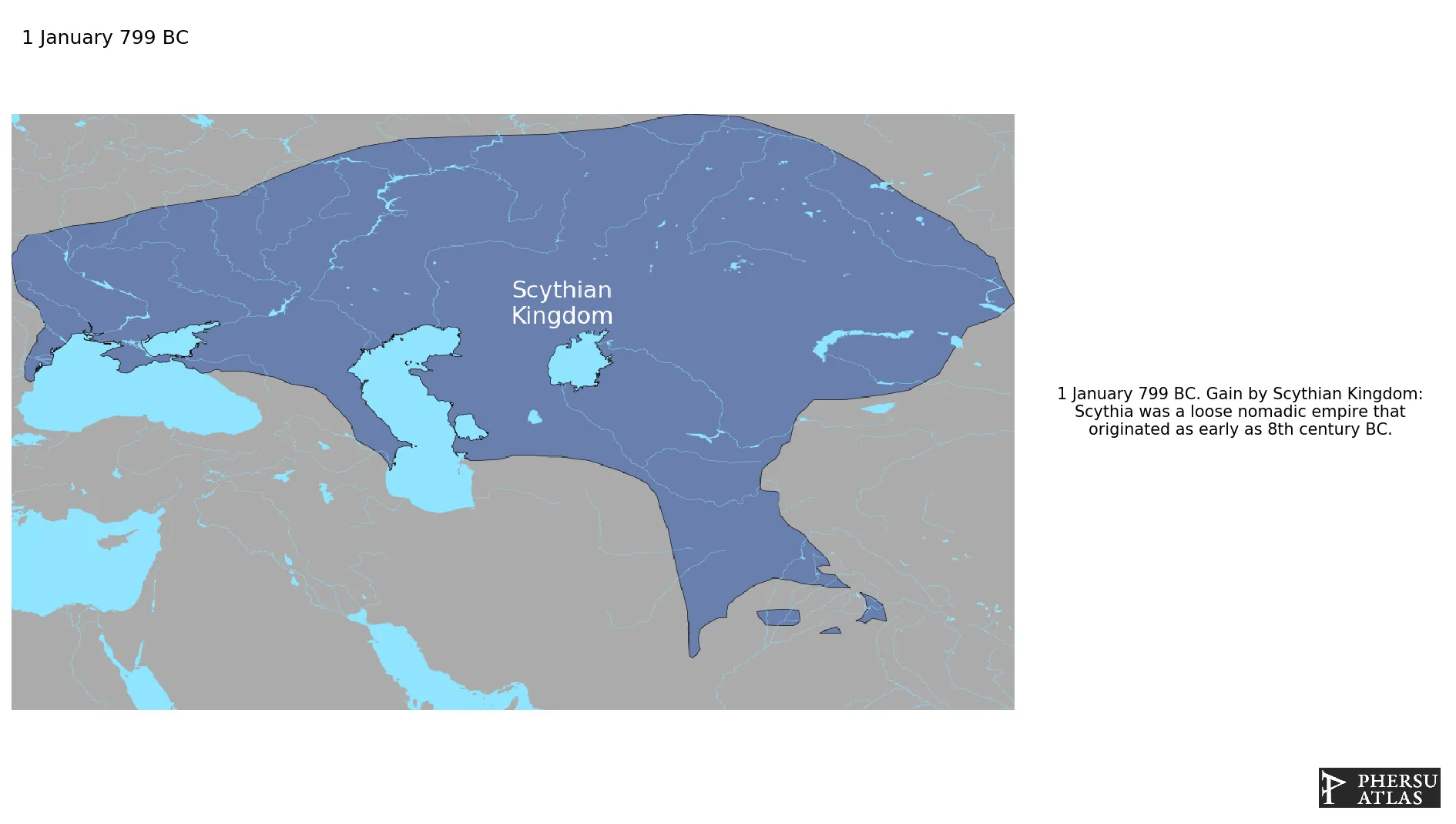
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
A loose nomadic empire that originated as early as 8th century BC.
Establishment
January 799 BC: Scythia was a loose nomadic empire that originated as early as 8th century BC.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Military campaign of Median king Cyaxares.
January 624 BC: Cyaxares II, the king of the Median Empire, ended the Scythian rule in Western and Eastern Iran in -625. This marked the restoration of Median control over the territory, consolidating their power in the region.
Were a series of expansionistic military campaigns by the first Achaemenid ruler Cyrus the Great.
January 549 BC: By the mid-6th century BC, Caucasian Albania was incorporated in the Achaemenid empire.
January 538 BC: Margiana, located in present-day Turkmenistan, was conquered by the Persian king Cyrus the Great. The territory became part of the Achaemenid Empire's satrapy of Bactria between 545 and 539 BC.
2.1.Conquest of Sogdia
Was an Achaemenid military campaign in Sogdia.
January 545 BC: Herodotus, a Greek historian, noted that Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, conquered and incorporated Sogdia into his empire during his military campaigns from 546-539 BC. Sogdia was a region located in Central Asia.
