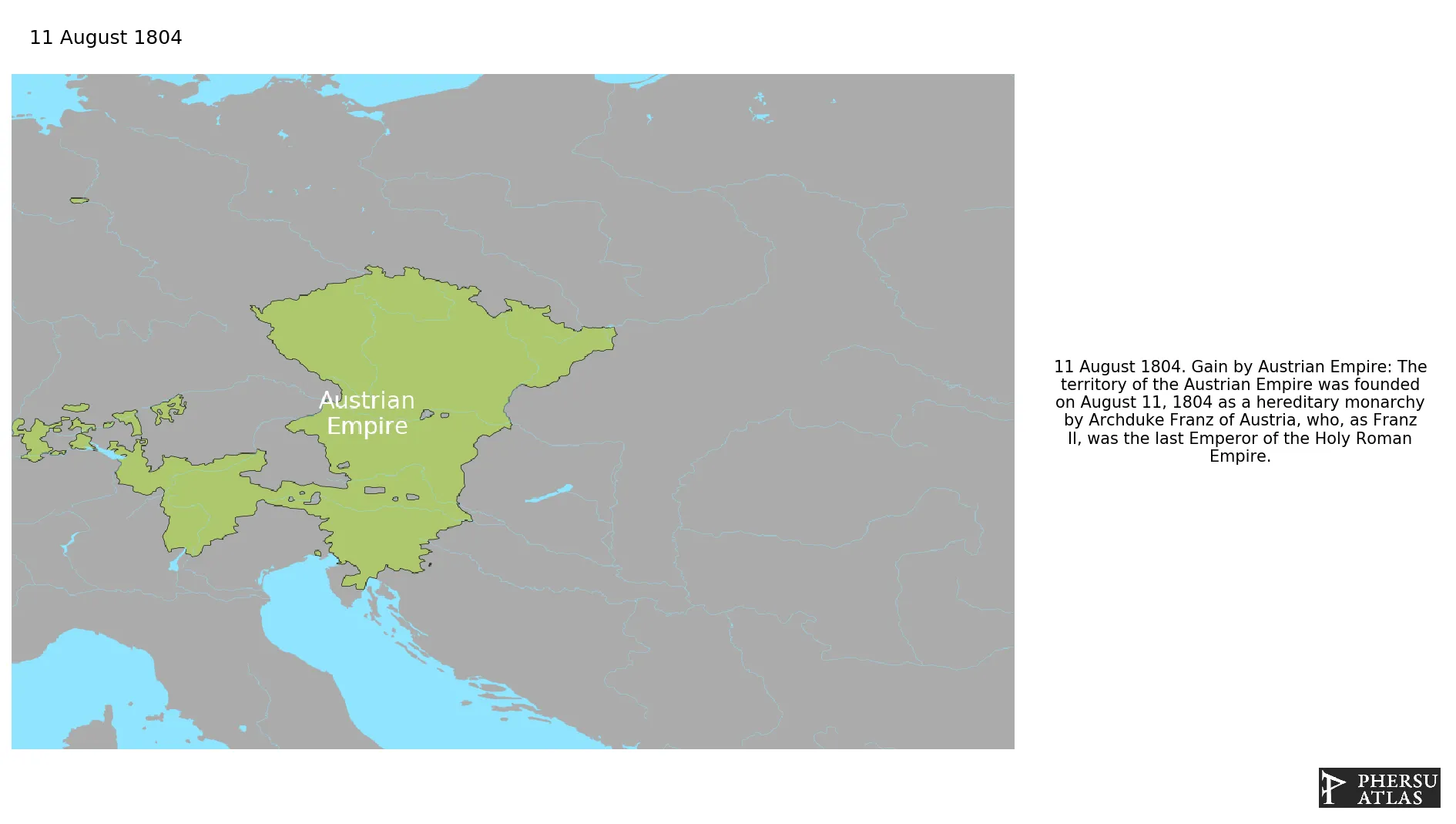
This article is about the specific polity Austrian Empire and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an Empire in Central and Eastern Europe created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs after the end of the Holy Roman Empire. During its existence, it was one of the most populous monarchies in Europe.
Summary
The Austrian Empire was established in 1804 when Francis II, the last Holy Roman Emperor, assumed the title of Emperor of Austria as Francis I. This was in response to the growing power of Prussia within the German Confederation, which had replaced the Holy Roman Empire.
