Data
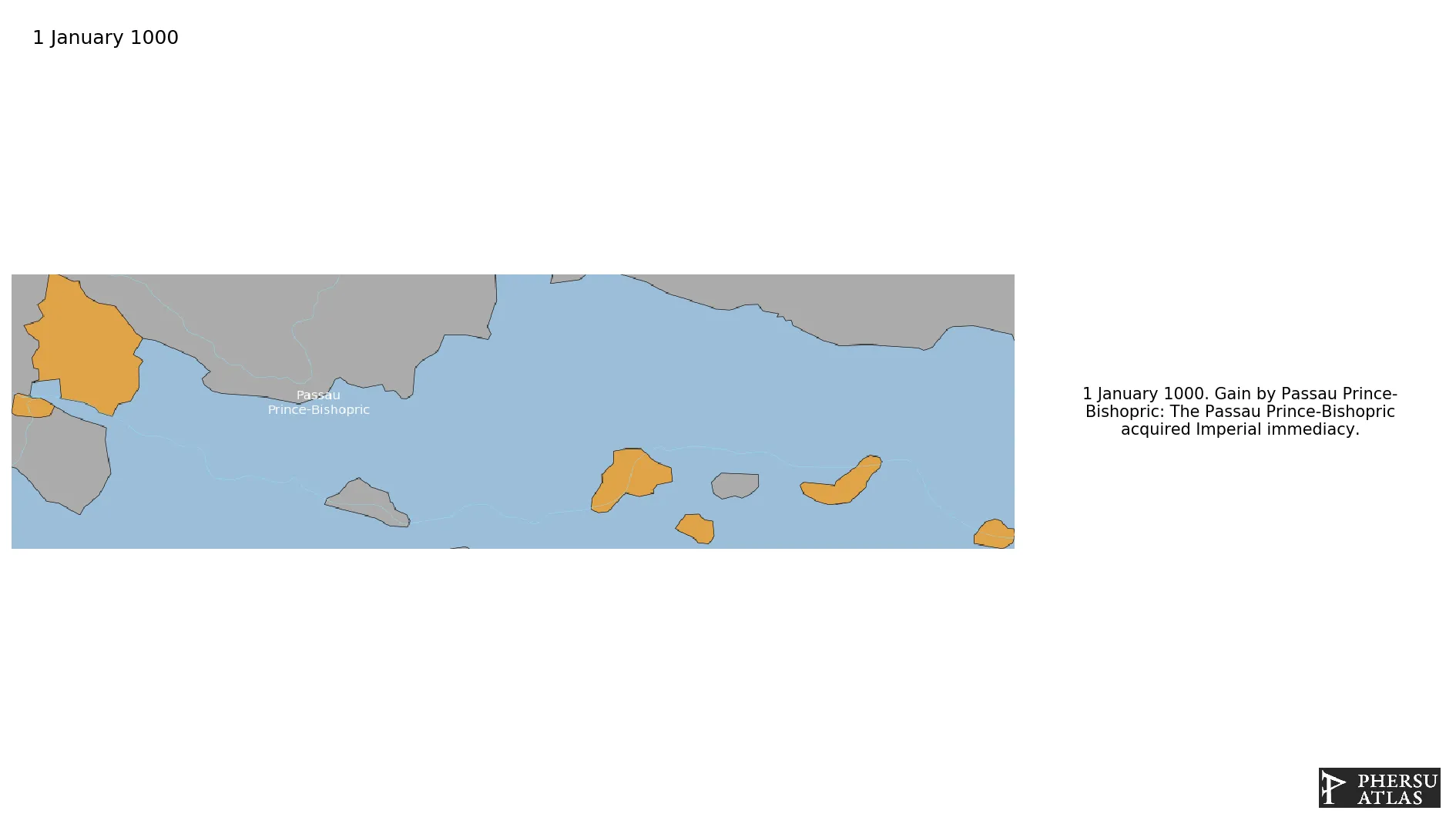
Name: Passau Prince-Bishopric
Type: Polity
Start: 1000 AD
End: 1803 AD
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Passau Prince-Bishopric
Passau Prince-Bishopric
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Mongol invasions and conquests
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
1.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
1.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
1.1.2.Second Mongol Invasion of Germany
The Mongols raided eastern Austria and southern Moravia again in December 1241 and January 1242.
2. European wars of religion
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
2.1.1.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
3. War of the Spanish Succession
The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters. It was a global war, with fighting taking place in Europe, Asia, and America. At the end of the war, Philip II, who was the successor chosen by Charles II as a descendant of Charles' paternal half-sister Maria Theresa, became King of Spain and of its overseas empire. The Spanish possessions in Europe were partitioned between various European Monarchies.
3.1.Dutch and German Theatre (War of the Spanish Succession)
Was the theatre of war of the War of the Spanish Succession in Germany and the Low Countries.
4. French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
4.1.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
4.1.1.German Front (War of the Second Coalition)
Was the German theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.