.svg.png.webp)
Data
Name: German Empire
Type: Polity
Start: 1871 AD
End: 1918 AD
Nation: germany
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
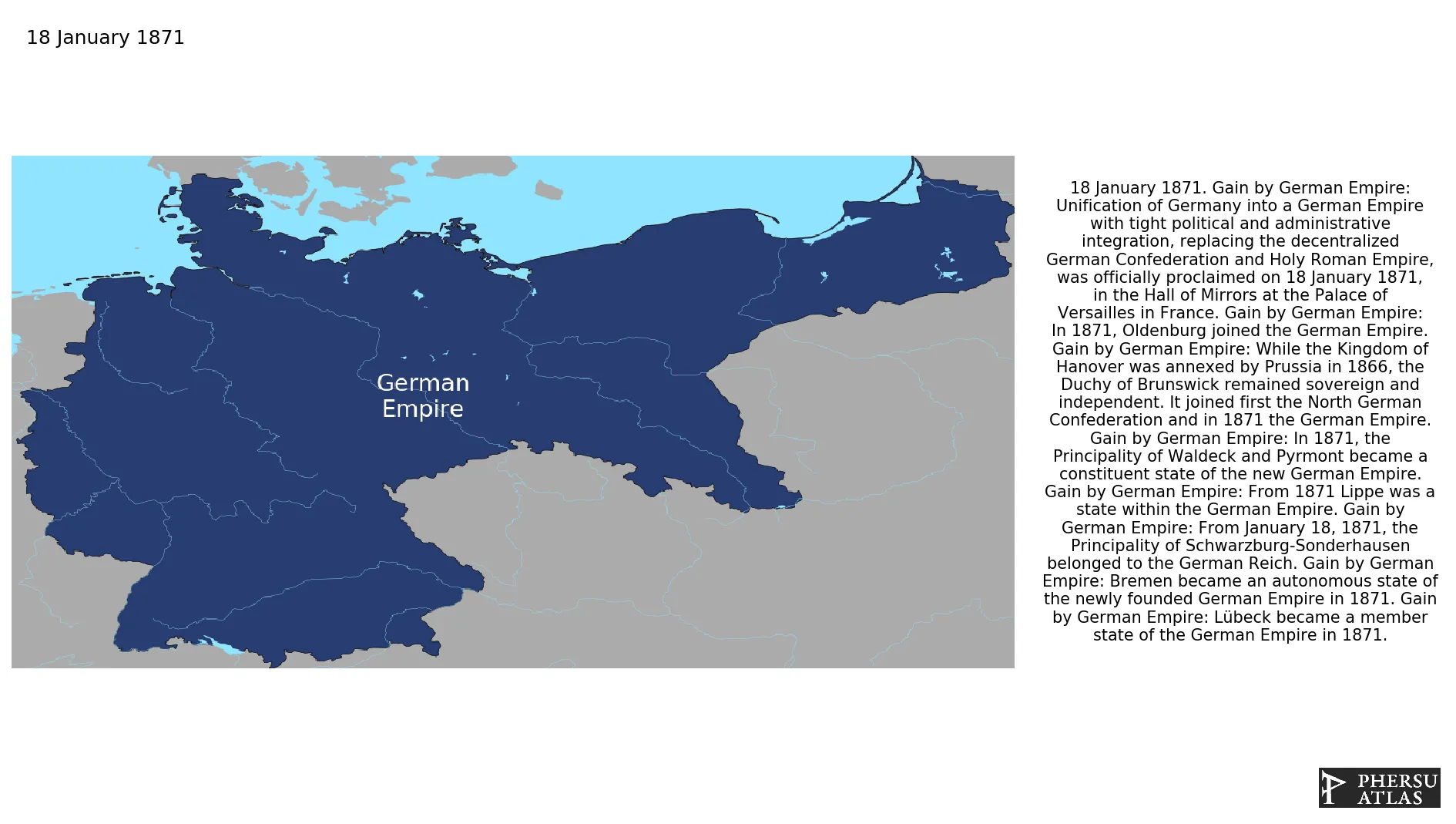
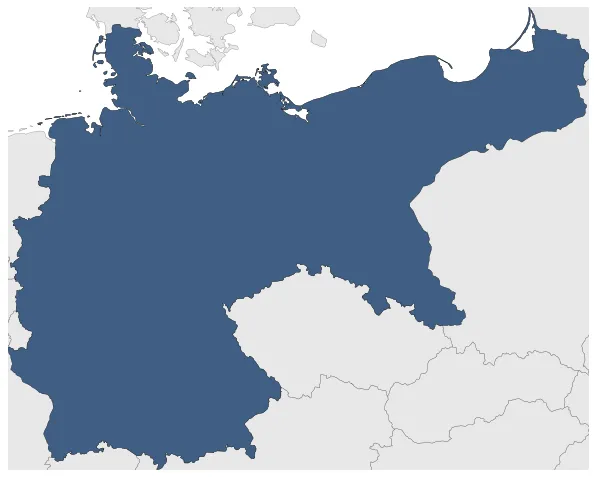
 German Empire
German Empire
This article is about the specific polity German Empire and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
The German Empire was created in 1871 after the defeat of France in the Franco-Prussian War. The alliance of states that defeated France merged to form the new country. The German Empire did also acquire Alsace-Lorraine from France. The Empire absorbed most of the German-speaking countries in Europe, but not Austria-Hungary. The dominant power of the new state was Prussia, whose King became the first Emperor of the German Empire. It was the first unitary form of the German state. The German Empire ended after its defeat in World War I.
Summary
The German Empire was established in 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War, when Otto von Bismarck united the German states under Prussian leadership. Bismarck became the first Chancellor of the new German Empire, with Wilhelm I as the first German Emperor.
Under Bismarck's leadership, the German Empire rapidly industrialized and became a major economic and military power in Europe. Bismarck pursued a conservative domestic policy, suppressing socialist and Catholic political movements. He also skillfully maneuvered Germany's foreign policy, maintaining a balance of power in Europe.
After Bismarck's dismissal in 1890, Germany's foreign policy became more assertive and aggressive under Kaiser Wilhelm II. Germany embarked on a program of naval expansion and colonial acquisition, which brought it into conflict with the other European powers. This contributed to the outbreak of World War I in 1914.
During World War I, the German Empire suffered devastating losses and was ultimately defeated. The German monarchy collapsed in 1918 with the abdication of Wilhelm II, and the Weimar Republic was established in its place. The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh terms on Germany, including the loss of territory, restrictions on its military, and heavy reparations payments. This laid the groundwork for future resentment and instability in Germany.
