a minor possession of the prince of Salm-Salm. Most of the area was taken from the dissolved Bishopric of Münster.
February 1803: Reichsdeputationsschluss: the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the Reichstag (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Empire. The law secularized nearly 70 ecclesiastical states and abolished 45 imperial cities to compensate numerous German princes for territories to the west of the Rhine that had been annexed by France as a result of the French Revolutionary Wars.
February 1803: With the German Mediatisation of 1803, Oldenburg acquired the Oldenburg Münsterland and the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck.
March 1806: On 15 March 1806, the French emperor created the Granduchy of Berg and put it under the rule of his brother-in-law Joachim Murat. The Grand Duchy was a Napoleonic creation on territories formally part of several German states. Its capital was Düsseldorf.
2.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
2.1.1.Flanders Campaign
Was a French military campaign in the Flanders.
January 1795: On 10 January French general Pichegru ordered a general advance across the frozen river between Zaltbommel and Nijmegen and the allies were forced to retreat behind the Lower Rhine.
June 1795: Territory evacuated by the French at the end of the Flanders Campaign. The surrender of Luxembourg on 7 June 1795 concluded the French conquest of the Low Countries, thus marking the end of the Flanders Campaign.
2.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
2.2.1.Suvorov Swiss campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Switzlerand.
October 1799: The Russian troops were forced by the French to abandon their hold on the left bank of the Rhine.
2.2.2.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
February 1801: After the French occupation of the west bank of the Rhine around 1798 (see Treaty of Campo Formio and Treaty of Lunéville), the Duke of Arenberg received new lands: the county of Vest Recklinghausen, the county of Meppen, and the lordship of Dülmen.
January 1253: The Münster Prince-Bishopric acquired Vechta.
January 1253: Meppen is sold to the Prince-Bishopric of Münster.
January 1344: Steinfurt is acquired by the Bishopric of Münster.
January 1355: shopric is declared a Free Imperial City.
January 1358: Steinfurt reestablished as an independent Lordship.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
January 1401: Tecklenburg County lost Cloppenburg, Friesoythe and Bevergern to Münster.
January 1478: Wildeshausen passed to Munster in the late Middle Ages.
January 1483: The city of Delmenhorst fell under Munster rule.
January 1548: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of the Reformation.
January 1548: Count Anton I of Oldenburg recaptured the castle and county of Delmenhorst.
January 1690: The Prince-Bishop of Münster, Christoph Bernhard von Galen, succeeded in freeing his territory from foreign troops.
January 1701: Wildeshausen came to the Electorate of Hanover in 1700.
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
March 1806: On 15 March 1806, the French emperor created the Granduchy of Berg and put it under the rule of his brother-in-law Joachim Murat. The Grand Duchy was a Napoleonic creation on territories formally part of several German states. Its capital was Düsseldorf.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 38-39
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Kreins, J. (2003): Histoire du Luxembourg, Paris (France), p. 63
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Swiss campaign of Suvorov and his wonder-heroes. Top War. 30 September 2011. https://en.topwar.ru/7227-shveycarskiy-pohod-suvorova-i-ego-chudo-bogatyrey.html

 Münster Prince-Bishopric
Münster Prince-Bishopric