This article is about the specific polity Bavaria-Palatinate and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
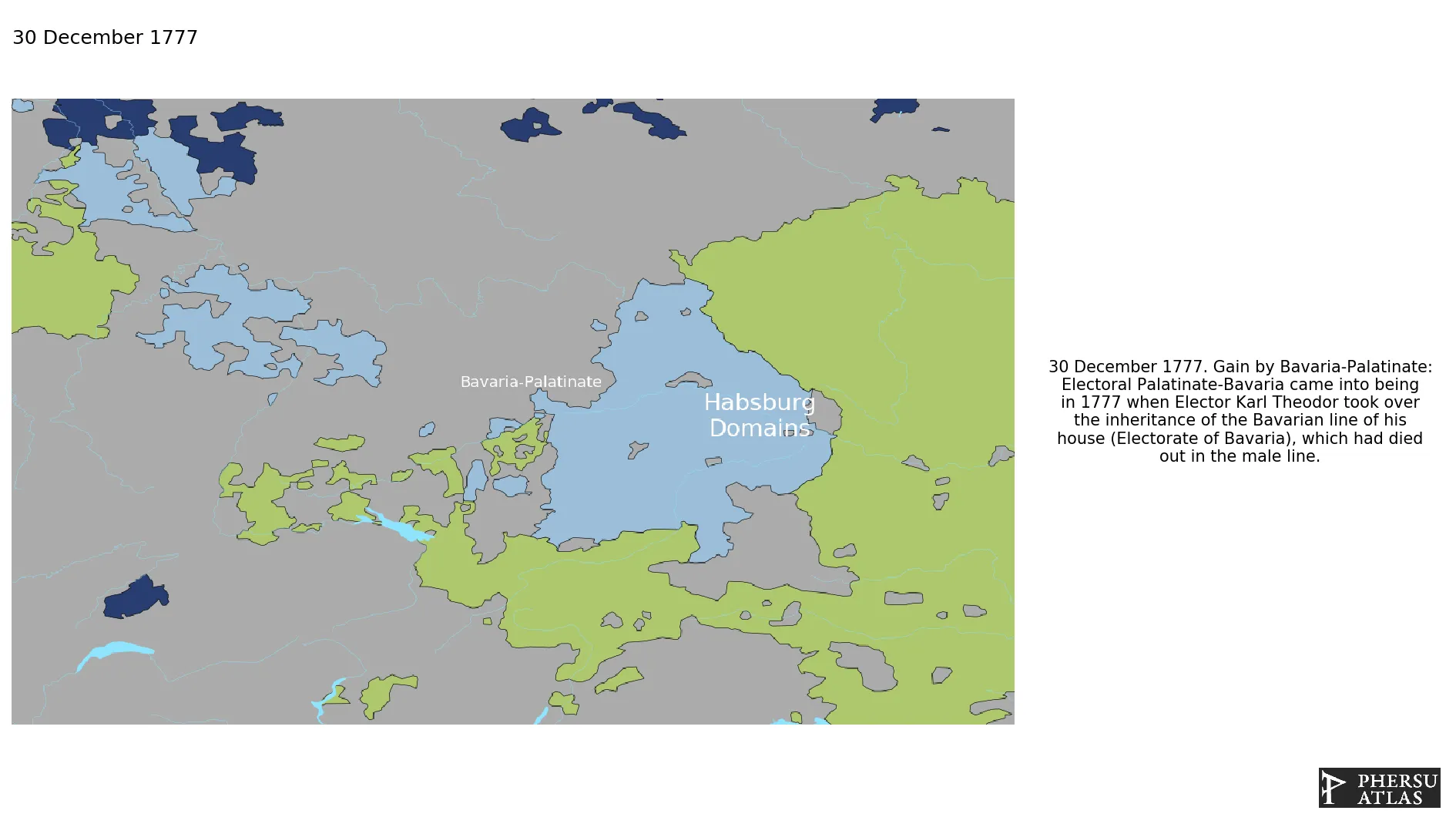
The Wittelsbach lines of Bavaria and Palatinate were united after the extinction of the Bavarian line in 1777.
Establishment
December 1777: Electoral Palatinate-Bavaria came into being in 1777 when Elector Karl Theodor took over the inheritance of the Bavarian line of his house (Electorate of Bavaria), which had died out in the male line.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a dispute between the Austrian Habsburg monarchy and an alliance of Saxony and Prussia over the succession to the Electorate of Bavaria after the extinction of the Bavarian branch of the House of Wittelsbach. Bavaria was finally united with Palatinate (where another Branche of the Wittelsbach ruled) but lost the Innviertel region ot Austria.
1.1.Treaty of Teschen
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Bavarian Succession.
