This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Bavaria and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
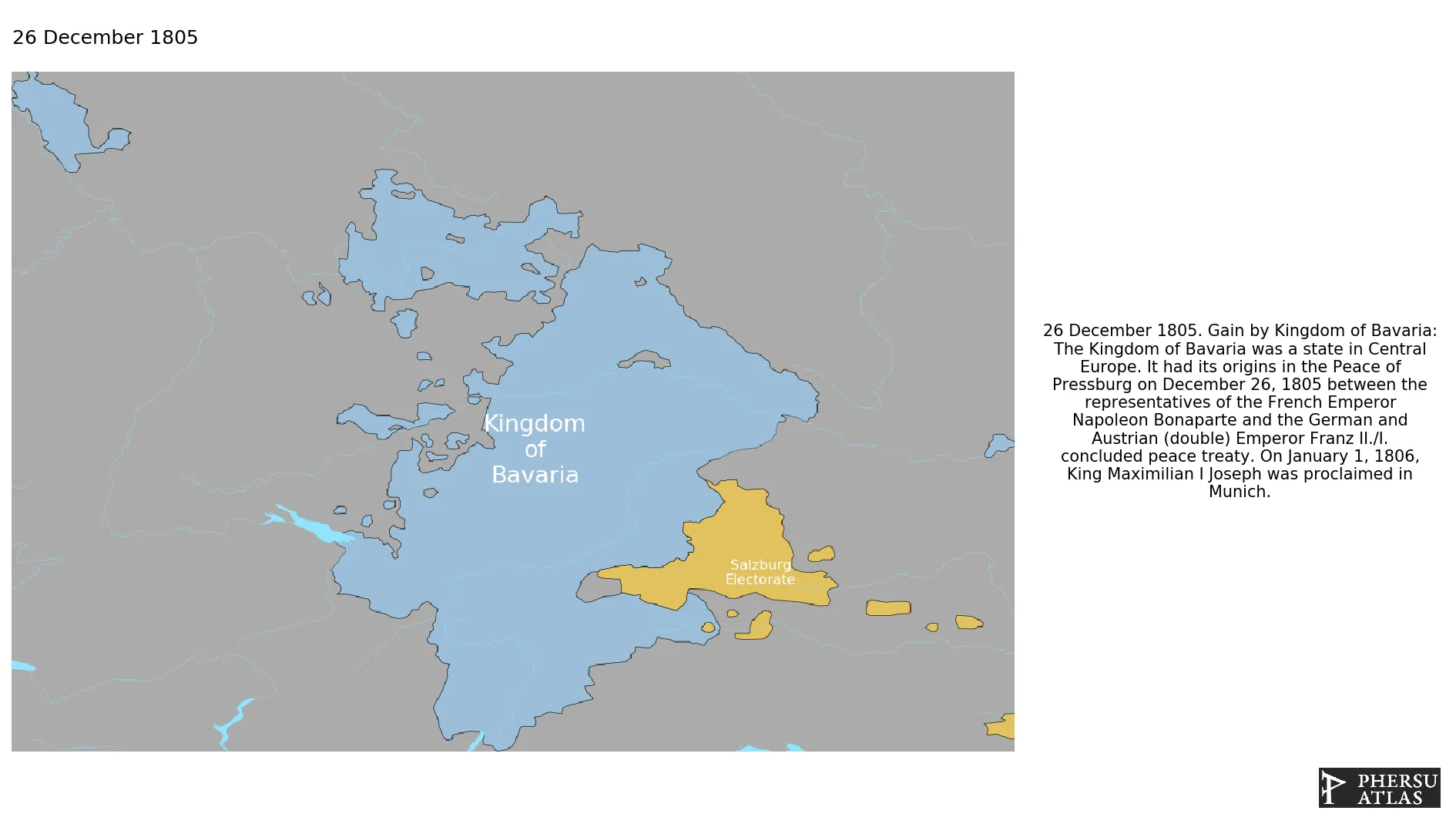
In 1805, after the Peace of Pressburg, the then-elector of Bavaria, Maximilian Joseph, raised himself to the dignity of King of Bavaria.
