If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Prince-Bishopric of the Holy Roman Empire.
Establishment
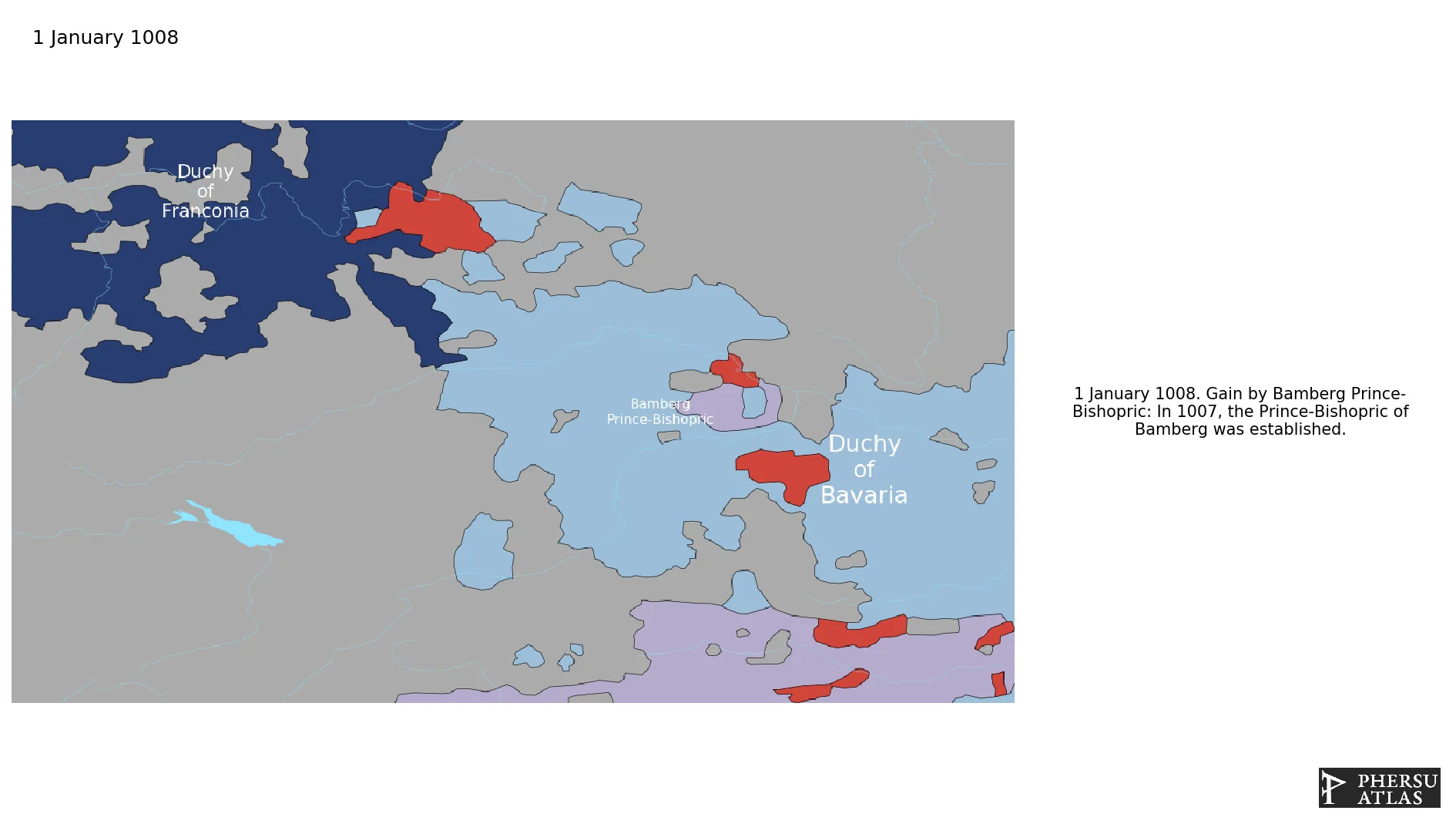
January 1008: In 1007, the Prince-Bishopric of Bamberg was established.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
1.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
1.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1241: The Mongols invaded the Holy Roman Empire without major clash of arms.The army invaded eastern Germany, and crossed the March of Moravia in April-May 1241.
June 1241: The Mongols left eastern Germany and Moravia.
1.1.2.Second Mongol Invasion of Germany
The Mongols raided eastern Austria and southern Moravia again in December 1241 and January 1242.
January 1242: The Mongols raided eastern Austria and southern Moravia again in January 1242.
February 1242: The Mongols raided eastern Austria and southern Moravia again in January 1242. After the raid, the Mongols left these regions.
Were a series of raids by the Ottomans in the Friuli region during the 15th and 16th centuries, in the context of tensions between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire.
January 1416: Ottoman incursion in Friuli of 1415.
February 1416: Ottoman incursion in Friuli of 1415. The Ottomans left the region after the incursion.
January 1464: Ottoman incursion in Friuli of 1463.
February 1464: Ottoman incursion in Friuli of 1463. The Ottomans left the region after the incursion.
