If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Were the French possessions in the Indian Subcontinent. For most of its existence the colony included several forts and cities scattered through the Indian Subcontinent. At its height, France controlled most of the central-eastern Indian coast.
Establishment
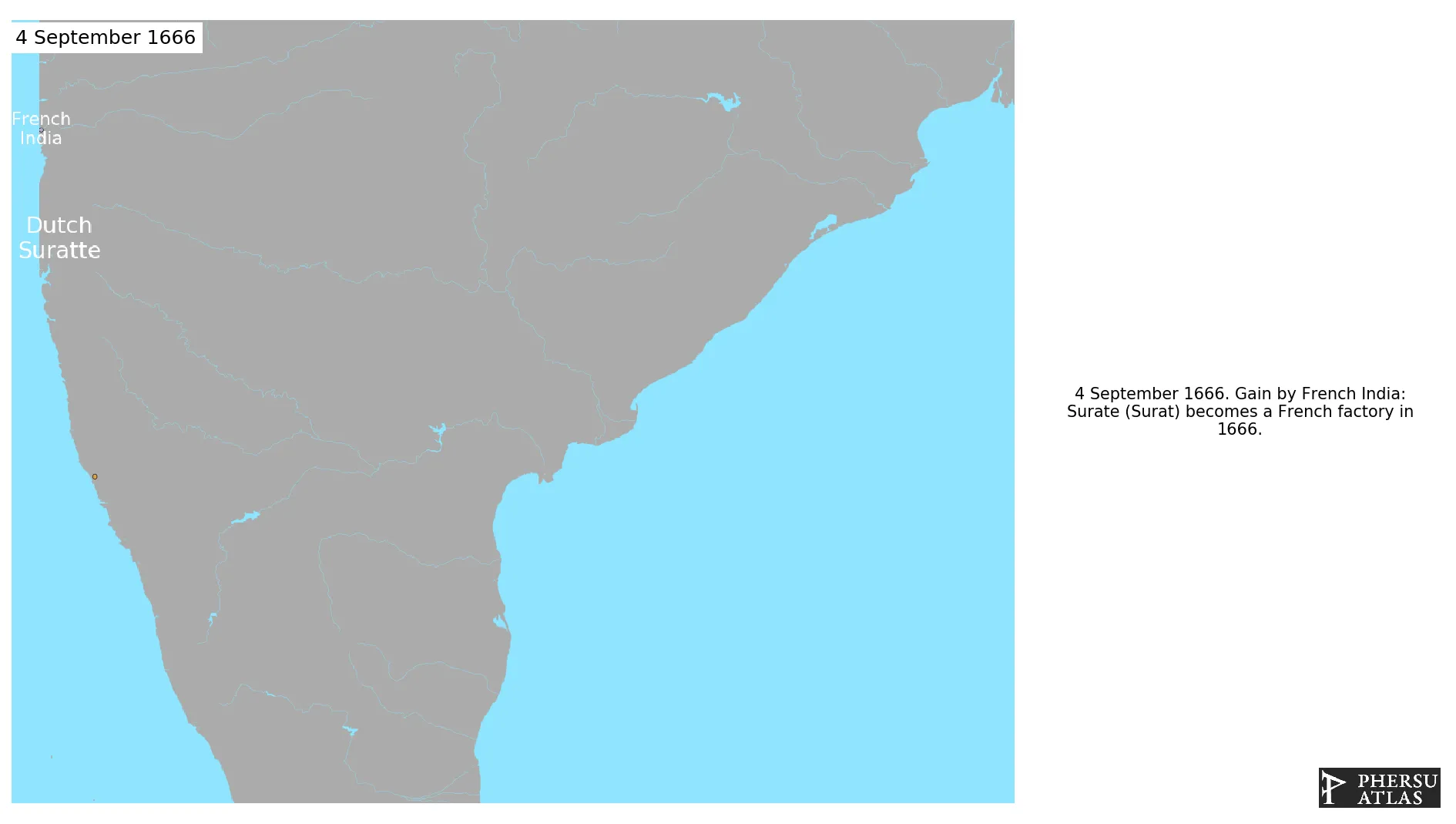
September 1666: Surate (Surat) becomes a French factory in 1666.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
1.1.Nine Years' War
Was a conflict between France and the Grand Alliance, a coalition including the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, and Savoy. It is considered the first war that saw fighting globally because battles occured in Europe, America, Africa and India.
1.1.1.Asia and the Caribbean (Nine Years' War)
Were battles that took place in Asia and in the Caribbean during the Nine Years' War.