Establishment
December 1805: The Kingdom of Bavaria was a state in Central Europe. It had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1806: The Kingdom of Bavaria had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
January 1806: Establishment of the Granduchy of Würzburg.
October 1806: In September 1802, the city of Nuremberg lost its imperial freedom and came under the control of Electoral Bavaria. In 1804, it was transferred to Prussia before finally becoming part of the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1806.
January 1807: In 1806, the city of Nuremberg was transferred to the Kingdom of Bavaria as part of the territorial changes brought about by the Napoleonic Wars. This decision was made as a result of the Treaty of Pressburg, signed between Napoleon Bonaparte and Emperor Francis II of Austria.
January 1807: In 1806, the territory of castell was transferred to the Kingdom of Bavaria as a result of the Treaty of Pressburg.
January 1807: The Kurpfalz-Bayern came to the Kingdom of Württemberg in 1806 through an exchange of territory.
January 1807: The domains of all Fuggers (Prince of Fugger-Babenhausen, Count of Fugger-Glött, Count of Fugger-Kirchberg-Weissenhorn, Count of Fugger-Kirchheim, Count of Fugger-Nordendorf) fell to Bavaria.
January 1807: In 1806, the city of Augsburg was transferred to the Kingdom of Bavaria as part of the territorial changes brought about by the Napoleonic Wars. This decision was made by the Treaty of Pressburg, signed by Emperor Francis II of Austria and Emperor Napoleon I of France.
January 1807: Pappenheim County was annexed ot Bavaria in 1806.
January 1807: In 1806, the various Hohenlohe territories were divided between the Kingdom of Württemberg and the Kingdom of Bavaria. This decision was made as part of the territorial reorganization following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1807: The Principality of Öttingen is acquired by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
January 1807: In 1806, in the reorganization of Germany occasioned by the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, Maximilian I Joseph, now King of Bavaria, ceded Berg to Napoleon in return for the Principality of Ansbach.
January 1807: The Sternstein County is acquired by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
January 1808: In 1806, in the reorganization of Germany occasioned by the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, Maximilian I Joseph, now King of Bavaria, ceded Berg to Napoleon in return for the Principality of Ansbach.
January 1811: Trento is annexed by the Kingdom of Italy.
January 1811: Regensburg and Windesheim are acquired by Bavaria.
January 1811: Bopfingen, Leutkirch, Ravensburg, Ulm and Wangen are annexed by the Kingdom of Württemberg.
January 1811: Schweinfurth is annexed by the Granduchy of Würzburg.
January 1811: In 1810, the Alpine territories surrounding Sillian and Lienz were added to the First French Empire under the rule of Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte.
January 1811: Parts of Bavaria are transferred to Württemberg.
1.1.War of the Third Coalition
Was a European conflict spanning the years 1805 to 1806. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, made up of the United Kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.
1.1.1.Peace of Pressburg
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Third Coalition.
1.2.War of the Fifth Coalition
Was a conflict between a colition of European monarchies and Napoleon's French Empire.
1.2.1.Danube Campaign (War of the Fifth Coalition)
Was a French military campaign in the Danube area during the War of the Fifth Coalition. The French forces defeated the Austrian army and occupied Vienna.
April 1809: The Austrian advance guard, led by Archduke Charles of Austria, beat back the Bavarians, commanded by Marshal Lefebvre, near Landshut in 1809 during the War of the Fifth Coalition. This victory led to the Austrian Empire occupying the territory.
1.2.2.Treaty of Schönbrunn
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Fifth Coalition.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna.Austria had to cede the Duchy of Salzburg to Bavaria.
January 1811: Due to the Peace of Schönbrunn in 1809, Bavaria once again took possession of the Innviertel in 1810.
1.3.Congress of Vienna
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
January 1815: The Granduchy of Würzburg is partitioned between Baden and Bavaria.
January 1815: Tirol is annexed by Austria.
January 1815: The region of Frankfurt was annexed by Bavaria in 1814.