During this period, the Habsburgs continued to rule their diverse domains as a unified entity, attempting to control the German Confederation and manage the growing demands for national autonomy from various ethnic groups within the empire. The industrial revolution began to have an impact on the Austrian economy, with the development of railroads and communication networks.
The 1848 revolutions, sparked by the February revolt in Paris, led to some short-term changes in Austria, such as the freedom of the press and the establishment of an elected parliament. However, the revolution ultimately failed, and Ferdinand I abdicated in favor of the 18-year-old Francis Joseph I, who ruled the empire of Austria, Hungary, and Bohemia, as well as parts of Italy, Poland, and the Balkans.
The empire was held together only by force during this time, as it faced growing Prussian strength and the pan-German ambitions of Otto von Bismarck. Finally, Austria was defeated by the Prussians in a brief war in 1866, leading to the reorganization of the empire.
Establishment
August 1804: The territory of the Austrian Empire was founded on August 11, 1804 as a hereditary monarchy by Archduke Franz of Austria, who, as Franz II, was the last Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1805: The County of Rothenfels briefly became part of Austria in 1804 with around 13,000 inhabitants and an area of around 450 square kilometers.
January 1805: The Bretzenheim Lordship is acquired by the Austrian Empire.
January 1806: The Kingdom of Bavaria had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
January 1806: The former Imperial Citiy of Konstanz is ceded to Baden.
January 1806: The Salzburg Electorate is acquired by the Austrian Empire.
January 1808: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Germany during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods.
January 1811: In 1810, the Alpine territories surrounding Sillian and Lienz were added to the First French Empire under the rule of Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte.
1.1.War of the Third Coalition
Was a European conflict spanning the years 1805 to 1806. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, made up of the United Kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.
1.1.1.Ulm Campaign
Was a series of French and Bavarian military maneuvers and battles to outflank and capture an Austrian army in 1805 during the War of the Third Coalition. It took place in the vicinity of and inside the city of Ulm.
October 1805: The French army crossed the Danube at Donauwörth.
October 1805: Battle at Wertingen between the Austrians led by Auffenburg troops and the French of Murat and Lannes.
December 1805: French forces seized Vienna in November 1805.
1.1.2.Venetian front or Italian campaign of 1805
Was the Venetian theatre of the War of the Third Coalition.
November 1805: By November 14th, 1805 the French armies had reached the Isonzo but the army of Archduke Charles of Austria prevented them to cross the river.
1.1.3.Peace of Pressburg
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Third Coalition.
December 1805: On December 16, 1805, the area of Königsegg-Rothenfels went to the Kingdom of Bavaria through the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: Territorial changes after the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: After the Austrian defeat at the Battle of Austerlitz and the Peace of Pressburg in 1805, Further Austria was entirely dissolved and the former Habsburg territories were assigned to the Grand Duchy of Baden (Breisgau), the Kingdom of Württemberg (Rottenburg and Horb) and the Kingdom of Bavaria (Weitnau Günzburg, Weißenhorn). Minor estates passed to Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and the Grand Duchy of Hesse.
December 1805: French evacuation of occupied territories after the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: The Fricktal passed to the Swiss Confederation with the Napoleonic Acts of Mediation.
1.2.Adriatic campaign of 1807-1814
Was the theatre of war in the Adriatic Sea during the Napoleonic Wars.
February 1814: By 16 February 1814 every French harbour in the Illyrian provinces had been captured by British or Austrian troops. Over 700 French merchant ships had been seized and the only remaining French outpost in the region was Corfu.
1.3.War of the Fifth Coalition
Was a conflict between a colition of European monarchies and Napoleon's French Empire.
1.3.1.Dalmatian Campaign (1809)
Was the Dalmatian theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
May 1809: In 1809, Marshal Marmont, a French military commander, achieved a significant victory over the Austrians at Pribudić.
May 1809: French forces under general Marmont take the city of Gospić.
June 1809: Ljubljana conquered by france.
1.3.2.Danube Campaign (War of the Fifth Coalition)
Was a French military campaign in the Danube area during the War of the Fifth Coalition. The French forces defeated the Austrian army and occupied Vienna.
May 1809: After defeating the Austrian forces led by Archduke Charles, Napoleon Bonaparte occupied Vienna in May 1809.
