This article is about the specific polity Russian Republic and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
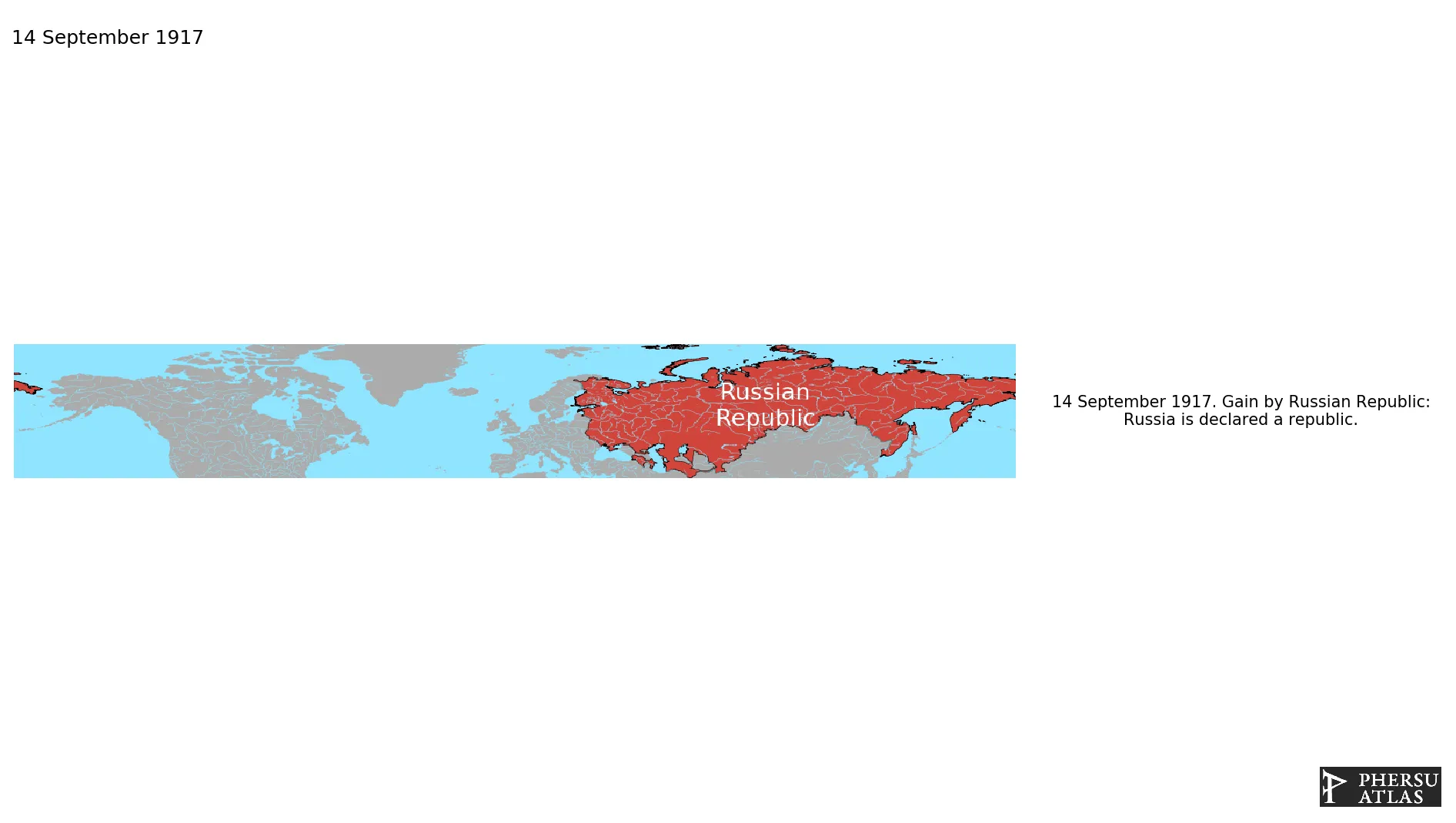
Was a short-lived state which controlled, de jure, the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Russian Provisional Government in 1917. It was quickly replaced by the RSFSR in all the territories it controlled.
Establishment
September 1917: Russia is declared a republic.
November 1917: The Bolshevik insurrection, which began on the night of November 6-7, 1917 in Petrograd, ended in success. The Bolsheviks formed a revolutionary government headed by Lenin and were able to progressively extend their power over most of the territories of the old Tsarist Empire.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Petrograd, Minsk, Novgorod, Ivanovo-Voznesensk and Tartu.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Ufa, Kazan, Yekaterinburg, and Narva.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Vitebsk, Yaroslavl, Saratov, Samara, and Izhevsk.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Rostov, Tver, and Nizhny Novgorod.
November 1917: The Transcaucasian Commissariat was established at Tbilisi on 11 November 1917, as the first government of the independent Transcaucasia following the October Revolution in Petrograd.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Voronezh, Smolensk, and Gomel.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Orel and Perm.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Pskov, Moscow, and Baku.
November 1917: A national-territorial autonomy proclaimed on November 15 1917 by the Bashkir regional Shuro and approved by the Constituent Congress of Bashkurdistan.
November 1917: In the Don Cossack capital, Novocherkassk, the Don Cossack Host had elected General Aleksei Maksimovich Kaledin to the position of Ataman at its traditional assembly, the Host Krug (1 July,O.S. 18 June, 1917). On 20 November (O.S. 7 November) 1917, not long after the Communists took control in central Russia, the Don Krug declared its independence.