September 1693: In 1693 the Dutch launched an expedition against their French commercial rivals at Pondichéry on the south-eastern coast of India; the small garrison under François Martin was overwhelmed and surrendered on 6 September.
1.1.2.Peace of Ryswick
Were a series of treaties that ended the Nine Years' War.
September 1697: The Dutch handed back Pondichéry in India to the french.
Expansion during the rule of Aurangzeb in the Mughal Empire.
April 1705: In March 1705, Mazulipatam was taken over by the Mughal Empire.
Expansion during the rule of Shahu I in the Maratha Empire.
January 1729: Yanaon (Yanam) was a French colony in India. It was abandoned from 1728 to 1731 during a period of conflict between the French and the Mughal Empire.
Was a European conflict caused by the succession to the Habsburg Domains. Maria Theresa succeeded her father Charles VI, and the opposition to female inheritance of the throne was a pretext for starting a war. It was a global conflict that saw fight in Europe, Asia, America and Africa.
4.1.Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
October 1748: France accepted the re-establishment of the status quo in the overseas territories. Madras given back to the British.
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
5.1.Carnatic Wars
The Carnatic Wars were a series of military conflicts in the middle of the 18th century in India's coastal Carnatic region. As a result of these military contests, the British East India Company established its dominance among the European trading companies within India.
5.1.1.First Carnatic War
Was the Indian theatre of the War of the Austrian Succession and the first of a series of Carnatic Wars. In this conflict the British and French East India Companies fought for control of their respective trading posts at Madras, Pondicherry, and Cuddalore.
5.1.2.Second Carnatic War
Was the continuation of the first Carnatic War in India despites the end of the War of the Austrian Succession in Europe.
January 1752: In 1751, however, Robert Clive led British troops to capture Arcot.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
6.1.Indian Theatre (Seven Years' War)
Was the theatre of war of the Seven Years' War in the Indian Subcontinent.
6.1.1.Third Carnatic War
The outbreak of the Seven Years' War in Europe in 1756 resulted in renewed conflict between French and British forces in India.
January 1761: British occupation of Pondichéry.
February 1761: Mahé, a French colony in India, fell to British forces led by Admiral George Pocock and Colonel William Draper on 17 Feb 1761 during the Seven Years' War. This marked the beginning of British military occupation in the region.
February 1765: Karikal was a French colonial territory in India. The territory was restored to French control on 18 Feb 1765 after being temporarily occupied by the British East India Company during the Seven Years' War. This event was significant in the history of French India and the colonial rivalry between France and Britain.
April 1765: In 1765, Pondichéry was restored to France as part of the Treaty of Paris, ending the Seven Years' War. This territory was a French colony in India, and its return was negotiated by French diplomat Louis François Armand de Vignerot du Plessis.
May 1765: French conquest of Yanaon.
May 1765: French conquest of Mahé.
June 1765: French conquest of Chandernagore.
Was the war of independence of the United States of America (at the time the Thirteen Colonies) against Great Britain.
7.1.Anglo-French War (1778-1783)
Was a war between France, allied to the United States, and Great Britain during the American Revolutionary War.
March 1779: In March 1779, during the Anglo-French War, British forces led by Admiral Edward Hughes and General James Stuart captured Mahé from the French, marking a significant victory for Great Britain in the Indian Ocean region.
January 1781: The French retook Mahé in 1780.
February 1785: In 1785, Pondichéry was restored to France as part of the Treaty of Paris. This territory had been under British control since 1761. The return of Pondichéry was negotiated by French diplomat Charles Maurice de Talleyrand and marked a significant victory for France in the region.
February 1785: Karikal was a French colonial territory in India. The territory was restored to French control on 26 Feb 1785 as part of a treaty between the French and the British East India Company. This event was significant for the French colonial presence in India during the late 18th century.
March 1785: British conquest of Yanaon.
June 1785: Chandernagore was a French colony in India. On 27 June 1785, the territory was transferred to British control following a treaty signed between Governor-General of India Warren Hastings and French Governor-General Marquis de Bussy-Castelnau.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
8.1.French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars - Theatre of war in the overseas colonies
The theatre of war in the overseas colonies during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
June 1793: Chandernagore was a French colony in India. In 1793, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the British East India Company captured the territory.
June 1793: Karikal conquered by great britain.
July 1793: Yanaon (Yanam) conquered by great britain.
July 1793: Mahé, a French colony, was occupied by British forces on 16 July 1793.
August 1793: In 1793, Pondichéry was occupied by the British military. This event was part of the larger conflict between Great Britain and France during the French Revolutionary Wars. Pondichéry was a French colonial territory in India, and its capture by the British was a significant blow to French influence in the region.