July 1809: After the Battle of Wagram, Napoleon's forces, led by Marshal Davout, pursued the retreating Austrians under Archduke Charles. The exhausted French troops caught up with the Austrians at Znaim in mid-July 1809, leading to a military occupation of the territory by France.
1.3.3.Austro-Polish War
Was a war between the Austrian Empire and the Napoleon-allied Duchy of Warsaw.
May 1809: Polish forces took the major cities of Lublin.
May 1809: In 1809, Sandomierz was incorporated into the Duchy of Warsaw.
May 1809: Zamość conquered by france.
May 1809: Lwów conquered by france.
June 1809: The Austrians took back Sandomierz and Lwów.
July 1809: Kielce and Kraków conquered by france.
1.3.4.Treaty of Schönbrunn
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Fifth Coalition.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna. Austria lost its access to the Adriatic Sea by waiving the Littoral territories of Gorizia and Gradisca and the Imperial Free City of Trieste, together with Carniola, the March of Istria, western ("Upper") Carinthia with East Tyrol, and the Croatian lands southwest of the river Sava to the French Empire (Illyrian provinces).
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna. West Galicia was ceded to the Duchy of Warsaw.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna.Austria had to cede the Duchy of Salzburg to Bavaria.
January 1811: Due to the Peace of Schönbrunn in 1809, Bavaria once again took possession of the Innviertel in 1810.
1.4.War of the Sixth Coalition
Was a war between France and a a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States. The coalition emerged after the decimation of the French army in the French invasion of Russia. The coalition ultimately invaded France and forced Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile.
January 1814: Following Napoleon's defeat at the Battle of Leipzig in 1813, the Congress of Vienna opted to mediatize the Leyen Principality and give it to Austria.
January 1814: Görz and Trient are annexed by Austria.
May 1814: The Valtellina, formerly owned by Graubunden, was granted to Austria.
1.5.Congress of Vienna
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
January 1815: Tirol is annexed by Austria.
June 1815: The Austrian Empire receives the Tarnopol district from Russia.
June 1815: Not all Austrian territories became part of the German onfederation.
The dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire occurred de facto on 6 August 1806, when the last Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, abdicated his title and released all imperial states and officials from their oaths and obligations to the Empire.
August 1806: End of the Holy Roman Empire.
Was a war between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire.
3.1.Treaty of Bucharest
The Treaty of Bucharest between the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire, was signed on 28 May 1812 at the end of the Russo-Turkish War of 1806-12. The eastern half of the Principality of Moldavia was ceded by the Ottoman Empire to Russia.
July 1812: The Treaty of Bucharest between the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire, was signed on 28 May 1812, in Manuc's Inn in Bucharest, and ratified on 5 July 1812, at the end of the Russo-Turkish War. The eastern half of the Principality of Moldavia, between Prut and Dniester Rivers, with an area of 45,630 km2 (Bessarabia), was ceded by the Ottoman Empire (to which Moldavia was a vassal) to Russia.
Were a series of wars that resulted in the creation of the German Empire under Prussian leadership in 1871.
4.1.Second Schleswig War
Was a war caused by the status of the duchies of Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg, that were Dnish possession but at the same also part of the German confederation. When the Danish King died without an heir acceptable to the German Confederation, Prussian and Austrian troops invaded and occupied the duchies.
4.1.1.Gastein Convention
Was an agreement between Prussia and Austria over the occupied duchies of Schleswig, Holstein and Saxe-Lauenburg. .
4.2.Austro-Prussian War
Was a war between the Kingdom of Prussia and the Austrian Empire over the dominance of the German states. The war resulted in a Prussian victory. The German confederation was abolished and in 1871 Prussia united all the German states but Austria in the German Empire.
4.2.1.Third Italian War of Independence
Was the last of the three traditional Italian Wars of Independence, and also represented the southern theatre of the larger Austro-Prussian War. It was fought by the Kingdom of Italy against the Austrian Empire, resulting in the Italian annexion of the remaining territories of the Austrian Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia.
July 1866: Battle of Condino.
July 1866: Siege of the Fort of Ampola.
July 1866: Battle of Bezzecca.
July 1866: The Italians occupy Levico.
July 1866: The Italians occupy Civezzano.