Were two disputes between the Free Imperial City of Nuremberg and the Principality of Brandenburg-Ansbach.
3.1.Second Margrave War
Was a dispute between the Free Imperial City of Nuremberg and the Principality of Brandenburg-Ansbach.
May 1552: On May 19, 1552, the Prince-Bishop of Bamberg, Georg von Schaumburg, had to admit defeat to Albert Alcibiades, Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach, during the military occupation of Bayreuth.
January 1553: Capture Forchheim Fortress, occupied Forchheim and threatened the episcopal city of Bamberg.
January 1554: In 1553, troops from Nuremberg, Würzburg, and Bamberg, led by the respective rulers Albrecht Alcibiades, Julius Echter von Mespelbrunn, and Veit von Würzburg, recaptured territories that had been seized during the Second Margrave War. The conflict was part of the larger struggle for power and influence in the region between various German states and the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1554: In 1553, troops from Nuremberg, led by Margrave Albert Alcibiades of Brandenburg-Kulmbach, Würzburg, led by Prince-Bishop Melchior Zobel von Giebelstadt, and Bamberg, under the rule of Prince-Bishop Veit von Würzburg, recaptured parts of their possessions in Forchheim from the Protestant forces during the Second Margrave War.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
4.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
4.1.1.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
April 1632: On April 15, during the Battle of Rain am Lech, east of Donauwörth, the Swedish troops under Gustavus Adolphus defeated the Imperial forces commanded by Tilly.
March 1633: Bernhard von Sachsen-Weimar, as the German imperial prince, was able to achieve a leading position. He occupied Bamberg in February 1633.
4.1.2.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
4.1.2.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1637: After the death of Swedish King Ferdinand II, his son and successor Ferdinand III brought the Swedish troops back to Pomerania, leaving the territories occupied by Sweden in Germany.
June 1648: In May 1648, there was the last major field battle of the Thirty Years' War between French-Swedish and Imperial-Bavarian armies near Augsburg.
4.1.3.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
October 1648: With the Peace of Westphalia Sweden received Western Pomerania (henceforth Swedish Pomerania), Wismar, and the Prince-Bishoprics of Bremen and Verden as hereditary fiefs. Sweden evacuated the remnant territories it had occupied in the Holy Roman Empire.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1803: The city and bishopric of Bamberg were promised to the Electorate of Bavaria as compensation for the loss of the Palatinate to France in the Treaty of Lunéville. Even before the final determination of borders in the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss (Imperial Recess) of 1803, Bavaria began to militarily occupy the territory of the bishopric on September 2, 1802, and declared the area a Bavarian province on November 29, definitively.
January 1009: In 1007, the imperial county of Mortenau passed to the diocese of Bamberg.
January 1201: Since the bishops of Bamberg could not personally exercise their rights in the county of Ortenau, which was far from Bamberg, they awarded the county to the dukes of Zähringen.
January 1227: Establishment of the Speckfeld County.
January 1250: After the death of the first Meranian Duke in 1159, his son Konrad III. was his successor. He is only mentioned as Duke of Merania, thus Croatia and Dalmatia had disappeared from the Duchy.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
January 1379: Landgrave Johann von Leuchtenberg acquired the feudal rights over the Hofmark from Bamberg's Bishop Lamprecht for 5,000 gold guilders and founded the new town of Osterhofen in 1378 near the former market town of Osterhofen.
January 1391: Truhendingen was sold to the Bishopric Bamberg.
January 1501: The town of Vilseck came back to the Bamberg Bishopric and was the seat of a Bamberg Obervogtamt.
January 1548: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of the Reformation.
January 1676: In 1675, the Bishopric of Bamberg relinquished sovereignty over the properties in Carinthia and sold them to the Habsburgs.
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
January 1803: The city and bishopric of Bamberg were promised to the Electorate of Bavaria as compensation for the loss of the Palatinate to France in the Treaty of Lunéville. Even before the final determination of borders in the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss (Imperial Recess) of 1803, Bavaria began to militarily occupy the territory of the bishopric on September 2, 1802, and declared the area a Bavarian province on November 29, definitively.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 38-39
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Giorgiutti, M. Le incursioni turche in Friuli nel secolo XV. RegioneStoria. Retrieved on 30 March 2024 on https://www.regionestoriafvg.eu/tematiche/tema/474/Le-incursioni-turche-in-Friuli-nel-secolo-XV
Lazzarin, R. (22 november 2020): INCURSIONI TURCHE. Mercurio. https://mer-curio.com/2020/11/22/incursioni-turche/
Schmidt, G. (2006): Der Dreißigjährige Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 65
Spindler, M. (2017): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, Munich (Germany), p. 266
Strakosh-Grassmann, G. (1893): Der Einfall der Mongolen in Mitteleuropa in den Jahren 1241 und 1242, Innsbruck (Austria), pp. 53-67
Westfälischer Friede - Vertrag von Osnabrück, https://de.wikisource.org/wiki/Westf%C3%A4lischer_Friede_%E2%80%93_Vertrag_von_Osnabr%C3%BCck

 Bamberg Prince-Bishopric
Bamberg Prince-Bishopric