December 1816: Pondichéry and Chandernagore restored to France.
January 1817: Karikal was a French colonial territory in India. The territory was restored to French control on January 14, 1817, after being temporarily occupied by the British during the Napoleonic Wars.
April 1817: Yanaon was given back to the French on 12 Apr 1817.
8.1.1.French India (Treaty of Amiens)
Restoration of French rule in French India according to the Treaty of Amiens.
8.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
8.2.1.Treaty of Amiens
Was a treaty between France and Great Britain that ended the War of the Second Coalition.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
9.1.World War II (All other Vichy France Colonies)
Refers to the events that happened in French Colonies that decided to be loyal to the German puppet state of Vichy France.
June 1940: Administration of French India loyal to "Vichy" France.
June 1940: Chandernagore switched allegiance to Free France.
September 1940: The administration of French India is loyal to "Free" France.
December 1669: From 9 December 1669 Mazulipatam (Masulipatnam/Machilipatnam) was home to a French factory established by the French East India Company.
February 1673: Pondichéry (Pondicherry) became a French possession.
May 1674: In April 1674 the French factory of Mazulipatam is lost to the Golconda Sultanate.
January 1688: In 1687, Mazulipatam was captured by the French under the leadership of Governor General François Martin.
May 1690: In 1690, Chandernagore (Chandernagor) became a French possession in India.
January 1699: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Dannemarksnagore in Bengal.
April 1699: Dutch occupation of Chandernagore.
September 1699: Dutch occupation of Chandernagore.
January 1721: Mazulipatam becomes a French possession.
April 1721: From 2 Apr 1721 to Feb 1725, Mahé was under French control.
January 1722: The Baroda State was founded in 1721, when the Maratha general Pilaji Gaekwad conquered Songadh from the Mughals.
January 1724: Yanaon (Yanam) became a French possession.
January 1725: The fourth Nizam Salabat Jang, a son of the Nizam al Mulk, who was indebted for his elevation to the throne to the French East India Company, granted the district of Kondavid (in the Guntur district) to the French in return for their services, and soon afterwards granted the other circars as well.
January 1725: Hyderabad State was founded by Mir Qamar-ud-din Khan who was the governor of Deccan under the Mughals from 1713 to 1721.
March 1725: In 1725, Mahé (Mahe) was left without a ruling entity after the French relinquished control.
January 1726: Mahé restored to France.
January 1732: Yanaon (Yanam) is re-occupied by the French.
January 1735: Kakinada was an important textile trading post after the loss of Draksharama and Palakol.
January 1742: In 1741, Governor Joseph François Dupleix arrived in India, aiming to establish a French territorial empire. Commanded by Marquis Bussy-Castelnau, Dupleix's forces gained control over the area from Hyderabad to Cape Comorin.
January 1750: After 1749, the British East India Company took possession of São Tomé de Meliapore.
June 1750: British forces occupied Mazulipatam in May-Jul 1750.
August 1750: British forces occupied Mazulipatam in May-Jul 1750.
December 1754: The Governor of French India, Charles Godeheu, signed a treaty with the British on December 26, 1754, agreeing to evacuate all the territories in India conquered by his predecessor, Joseph Dupleix. The British also agreed to leave the territories of French India that they had occupied.
June 1757: British Lieutenant Colonel Robert Clive defeated Indian and French forces in the Battle of Plassey.
January 1759: The British East India Company, seeking an overland connection between its holdings at Madras and Bengal, sought to gain access to the Northern Circars, a series of coastal territories held by the French until 1758, when they were ousted with British military support.
July 1778: Chandernagore was a French colony in India. The military occupation by Great Britain in 1778 was part of the Anglo-French War. The British forces were led by Admiral Sir Edward Hughes and General Sir Hector Munro. The occupation lasted until 1783.
August 1778: Karikal conquered by great britain.
October 1778: British occupation of Pondichéry.
May 1950: Chandernagore (Chandernagor) is transferred from France to India (ratified 11 Apr 1952).
June 1954: Yanaon is taken by Indian military police.
July 1954: Mahé taken by pro-Indian groups.
November 1954: Remaining territories (Pondichéry and Karikal) transferred to india de facto.
Disestablishment
June 1954: Yanaon is taken by Indian military police.
July 1954: Mahé taken by pro-Indian groups.
November 1954: Remaining territories (Pondichéry and Karikal) transferred to india de facto.
Selected Sources
Larsen, K. (1940): Guvernører, Residenter, Kommadanter og Chefer samt enkele andre fremtradende personer i de tidligere Danske Tropokolonier, Copenhagen (Denmark), p. 18
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.235-237
 French India
French India