June 1815: Territories awarded to the Kingdom of Bavaria by the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: Rieneck is ceded to Bavaria.
Were a series of wars that resulted in the creation of the German Empire under Prussian leadership in 1871.
2.1.Austro-Prussian War
Was a war between the Kingdom of Prussia and the Austrian Empire over the dominance of the German states. The war resulted in a Prussian victory. The German confederation was abolished and in 1871 Prussia united all the German states but Austria in the German Empire.
2.1.1.Campaign of the Main
Was a campaign of the Prussian army in the area of the river Main against the allies of Austria in Southern Germany during the Austro-Prussian War of 1866.
July 1866: Battle of Kissingen.
July 1866: The Prussians won the battle near Laufach against Hessian-Darmstadt troops and stormed Aschaffenburg on July 14 in fierce street fighting against Austrian troops under Field Marshal Erwin von Neipperg.
July 1866: Battle of Helmstadt.
July 1866: Battle of Rossbrunn.
August 1866: Battle of Rossbrunn.
2.1.2.Peace Treaties (Austro-Prussian War)
Were a series of treaties that ended the Austro-Prussian War. Prussia annexed the Austro-Prussian condominium of Schleswig and Holstein and several other territories. The German Confederation was dissolved, and a Prussian domained Northern German Confederation, that excluded the southern German states, was created.
September 1866: At the end of the Austro-Prussian War, Prussia left the territories occupied in Bavaria.
2.2.Franco-Prussian War
Was a war that saw the Second French Empire fight against an alliance of German states led by the Kingdom of Prussia. The war was caused by the struggle over dominance in continental Europe between Prussia and France. The German states were victorious and in 1871 merged to form the German Empire. France was occupied and forced to cede Alsace-Lorraine to Germany.
2.2.1.Unification of Germany (1871)
Was the unification of 25 German states into the German Empire under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
January 1871: Unification of Germany into a German Empire with tight political and administrative integration, replacing the decentralized German Confederation and Holy Roman Empire, was officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
January 1811: The Bishopric of Regensburg was given to Bavaria. Its ruler, Karl Theodor von Dalberg, obtained Frankfurt.
May 1816: Only in the Munich Treaty did the Kingdom of Bavaria finally cede the Innviertel and other areas to the Austrian Empire on May 1, 1816.
July 1816: Based on an agreement between Austria, Prussia and Hesse-Darmstadt, some territories in Lower Franconia were ceded to the Kingdom of Bavaria.
Disestablishment
January 1871: Unification of Germany into a German Empire with tight political and administrative integration, replacing the decentralized German Confederation and Holy Roman Empire, was officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
Selected Sources
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, C.H. Beck München, pp. 28-31
O'Mahony, C. I. (2013). War within the Walls: Conflict and Citizenship in the Murals of the Hôtel de Ville, Paris. Journal of War & Culture Studies, 6(1), 6-23.
.svg.png.webp)
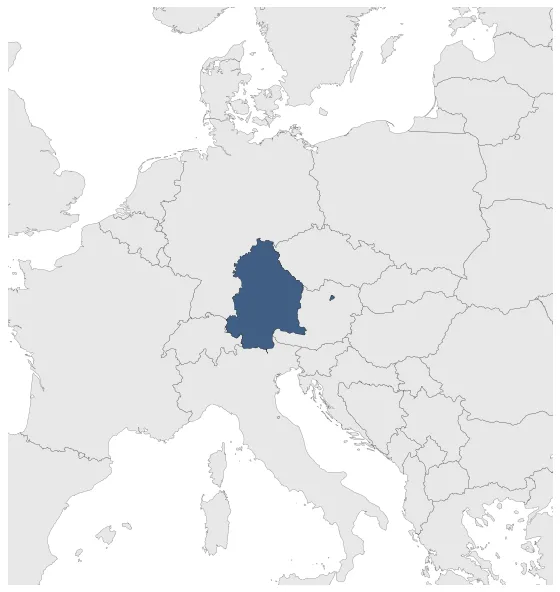
 Kingdom of Bavaria
Kingdom of Bavaria