May 1779: By the peace of Teschen (13 May 1779) the Innviertel was ceded to Austria.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
October 1802: In September 1802, Weissenburg in Bayern lost its imperial freedom and became part of Electoral Bavaria. In 1804, it was transferred to Prussia before finally becoming part of the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1806.
January 1803: The Augsburg Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Bavaria-Palatinate.
January 1803: As part of the mediatisation following the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss, Memmingen fell to the Electorate of Bavaria in 1803.
January 1803: The city and bishopric of Bamberg were promised to the Electorate of Bavaria as compensation for the loss of the Palatinate to France in the Treaty of Lunéville. Even before the final determination of borders in the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss (Imperial Recess) of 1803, Bavaria began to militarily occupy the territory of the bishopric on September 2, 1802, and declared the area a Bavarian province on November 29, definitively.
January 1803: In the year 1802, Dinkelsbühl lost its status as an imperial city and became part of the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1803: In 1802, the Prince-Bishopric of Eichstätt was secularized by the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1803: The Reichsdeputationshauptschluss assigned Schweinfurt to Bavaria in 1802.
January 1803: In 1802Ulm lost its independence and was incorporated into the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1803: In the course of mediatisation in 1802, Windsheim lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1803: As part of the mediatisation, Wangen lost its status as an imperial city in 1803 and became part of the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1803: In 1802, Bopfingen lost its imperial immediacy and came under the control of Bavaria.
February 1803: Since the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of 1803, the town of Irsee has belonged to Bavaria.
February 1803: Reichsdeputationsschluss: the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the Reichstag (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Empire. The law secularized nearly 70 ecclesiastical states and abolished 45 imperial cities to compensate numerous German princes for territories to the west of the Rhine that had been annexed by France as a result of the French Revolutionary Wars.
February 1803: The Imperial City of Nördlingen is acquired by the Bavaria-Palatinate as a result of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Ravensburg lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: The Passau Prince-Bishopric is divided between Bavaria and Salzburg.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Leutkirch lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: In 1803, the princes of the Leiningen-Dagsburg-Hardenburg line were compensated for their lost possessions in the Palatinate on the left bank of the Rhine with a new territory, which became part of the Principality of Leiningen. This territory was located in present-day Germany.
January 1804: Some Palatine right-bank territories of the Rhine River were transferred to the Electorate of Baden as part of the territorial changes brought about by the Napoleonic Wars.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Kempten is acquired by Bavaria-Palatinate.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Kaufbeuren lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Rothenburg lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: In 1803, the Prince-Bishopric of Würzburg was secularized by the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1804: Eichstädt is acquired by the Salzburg Electorate.
January 1804: Kempten was annexed to the Electorate of Bavaria in the course of the German mediatization in 1803.
January 1804: The Freising Prince-Bishopric is acquired by Bavaria-Palatinate as a result of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss.
October 1804: In 1804 Weißenburg in Bayern was annexed by Prussia.
2.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
July 1794: The Battle of Trippstadt was a relatively minor French military action in 1794. This victory gave the French control of the mountain passes across the lower Vosges ( Kaiserslautern, Trippstadt, Schänzel, Neustadt and along the banks of the Speyerbach River).
September 1794: In mid-September 1794, the Prussians, led by Frederick William II, attacked the weakened French forces, commanded by General Lazare Hoche, in the north-eastern frontier and reoccupied Kaiserslautern, which was part of the territory of Bavaria-Palatinate at the time.
January 1795: The French armies drove the Austrians, British, and Dutch beyond the Rhine, occupying Belgium, the Rhineland, and the south of the Netherlands.
2.1.1.Rhineland campaign of 1792
Was a French military campaign in the Rhineland.
September 1792: The French attacked Speyer on 29 September and conquered it the next day.
October 1792: French troops occupy Worms and Philippsburg without a fight.
October 1792: French general Custine captured Mainz on 21 October 1792.
October 1792: The French army penetrated as far as Frankfurt, which surrendered.
2.1.2.Flanders Campaign
Was a French military campaign in the Flanders.
December 1794: By 28 December the French had occupied the Bommelwaard and the Lands of Altena.
January 1795: On 10 January French general Pichegru ordered a general advance across the frozen river between Zaltbommel and Nijmegen and the allies were forced to retreat behind the Lower Rhine.
June 1795: Territory evacuated by the French at the end of the Flanders Campaign. The surrender of Luxembourg on 7 June 1795 concluded the French conquest of the Low Countries, thus marking the end of the Flanders Campaign.
2.1.3.Peace of Basel
Were a series of Treaties between the French Republic and Prussia, Spain and Hesse-Kassel that ended the War of the First Coalition with these countries.
April 1795: Peace of Basel of 1795 at the end of the War of the First Coalition between the Kingdom of Prussia and the French Republic. France gained the left bank of the Rhine.
2.1.4.Italian theatre (War of the first coalition)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
February 1797: French troops advanced directly toward Austria over the Julian Alps. General Barthélemy Joubert invaded Tyrol.