November 1917: The Rada announced a wider autonomy for the Ukrainian Republic, still maintaining ties to Russia.
November 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Tsaritsyn.
November 1917: Turkestan Autonomy, or Kokand Autonomy, was an unrecognized state in Central Asia that existed at the beginning of the Russian Civil War. It was formed on 27 November 1917.
December 1917: Bolsheviks take control of Mogilev.
December 1917: The Bolsheviks took over Turkestan.
December 1917: The Alash Autonomy was a short- lived Kazakh state that existed from December 13, 1917.
December 1917: With the fall of Nicholas II, many parts of the Russian Empire took the opportunity to declare their independence, one of which was Finland, which did so in December 1917.
December 1917: On 8 December 1917, Vyatka was taken over by the Bolsheviks during the Russian Revolution.
December 1917: A local Council of Workers and Soldiers' Ambassadors convened on Naissaar, declaring the local People's Commissar Council.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a Civil War in Russia that involved varios factions but mainly the Bolsheviks and the conservative White Army in the core Russian territories, as well as a multitude of local secessionist states. At the end of war the Bolsheviks were victorious and established the Soviet Union.
February 1918: The Finnish Civil War expanded to Åland on 10 February, as a squad of 460 White Guard members, led by the captain Johan Fabritius, from the Vakka-Suomi region landed the islands. On 14 February, they took the Prästö telegraph station in Sund, capturing 20 Russian soldiers.
February 1918: The Kuban People's Republic was proclaimed by the Kuban Rada on 28 January 1918 and declared its independence on 16 February.
1.1.Pro-independence movements in the Russian Civil War
Local independence movement caused several secessions and revolts during the Russian Civil War.
1.1.1.Pro-independence and White movements in the Russian Far East during the Russian Civil War
Were a series of revolts and secessions in the Russian Far East during the Russian Civil War.
February 1918: The Provisional Siberian Government (later the Provisional Government of Autonomous Siberia), was an ephemeral government for Siberia created by the White movement.
1.1.2.Secession of Bashkurdistan
Was the secession of Bashkurdistan during the Russian Civil War.
1.1.3.Pro-independence movements in central Asia during the Russian Civil War
Were a series of revolts and secessions in central Asia during the Russian Civil War.
January 1918: During the Russian Civil War, the Confederated Republic of Altai was established in 1917, and declared as the first step to rebuilding Genghis Khan's Mongol Empire.
1.2.Bolsheviks take control of most of European Russia
Were a series of insurrections that resulted in the Bolshevik conquest of most of European Russia.
January 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Petrozavodsk.
January 1918: Establishment of the Odesa Soviet Republic.
February 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Astrakhan.
February 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Kyiv and Vologda.
February 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Arkhangelsk.
February 1918: The Bolsheviks occupied most of Ethnical Russia, ending the Russian Republic.
1.3.Ice March
Was a military withdrawal during the Russian Civil War. Under attack by the Red Army advancing from the north, the forces of the Volunteer Army, sometimes referred to as the White Guard, began a retreat from the city of Rostov south towards the Kuban.
1.4.Ukrainian-Soviet War
Was a conflict between Ukrainian nationalist forces and the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War. It also included a multitude of ethnical and local factions.
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
2.1.World War I eastern Front
Was the theatre of war in eastern Europe during World War I.
January 1918: Following the Russian Revolution in 1917, Estonia declared independence. However, German forces occupied the territory shortly after, with General Rüdiger von der Goltz leading the military administration.
2.1.1.Operation Faustschlag
Was a Central Powers offensive in World War I. It was the last major action on the Eastern Front. The northern force, consisting of 16 divisions, captured the key Daugavpils junction on the first day.
February 1918: Daugavpils conquered by Austrian and German forces.
February 1918: Minsk was captured by the Central Powers together with the headquarters of the Western Army Group.
2.2.World War I Middle East Theatre
Was the theatre of war in the Middle East during World War I.
2.2.1.Caucasus campaign (World War I)
Was an armed conflict mainly between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire in the Caucasus area during World War I.
2.2.1.1.Russian Conquest of Armenia
Was the Russin offensive in Armenia during World War I.
Disestablishment
January 1918: Following the Russian Revolution in 1917, Estonia declared independence. However, German forces occupied the territory shortly after, with General Rüdiger von der Goltz leading the military administration.
January 1918: During the Russian Civil War, the Confederated Republic of Altai was established in 1917, and declared as the first step to rebuilding Genghis Khan's Mongol Empire.
January 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Petrozavodsk.
January 1918: Establishment of the Odesa Soviet Republic.
February 1918: The Provisional Siberian Government (later the Provisional Government of Autonomous Siberia), was an ephemeral government for Siberia created by the White movement.
February 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Astrakhan.
February 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Kyiv and Vologda.
February 1918: The Finnish Civil War expanded to Åland on 10 February, as a squad of 460 White Guard members, led by the captain Johan Fabritius, from the Vakka-Suomi region landed the islands. On 14 February, they took the Prästö telegraph station in Sund, capturing 20 Russian soldiers.
February 1918: The Kuban People's Republic was proclaimed by the Kuban Rada on 28 January 1918 and declared its independence on 16 February.
February 1918: Bolsheviks take control of Arkhangelsk.
February 1918: Daugavpils conquered by Austrian and German forces.
February 1918: Minsk was captured by the Central Powers together with the headquarters of the Western Army Group.
February 1918: The Bolsheviks occupied most of Ethnical Russia, ending the Russian Republic.

 Russian Republic
Russian Republic