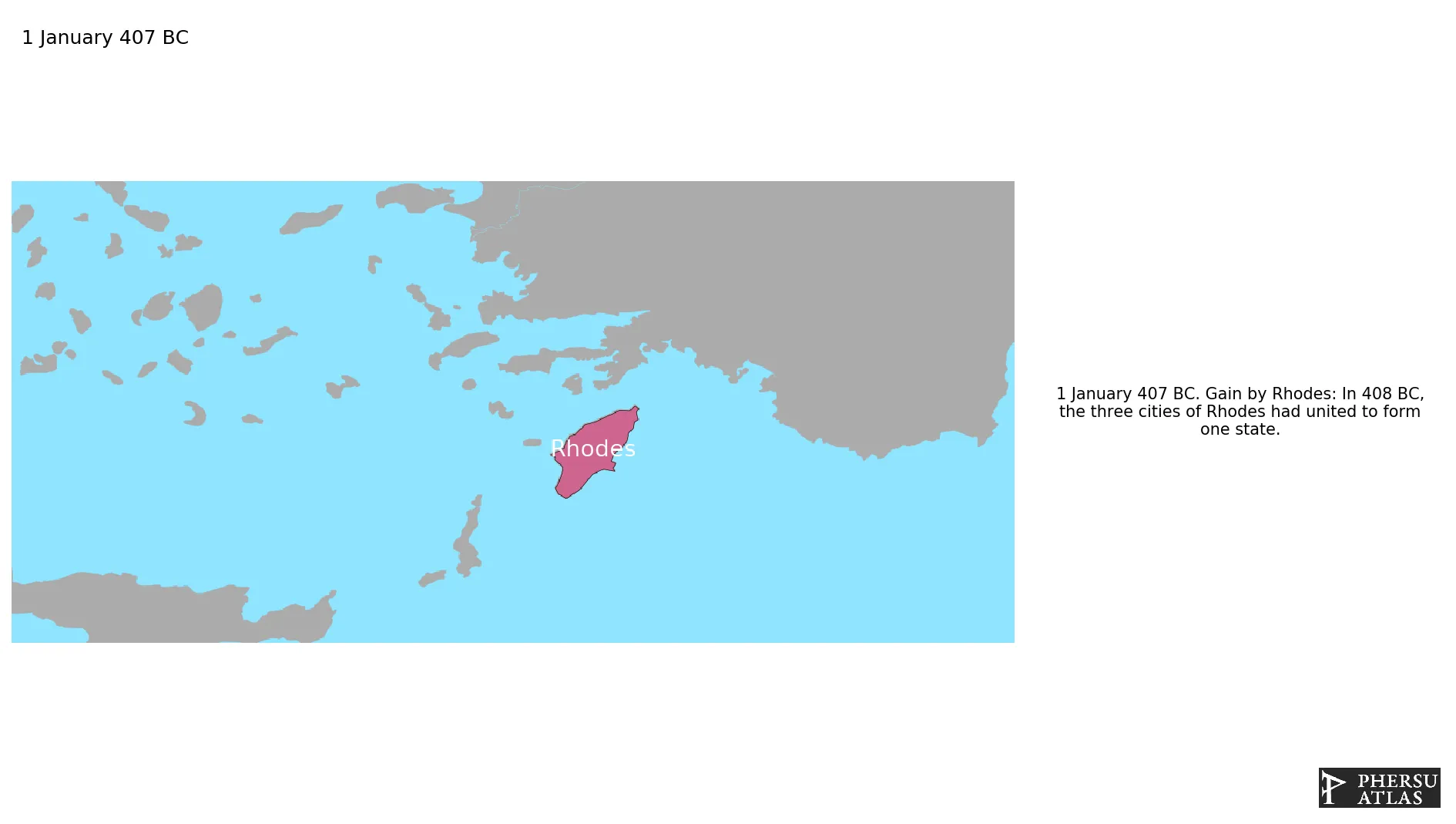
Data
Name: rhodes
Type: Cluster
Start: 407 BC
End: 74 AD
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 rhodes
rhodes
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Peloponnesian War
Was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world.
1.1.Second Phase - Deceleian War
Was the second phase of the Peloponnesian War, where Sparta allied with Persia against Athens, which capitulated and lost its empire.
2. Creation of the Second Athenian League
Creation of the Second Athenian League (a league of ancient Greece).
3. Wars of Alexander the Great
Were a series of conquests that were carried out by Alexander III of Macedon (known as Alexander "The Great") from 336 BC to 323 BC. Alexander conquered the Persian Empire and also expanded his kingdom into the Indian Subcontinent.
Were the military campaigns by Alexander the Great King of Macedon in the territories of the Achaemenid Empire.
3.1.1.Conquest of the Achaemenid Empire
Was a military campaign by Alexander the Great King of Macedon in Asia that resulted in the conquest of the Achaemenid Empire.
4. Cretan War (204-199 BC)
Was fought by King Philip V of Macedon, the Aetolian League, many Cretan cities (of which Olous and Hierapytna were the most important) and Spartan pirates against the forces of Rhodes and later Attalus I of Pergamum, Byzantium, Cyzicus, Athens, and Knossos.
5. Macedonian Wars
Were a seris of conflicts between the Roman Republic and Antigonid Macedonia over control of Greece and the eastern Mediterranean Basin. .
Was a war fought by Rome, allied with the Kingdoms of Pergamons and Rhodes, against Antigonid Macedonia.
Was a war fought by Rome against Antigonid Macedonia. The war was won by Rome, and Macedonia was divided in four client states of Rome.
6. Roman-Seleucid War
Was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting ended with a clear Roman victory. In the Treaty of Apamea, the Seleucids were forced to give up Asia Minor, which fell to Roman allies.
Was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman-Seleucid War.