2.2.Achaemenid invasion of the Indus Valley
Were a series of military campaigns by the Achaemenid rulers in the Indus valley.
January 538 BC: Cyrus the Great expanded the Achaemenid Empire as far as to the banks of the Indus river and organized the conquered territories under the Satrapy of Gandara.
January 517 BC: The Gandhara Kingdom, ruled by King Ambhi, was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire under the leadership of King Darius I in 518 BC. This marked the incorporation of Gandhara into the vast Persian Empire.
January 515 BC: The Achaemenids under Darius penetrated to the region in 516 BC and annexed other parts of modern-day Punjab, Pakistan west to the Indus river and Sindh.
The upper Indus region, comprising Gandhara and Kamboja, formed the 7th, Gandhara satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire.
January 509 BC: Conquests of Achaemenid ruler Darius I in India (Gandara and Sattagydia), circa 510 BC.
Conquests by Achaemenid ruler Darius I.
January 512 BC: Darius the Great invaded European Scythia in 513 BC.
January 499 BC: By the 5th century BC the Kings of Persia were either ruling over or had subordinated territories encompassing not just all of the Persian Plateau and all of the territories formerly held by the Assyrian Empire (Mesopotamia, the Levant, Cyprus and Egypt), but beyond this all of Anatolia and Armenia, as well as the Southern Caucasus and parts of the North Caucasus, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, all of Bulgaria, Paeonia, Thrace and Macedonia to the north and west, most of the Black Sea coastal regions, parts of Central Asia as far as the Aral Sea, the Oxus and Jaxartes to the north and north-east, the Hindu Kush and the western Indus basin (corresponding to modern Afghanistan and Pakistan) to the far east, parts of northern Arabia to the south, and parts of northern Libya to the south-west, and parts of Oman, China, and the UAE.
3.1.Scythian campaign of Darius I
The Scythian campaign of Darius I was a military expedition into parts of European Scythia by Darius I, the king of the Achaemenid Empire, in 513 BC.
January 512 BC: The Scythian campaign of Darius I was a military expedition into parts of European Scythia by Darius I, the king of the Achaemenid Empire, in 513 BC.
Were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states.
4.1.Greek reconquests after the Second Persian Invasion of Greece
The final defeat of the Persians at Mycale during the Second Persian Invasion of Greece encouraged the Greek cities of Asia to revolt, and the Persians lost all of their territories in Europe.
January 478 BC: The final defeat of the Persians at Mycale, led by the Greek general Leotychides and the Spartan general Xanthippus, encouraged the Greek cities of Asia to revolt. This resulted in the Persians losing all of their territories in Europe, allowing Macedonia to regain its independence under King Alexander I.
Conquests by Spartokos I, ruler of Bosporan Kingdom.
January 437 BC: According to Greek historian Diodorus Siculus (XII. 31) the region was governed between 480 and 438 BC by a line of kings called the Archaeanactidae, probably a ruling family, usurped by a tyrant called Spartocus (438-431 BC), who was a Thracian.
Expansion of Macedonia under King Philip II.
January 338 BC: The year 339 BC proved a culminating year for the Second Scythian Kingdom, and the beginning of its decline. The war with Philip II of Macedon ended in a victory for Philip (the father of Alexander the Great).
Were a series of conquests that were carried out by Alexander III of Macedon (known as Alexander "The Great") from 336 BC to 323 BC. Alexander conquered the Persian Empire and also expanded his kingdom into the Indian Subcontinent.
7.1.Alexander's War in Persia
Were the military campaigns by Alexander the Great King of Macedon in the territories of the Achaemenid Empire.
7.1.1.Campaigns of Alexander the Great against the Achaemenid rebel Satrapies
Were a series of military campaign by Alexander the Great, King of Macedon, in the regions of the Achaemenid Empire that had become de facto independent after the collapse of the Empire.
November 329 BC: Territories north of the Jaxartes River are conquered by the Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 325 BC: Modern Hund, Pakistan, conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
7.2.Alexander's War in India
After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the Indian subcontinent.
June 326 BC: Battle of Hydaspes River against Purava king Porus. Alexander the Great annexed large areas of the Punjab region from the Hydaspes to the Hyphasis (the entire Purava reign of Porus).
March 325 BC: Mallian Campaign against the Malli of the Punjab. Alexander was defining the eastern limit of his power by marching down-river along the Hydaspes to the Acesines (now the Jhelum and Chenab), but the Malli and the Oxydraci combined to refuse passage through their territory. Alexander sought to prevent their forces meeting, and made a swift campaign against them which successfully pacified the region between the two rivers.
Military campaign of Chandragupta Maurya, founder of the Mauryan Empire.
January 316 BC: Expansion of the Magadha Kingdom until 317 BC.
Was a war of succession that happened in the Bosporan Kingdom somewhere between 311 and 308 BCE and lasted for about a year.