October 1866: Through the Treaty of Vienna the third war of independence was declared closed. Under the peace agreement, the Austrian Empire would have ceded Veneto, Friuli and the province of Mantua (the last remaining territories of the Lombard-Veneto kingdom) to France , which in turn would then transfer them to the Kingdom of Italy, subject to the consent of the inhabitants of the territories concerned, through a plebiscite.
October 1866: Through the Treaty of Vienna the Third Italian War of Independence was declared closed. Under the peace agreement, the Austrian Empire would have ceded Veneto, Friuli and the province of Mantua (the last remaining territories of the Lombard-Veneto kingdom) to France , which in turn would then transfer them to the Kingdom of Italy.
4.2.2.Front in Bohemia (Austro-Prussian War)
Was the Bohemian front of the Austro-Prussian War.
June 1866: Battle of Hühnerwasser (modern-day Kuřívody, Czech Republic).
June 1866: Battle of Nachod.
June 1866: Battle of Podol.
June 1866: Battle of Trautenau.
June 1866: Battle of Skalitz.
June 1866: Battle of Munich Grätz.
June 1866: Battle of Gichin.
June 1866: Battle of Königinhof (modern-day Dvůr Králové nad Labem, Czech Republic)
June 1866: Battle of Schweinschädel (modern-day Bitva u Svinišťan, Czech Republic).
July 1866: The Battle of Königgrätz was the culminating military event in the 1866 Austro Prussian War. It was also the largest European land battle before World War I. The battle was won by Prussia, that become the dominant German state.
July 1866: Battle of Trautenau.
4.2.3.Peace Treaties (Austro-Prussian War)
Were a series of treaties that ended the Austro-Prussian War. Prussia annexed the Austro-Prussian condominium of Schleswig and Holstein and several other territories. The German Confederation was dissolved, and a Prussian domained Northern German Confederation, that excluded the southern German states, was created.
August 1866: Peace of Prague: renunciation of rights to the condominium in Schleswig and Holstein; Recognition of Prussian supremacy in northern Germany.
September 1866: After the Austro-Prussian War, Prussia evacuated the territories it had occupied in Austria.
October 1809: The Tarnopolsky District of Austria within the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria was cquired by Russia under an agreement.
May 1816: Only in the Munich Treaty did the Kingdom of Bavaria finally cede the Innviertel and other areas to the Austrian Empire on May 1, 1816.
January 1819: The former Bohemian area of Auschwitz-Zator is transferred to the Austrian territories that were within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire.
October 1819: In 1818 the Principality von der Leyen passed to the Grand Duchy of Baden.
August 1866: In 1866, the German Confederation was dissolved following the Austro-Prussian War.
June 1867: After Austria was defeated in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 was adopted, joining together the Kingdom of Hungary and the Empire of Austria to form Austria-Hungary.
Disestablishment
June 1867: After Austria was defeated in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 was adopted, joining together the Kingdom of Hungary and the Empire of Austria to form Austria-Hungary.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 48-49.
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, Munich (Germany), p. 248
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, Munich (Germany), pp. 791-792
Phillipson, C. (2008): Termination of War and Treaties of Peace, Clark (USA), p. 273
Schneid, F. (2002): Napoleon's Italian campaigns, 1805-1815, Greenwood (USA), pp. 41-42
Spindler, M. / Kraus, A. (2011): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts (Handbuch der bayerischen Geschichte. Band 3: Franken, Schwaben, Oberpfalz bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts.), Munich (Germany), p. 384ff.
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.352

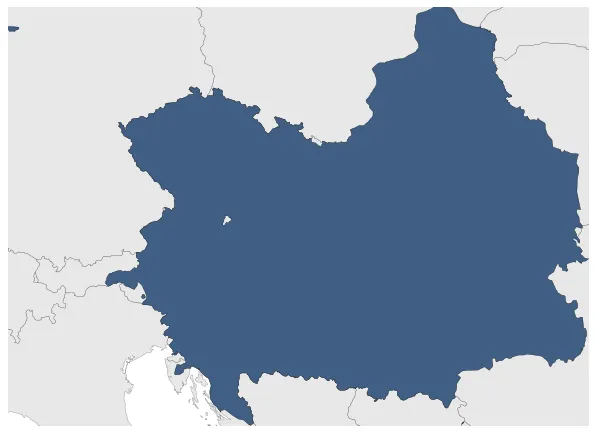
 Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire