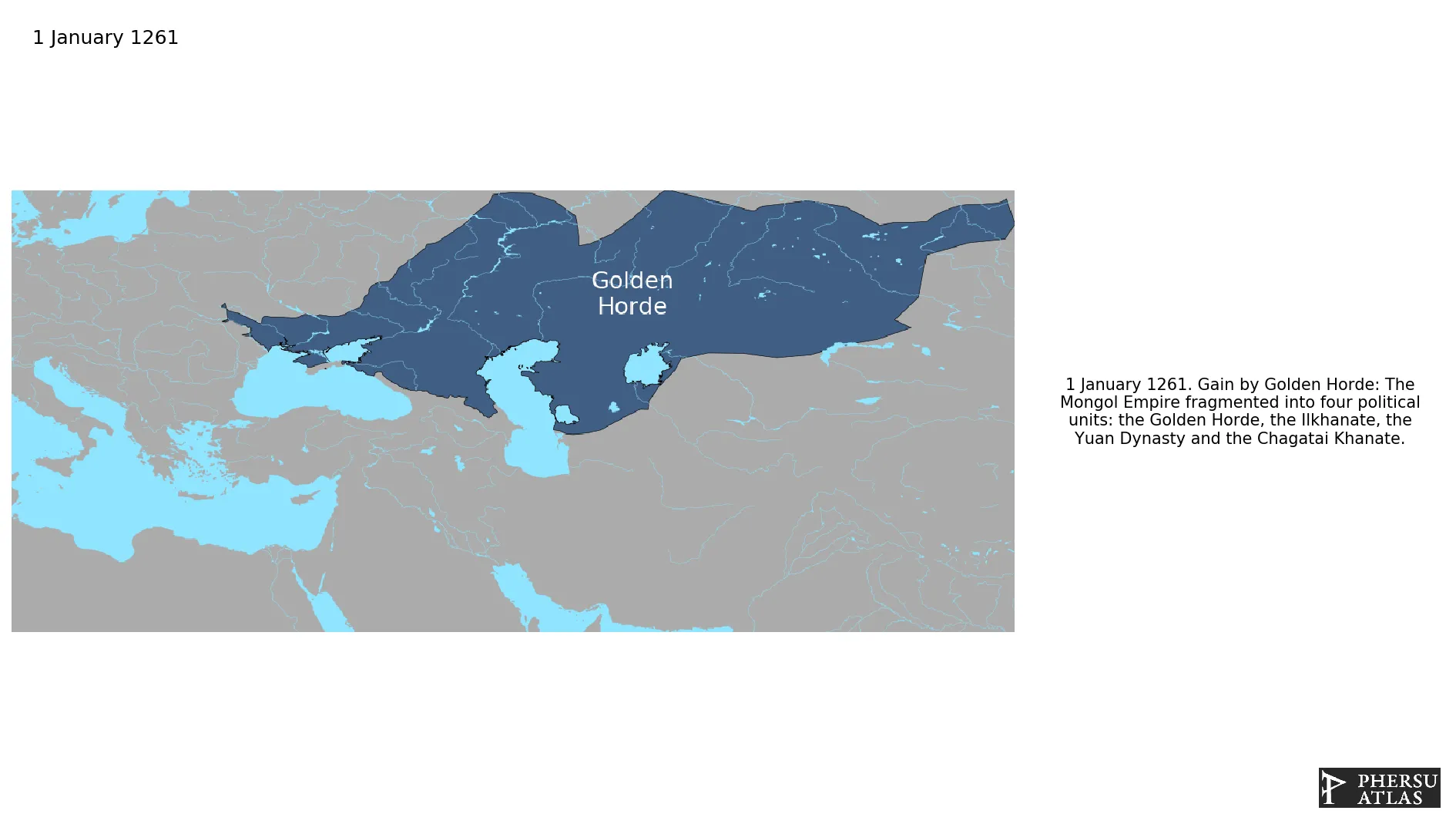
This article is about the specific polity Golden Horde and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the successor state of the Mongol Empire in its territories of Europe and of the Pontic Steppe. It fragmented in several successor states, most notably the Great Horde and the Crimean Khanate.
Establishment
January 1261: The Mongol Empire fragmented into four political units: the Golden Horde, the Ilkhanate, the Yuan Dynasty and the Chagatai Khanate.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars between the successor states of the Mongol Empire.
1.1.Toluid Civil War
Was a war of succession over the Mongol Empire fought between Kublai Khan and his younger brother, Ariq Böke, from 1260 to 1264.
1.1.1.Division of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire fragmented into four successor states at the beginning of the Toluid Civil War.
1.2.Berke-Hulagu war
Was a war between two successor states of the Mongol Empire, the Ilkhanate and the Golden Horde, that took place mainly in the Caucasus, a border area between the two states.
January 1263: Ilkhan Hulegu marched northwards through the pass of Derbend. On the banks of the Terek, he was ambushed by an army of the Golden Horde under Nogai, and his army was defeated at the Battle of the Terek River.
February 1263: After Ilkhan Hulegu was defeated at the Battle of the Terek River, his army left the area.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
2.1.Mongol Invasions of Poland
Were a series of Mongol raids in Poland.
January 1287: In 1286, Talabuga, a Mongol general, and Nogai, a prominent Mongol leader, launched a devastating attack on Poland as part of the Golden Horde's expansionist campaigns. The invasion resulted in widespread destruction and plundering of the Polish territory.
February 1287: In 1286, Mongol generals Talabuga and Nogai led an attack on Poland, causing widespread devastation in the country. This event marked a period of conflict between the Mongol Empire and the Kingdom of Poland.
2.1.1.Third Mongol Invasion of Poland
The third Mongol invasion of Poland was carried out by Nogai Khan and Talabuga in 1287-1288. As in the second invasion, its purpose was to loot Lesser Poland.
December 1287: The third Mongol invasion of Poland was carried out by Nogai Khan and Talabuga in 1287.1288. Its purpose was to loot Lesser Poland.
January 1288: Mongol forces leave Poland after looting the region.
2.2.Mongol Invasions of Hungary
Were a series of Mongol raids in Hungary.
2.2.1.Second Mongol Invasion of Hungary
Was a Mongol raid in Hungary.
January 1286: Kingdom of Hungary raided by the Golden Horde.
February 1286: The Golden Horde leaves the Kingdom of Hungary.
2.3.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
2.3.1.Third Mongol Invasion of Germany
The Mongols raided the March of Brandenburg.
January 1341: In 1340, the Golden Horde, led by Khan Jani Beg, raided the March of Brandenburg.
February 1341: End of Mongol raid in Brandenburg.
2.4.Mongol Invasions of Lithuania
Was a Mongol raid in Lithuania.
January 1276: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
February 1276: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
January 1280: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
February 1280: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
January 1326: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
February 1326: Mongols raided Lithuania in 1275, 1279 and 1325.
2.5.Invasion of Thrace
Was a Mongol invasion of Byzantine Thrace.
January 1264: The Mongol invasion of Byzantine Thrace in 1263 was led by Berke Khan of the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate in Eastern Europe. The invasion was part of the wider Mongol conquests in the region, with the goal of expanding Mongol influence and control.
February 1264: The Mongol invasion of Byzantine Thrace in 1264 was led by the Mongol general Nogai Khan, who was a prominent military leader in the Golden Horde. The invasion resulted in the territory of Thrace falling under the control of the Byzantine Empire.
Expansion during the rule of Gediminas in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
January 1341: Expansion of Lithuania by 1340.
Were several wars fought in the years 1340-1392 over the succession in the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia.
April 1341: During the winter of 1340-1341, the Golden Horde (probably with Lithuanian help) attacked Poland and reached Lublin as a result of diminished tribute from the principality to the Mongol khan. The raid weakened Polish influence in the principality.
May 1341: During the winter of 1340-1341, the Golden Horde (probably with Lithuanian help) attacked Poland and reached Lublin as a result of diminished tribute from the principality to the Mongol khan. The raid weakened Polish influence in the principality.
Expansion during the rule of Algirdas in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
December 1363: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led by Grand Duke Algirdas and his brother Kęstutis, launched a successful campaign against the Golden Horde in 1363. The Battle of Blue Waters resulted in the capture of Kiev and Podolia, expanding the territory of the Grand Duchy.
Military campaigns of Timur (or Tamerlane), a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia.
January 1382: Tamerlan ruled over much of Persian Khorasan by 1381.
6.1.Tokhtamysh-Timur war
Was a war between the Golden Horde and the Timurid Empire.
6.1.1.Timur's invasions of Georgia
Was the military invasion of Georgia by the Timurid Empire.
January 1386: After having overrun Azerbaijan and Kars, Timur marched into Georgia.
November 1386: Tamerlan occupied Tbilisi and captured the Georgian king Bagrat V.
June 1387: When Timur was informed that Tokhtamysh, Khan of the Golden Horde, was approaching Iran, he temporarily withdrew from the territories he had occupied in Georgia.
Was a series of wars fought between the Grand Duchy of Moscow and the Khanate of Kazan from 1439, until Kazan was finally conquered by the Tsardom of Russia under Ivan the Terrible in 1552.
7.1.Wars of Vasily II
Russian military campaign against the Khanate of Kazan by Vasily II.
January 1440: In 1439, a year after the khanate's foundation, the very first khan of Kazan, Ulugh Muhammad, advanced on Moscow with a large army. Vasily II of Moscow fled from his capital across the Volga River.
January 1440: Tatars devastated the outskirts of Moscow for 10 days and on their way back to Kazan burned Kolomna. They also took many captives.
January 1446: Vasily II of Moscow mustered an army and defeated the Tatars near Murom and Gorokhovets.
January 1446: Khan Maxmut took the strategic fortress of Nizhny Novgorod and invaded Muscovy.
January 1285: In 1284, Saqchi, a town in Bulgaria, was conquered by the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate. As a result of the invasion, coins were minted in the name of the ruling Khan, marking the town's submission to Mongol rule.
January 1300: Chaka reigned as tsar of Bulgaria from 1299 to 1300. Chaka was the son of the Mongol leader Nogai Khan.
January 1301: Establishment of Zichia.
January 1301: In 1300, Theodore Svetoslav of Bulgaria took advantage of a civil war in the Golden Horde, overthrew Chaka (the son of the Mongol leader Nogai Khan), and presented his head to the Mongol khan Toqta (who was at war with Chaka). This brought an end to Mongol interference in Bulgarian domestic affairs and secured Southern Bessarabia as far as Bolgrad to Bulgaria.
January 1301: The 14th century newly established Avar Khanate managed maintain independence from the Mongols.
January 1309: In 1308, Caffa was plundered by the Mongols.
January 1311: Vosporo (today's Kerč) was a Genoese colony since 1310.
January 1319: The Golden Horde, led by Uzbeg Khan, invaded the Ilkhanate under Abu Sa'id in 1318. The Ilkhanate was a Mongol khanate established in Persia, while the Golden Horde was a Mongol khanate in Russia and Eastern Europe. Abu Sa'id was the last ruler of the Ilkhanate.
February 1319: The Golden Horde, led by Uzbeg Khan, invaded the Ilkhanate under Abu Sa'id in 1318. The Ilkhanate was a Mongol khanate established in Persia, while the Golden Horde was a Mongol khanate in Russia. Abu Sa'id was the last ruler of the Ilkhanate, facing internal strife and external threats during his reign.
January 1320: Öz Beg was the ruler of the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate in Eastern Europe. Thrace was a region in southeastern Europe. Bulgaria was engaged in wars against Byzantium and Serbia during this time, and Öz Beg supported them with his massive army, which exceeded 300,000 soldiers.
February 1320: Öz Beg was the khan of the Golden Horde, a Mongol state in Eastern Europe. The Byzantine Empire was facing threats from both Bulgaria and Serbia, and Öz Beg's massive army supported Bulgaria in their conflicts with Byzantium and Serbia in Thrace in 1319.
January 1325: Öz Beg was the khan of the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate in Eastern Europe. In 1324, his armies invaded Thrace, a region in southeastern Europe, and pillaged it for 40 days.
January 1325: In 1324, the Ilkhanate territory was raided by the Golden Horde, led by their ruler Ozbeg Khan. This military raid was part of the ongoing power struggles and conflicts between the Mongol successor states in the aftermath of the Mongol Empire's fragmentation.
February 1325: In 1325, the Ilkhanate territory was raided by the Golden Horde, led by the Mongol ruler Ozbeg Khan. After the raid the Golden Horde left the territory.
February 1325: Öz Beg's armies left Thrace.
January 1333: Venetian Tanais (Tana), 13C-1332.
January 1336: In the year 1335 Ilkhanate was annexed by the Golden Horde.
February 1336: End of the brieft control of the Ilkhanate by the Golden Horde.
January 1338: For 15 days in 1337, the territory of Thrace was under the control of the Golden Horde, a Mongol and Turkic khanate founded by Batu Khan, a grandson of Genghis Khan. This event marked a period of influence and power for the Golden Horde in the region.
February 1338: For 15 days in 1337, the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos besieged the city of Adrianople in Thrace, as part of his campaign to reclaim territories lost to the Bulgarian Empire. The siege ended in 1338 when the city surrendered to the Byzantine Empire.
November 1341: The Nizhny Novgorod-Suzdal principality was formed in October 1341, when the Khan of the Golden Horde, Uzbek Khan, divided the Vladimir Grand Duchy, transferring Nizhny Novgorod and Gorodets to the Suzdal Prince Konstantin Vasilyevich.
January 1347: In the 14th century, King Charles I of Hungary attempted to expand his realm and the influence of the Catholic Church eastwards after the fall of Cuman rule, and ordered a campaign under the command of Phynta de Mende (1324). In 1342 and 1345, the Hungarians were victorious in a battle against Tatar-Mongols and founded the Moldavian mark in 1346.
January 1357: Khan Jani Beg asserted Jochid dominance over the Chagatai Khanate and conquered Tabriz, ending Chobanid rule there in 1356.
January 1358: Following the assassination of Jani Beg, the Golden Horde quickly lost Azerbaijan to the Jalayir king Shaikh Uvais in 1357.
January 1360: Bogdan of Cuhea, voivode fof the Wallachians, who had fallen out with the Hungarian king, crossed the Carpathians in 1359, took control of Moldavia, and succeeded in becoming thre first independent ruler of Moldavia.
January 1362: The Sufid dynasty gained independence in Khwarazm in 1361 but their rule only lasted until 1379. The Sufids were a prominent Persian dynasty known for their contributions to art, culture, and literature in the region.
July 1365: On 19 July 1365, a Genoese force from Kaffa seized the city of Sudak.
January 1382: In 1381, the territory of Meshchera (Мещёрская) was purchased by the Grand Duchy of Moscow from local princes.
January 1393: The Grand Duchy of Moscow purchases the principalities of Murom and of Suzdal-Nizhny Novgorod from the khan of the Golden Horde.
January 1398: In 1397, the cavalry of the voivode of Moldavia Stephen, allied with the governor of Lithuania Vitold, reached without resistance23 the western bank of the lower Dnieper and the Pontic shores.
August 1399: In 1399, Grand Duke Vytautas of Lithuania and Tokhtamysh, former khan of the Golden Horde, attacked Temür Qutlugh and Edigu at the Battle of the Vorskla River. The Golden Horde emerged victorious, securing control over Kiev, Podolia, and some land in the lower Bug River basin.
January 1400: Athe lliance of the Four Oirat Tribes or Oirat Confederacy, which lasted from 1399 to 1634, was a confederation of the Oirat tribes, which marked the rise of the Western Mongols in Mongolian history.
January 1401: The Shamkhalate of Tarki originated "no later than XIV-XV centuries".
January 1401: By the 14th century the newly established Avar Khanate managed to maintain independence from the Mongols.
January 1406: The Khanate of Sibir was ruled by a dynasty originating with Taibuga in 1405 at Chimgi-Tura. Taibuga was a prominent leader of the Siberian Khanate and played a key role in expanding its territory and influence in the region.
January 1407: Timur died in 1405 and Khan Edigu took advantage to seize Khwarezm.
January 1413: The armies of the Grand Duke of Lithuania, Vitold, and his vassal, the Voivode of Moldavia, Alexander the Good, reached the Black Sea, making Yedisan a Lithuanian land.
January 1415: In 1414, Shah Rukh of the Timurids conquered Khwarezm.
January 1420: In 1419, the Republic of Genoa gained control of Tmutarakan, a strategic trading outpost on the Black Sea. The Genoese presence in the region lasted until 1482, when the territory was eventually lost to the expanding Russian Empire.
January 1421: Tabarinskoe Principality is established on the lands at the mouth of the Tabara River (modern Iska River) including Tabaryn town.
January 1426: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1425.
January 1429: Abu'l-Khayr Khan founded the Uzbek Khanate.
January 1435: Modern-day Penza region and Republic of Mordovia are annexed by Russia.
January 1446: In 1445, Ulugh Muhammad, the ruler of the Golden Horde, was murdered by his son, Mäxmüd of Kazan. Mäxmüd fled to the middle Volga region and established the Khanate of Kazan. This event marked the beginning of the Khanate of Kazan's independence from the Golden Horde.
January 1450: In 1449, Hacı I Giray seized Crimea from Sayid Ahmad I, and founded the Crimean Khanate.
January 1451: By the 1440s, a descendant of Edigu by the name of Musa bin Waqqas was ruling at Saray-Jük as an independent khan of the Nogai Horde.
January 1453: Ulugh Muhammad was a prominent ruler of the Golden Horde. His son, Qasim Khan, sought refuge in Moscow and was granted land by Vasily II, establishing the Qasim Khanate in 1452. This territory was located in the modern-day Republic of Tatarstan, Russia.
January 1454: In 1453, the territory of Kabardia, located in the North Caucasus region, gained better political organization under the leadership of the Kabardian princes. The society had a feudal social structure and had been a political entity since at least the 15th century.
January 1454: The Circassian Confederation was established between 1427 and 1453 in the region of Circassia, located in the North Caucasus. It was a union of various Circassian tribes led by local princes and nobles.
January 1467: After 1466, Mahmud bin Küchük's descendants continued to rule in Astrakhan as the khans of the Astrakhan Khanate.
January 1467: The Khanate of Astrakhan is said to have been founded 1466.
January 1467: The Great Horde was a Tatar-Mongol khanate that existed from about 1466 to 1502. It was the steppe remnant of the Golden Horde.
January 1476: An attack by Akhmat Khan (Khan of the Golden Horde 1465-81) forced Crimean Khan Meñli to flee to the Ottoman Empire.
January 1479: In 1478 the Crimean Khanate recognized Ottoman suzerainty.
Disestablishment
January 1510: Nogays move into lands vacated by Great Horde.
Selected Sources
Kopalyan, N. (2017): World Political Systems after Polarity, Taylor & Francis, p. 164
VKL-1462-ru. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A4%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BB:VKL-1462-ru.png
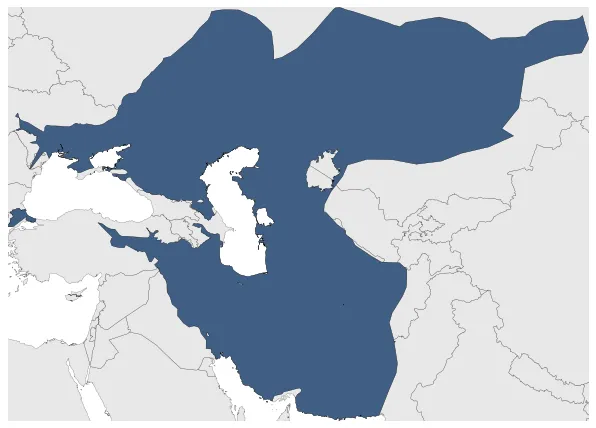
 Golden Horde
Golden Horde