Overall, the German Empire was a relatively short-lived but highly influential era in German history. It saw Germany emerge as a major economic and military power, but also sowed the seeds for future conflicts that would shape the 20th century.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. German Unification Wars
Were a series of wars that resulted in the creation of the German Empire under Prussian leadership in 1871.
Was a war that saw the Second French Empire fight against an alliance of German states led by the Kingdom of Prussia. The war was caused by the struggle over dominance in continental Europe between Prussia and France. The German states were victorious and in 1871 merged to form the German Empire. France was occupied and forced to cede Alsace-Lorraine to Germany.
1.1.1.Unification of Germany (1871)
Was the unification of 25 German states into the German Empire under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
1.1.2.Cession of Alsace-Lorraine
According to the peace treaty signed in Frankfurt on 10 May 1871, at the end of the Franco-Prussian War, the region of Alsace-Lorraine was ceded by France to Germany.
2. World War I
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
Was the theatre of war in western Europe during World War I.
2.1.1.German Offensive in Flanders (World War I)
Was the German offensive in the Flanders at the beginning of World War I.
Was the theatre of war in eastern Europe during World War I.
2.2.1.Russian invasion of East Prussia
Was the Russian invasion of East Prussia in the early phases of World War I.
2.2.2.Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes
Was the northern part of the Central Powers' offensive on the Eastern Front in the winter of 1915.
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
2.3.1.Aftermath of World War I in Poland
Events that happened shortly after the end of World War I in Poland.
Was a civil conflict in the German Empire at the end of the First World War that resulted in the replacement of the German federal constitutional monarchy with a democratic parliamentary republic.
A series of short-lived states were proclaimed in various territories of the German Empire in the aftermath of World War I.
2.3.1.2.Republic proclamation in Germany
Proclamation of a republic in Germany on 9 November 1918.