January 309 BC: In 310-309 BC King Aripharnes took part in the Bosporan Civil War.
Conquests by Prytanis, ruler of Bosporan Kingdom.
January 309 BC: Conquests of Paerisades I (349 - 310 BC).
January 686 BC: The Kabul valley, located in present-day Afghanistan, was under the rule of the Median Empire, which was a powerful ancient Iranian civilization. The Median Empire was founded by King Deioces and later ruled by King Cyaxares.
January 652 BC: Scythian domination on Media.
January 632 BC: In 633 BC Tomis, a greek polis in the West Coast of ancient Pontos, was founded by Miletus.
January 629 BC: Scymnus of Chios (ca 110 BC), dated its founding to 630 BC, while Eusebius of Caesarea set it during the time of the 33rd Olympic Games (657 - 656 BC).
January 600 BC: Orgame was founded around the VII century BC
January 599 BC: The Kingdom of Kapisa was a state located in what is now Afghanistan during the late 1st millennium AD.
January 599 BC: Foundation of Teodosia along the Black Sea.
January 599 BC: Settlers of Miletus found Tyras near the river Dnestr.
January 599 BC: Milesian foundation of Olbia Pontica along the Dnepr (Ukraine).
January 599 BC: Foundation of Callatis (Mangalia, Romania) by macedonian settlers, guided by king Aminta III.
January 574 BC: Greek colony established by Miletos in 575 BC.
January 569 BC: Greek colony established by Miletos 580-570 BC.
January 569 BC: Greek colony established by Ionians ca. 580-570 BC.
January 559 BC: Greek colony established by Ionians 580-560 BC.
January 559 BC: Greek colony established by Miletos or by Samos 560-570 BC.
January 549 BC: The year of foundation of the polity of Labrys is based on peer group of similar polities in the same region (Phersu Atlas assumption).
January 540 BC: Greek colony established in the VI century BC by East Greeks.
January 539 BC: Greek colony established by Theos ca. 540 BC.
January 530 BC: Greek colony established in the VI century BC.
January 527 BC: Greek colony established by Herakleia Pontike and Delion in 528 BC.
January 499 BC: The Kingdom of Trigarta is first mentioned by sources in the V century BC.
January 430 BC: In -431, Teres and his son Sitalces, rulers of the Odrysian Kingdom, expanded their territory from the Danube in the north to the outskirts of Abdera at the Aegean Sea. Teres was a powerful king of the Odrysians, while Sitalces succeeded him and further expanded their realm.
January 399 BC: During western expansion, Ateas fought the Triballi. An area of Thrace was subjugated and levied with severe duties.
January 299 BC: In the third century BC, the Sarmatians drove the Scythians from the Pontic steppe in the Crimea, and replaced them in most of the European steppes. Settled and Hellenized, the ancient Scythians of the Black Sea constituted under the authority of King Scilurus a small kingdom between the lower Dnieper and northern Crimea.
January 199 BC: By the end of the 3rd century, the town declined economically[note 1] and accepted the overlordship of King Skilurus of Scythia.
January 38: Conquest of Aspurgus (8 BC - 37 AD).
January 70: Conquest of Cotys I (45 - 69).
Disestablishment
January 194: At the end of the 2nd century AD, King Sauromates II critically defeated the Scythians and included the Crimea into his Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus, a Roman client state.
Selected Sources
Behistun inscription, Column i, lines 9-17
Bosporan Kingdom growth map-fr. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 7 Aptril 2024 on https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bosporan_Kingdom_growth_map-fr.svg
Hansen, M. G. / Nielsen, T. H. (2004): An inventory of archaic and classic polities, Oxford University Press, p. 1394
Schwartzberg,J. E. (1992): A Historical Atlas of South Asia, Minneapolis (USA), Plate III.B.4b (p.18) and Plate XIV.1a-c (p.145).
Sen, S. N. (1999): Ancient Indian History and Civilization, New Delhi (India), pp. 116-117
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXII
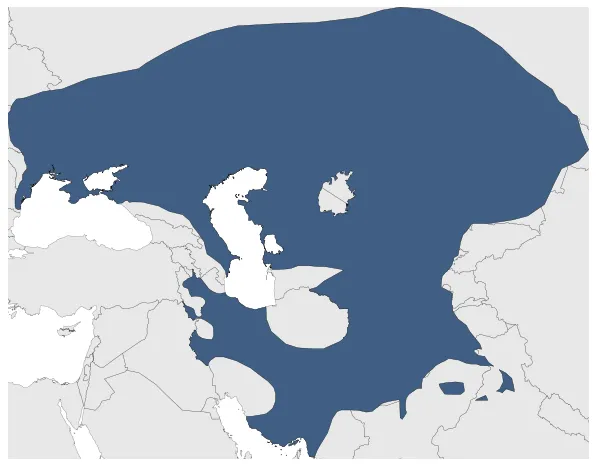
 Scythian Kingdom
Scythian Kingdom