2.1.5.Rhine campaign of 1796
Were a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
June 1796: A division of French general Kléber's troops seized a bridge over the Sieg from Michael von Kienmayer's Austrians at Siegburg.
2.1.6.Treaty of Campo Formio
Was a treaty between France and Austria that ended the War of the First Coalition.
January 1798: The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI). The treaty transferred the Austrian Netherlands to France. The territories of Venice were partitioned, most were acquired by Austria. Austria recognized the Cisalpine Republic and the newly created Ligurian Republic. Extension of the borders of France up to the Rhine, the Nette, and the Roer.
2.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
2.2.1.German Front (War of the Second Coalition)
Was the German theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
June 1800: After being defeated by the French at the Battle of Höchstädt, Hungarian General Paul Kray retreated to Munich.
December 1800: The French victory in the Battle of Hohenlinden ended the War of the Second Coalition against France.
December 1800: French General of Division Claude Lecourbe's Right Wing brushed aside Riesch at Rosenheim.
December 1800: The French army occupied Salzburg.
December 1800: Austria was defeated by France in the Battle of Hohenlinden (3 December 1800). By december, 25th the French forces were 80 km from Vienna. The Austrians requested an armistice, which French general Moreau granted on 25 December.
2.2.2.Suvorov Swiss campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Switzlerand.
October 1799: The Russian troops were forced by the French to abandon their hold on the left bank of the Rhine.
2.2.3.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
2.3.War of the Third Coalition
Was a European conflict spanning the years 1805 to 1806. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, made up of the United Kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.
2.3.1.Ulm Campaign
Was a series of French and Bavarian military maneuvers and battles to outflank and capture an Austrian army in 1805 during the War of the Third Coalition. It took place in the vicinity of and inside the city of Ulm.
October 1805: The French army crossed the Danube at Donauwörth.
October 1805: By 10 October French officer Loison's division held Elchingen.
2.3.2.Venetian front or Italian campaign of 1805
Was the Venetian theatre of the War of the Third Coalition.
November 1805: By November 14th, 1805 the French armies had reached the Isonzo but the army of Archduke Charles of Austria prevented them to cross the river.
2.3.3.Peace of Pressburg
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Third Coalition.
December 1805: On December 16, 1805, the area of Königsegg-Rothenfels went to the Kingdom of Bavaria through the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: French evacuation of occupied territories after the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: The Kingdom of Bavaria was a state in Central Europe. It had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
January 1788: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
October 1805: The French army crossed the Danube at Donauwörth.
October 1805: By 10 October French officer Loison's division held Elchingen.
November 1805: By November 14th, 1805 the French armies had reached the Isonzo but the army of Archduke Charles of Austria prevented them to cross the river.
December 1805: On December 16, 1805, the area of Königsegg-Rothenfels went to the Kingdom of Bavaria through the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: The Kingdom of Bavaria was a state in Central Europe. It had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
December 1805: French evacuation of occupied territories after the Peace of Pressburg.
Selected Sources
Addington, L. (1994): The Patterns of War Since the Eighteenth Century, Bloomington (USA), p.24
Articles secrets et convention additionelle du traité de Campo Formio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2024 on https://books.google.de/books?id=SStJAAAAcAAJ&dq=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&hl=de&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&f=false
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 48
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Fournier. A (1913): Napoleon I. Eine Biographie, Vienna (Austria), p. 255
Frieden von Campoformio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2014 on https://books.google.de/books?id=UbGMtENHaBIC&pg=PA9#v=onepage&q&f=false
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Guthrie, W. (1798): A New geographical, historical and commercial grammar and present state of the several kingdoms of the world, printed for Charles Dilly and G.G. and J. Robinson, p. 473
Jorio, M. (2002): Basel, Frieden von (1795). Historisches Lexikon der Schweiz. https://hls-dhs-dss.ch/de/articles/044887/2002-05-01/
Kreins, J. (2003): Histoire du Luxembourg, Paris (France), p. 63
Phillipson, C. (2008): Termination of War and Treaties of Peace, Clark (USA), p. 273
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Schneid, F. (2002): Napoleon's Italian campaigns, 1805-1815, Greenwood (USA), pp. 41-42
Smith, D. (1998): Napoleonic Wars Databook, London (UK), p. 178
Spindler, M. / Kraus, A. (2011): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts (Handbuch der bayerischen Geschichte. Band 3: Franken, Schwaben, Oberpfalz bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts.), Munich (Germany), p. 384ff.
Swiss campaign of Suvorov and his wonder-heroes. Top War. 30 September 2011. https://en.topwar.ru/7227-shveycarskiy-pohod-suvorova-i-ego-chudo-bogatyrey.html
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.274
.svg.png.webp)
 Bavaria-Palatinate
Bavaria-Palatinate