This article is about the specific polity Nassau Domains and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
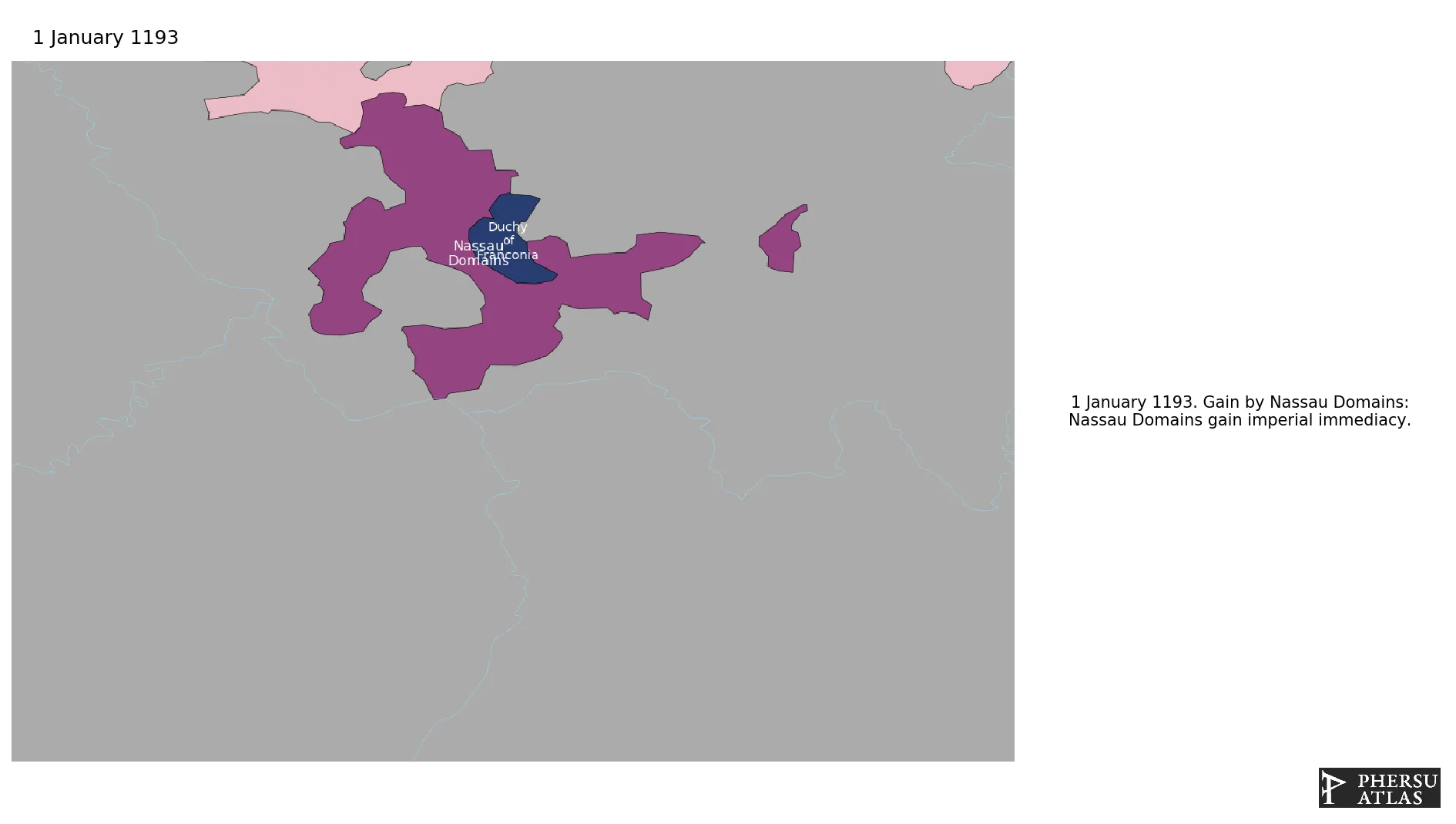
Was a German state within the Holy Roman Empire, governed by the house of Nassau.
Establishment
January 1193: Nassau Domains gain imperial immediacy.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
1.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
1.1.1.Bohemian-Palatine period
Was the first period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with a protestant revolt in Bohemia, at the time a territory of the Habsburg Domains.
1.1.1.1.War in Palatinate
Was the theatre of war in Palatinate during the first phase of the Thirty Years' War.
December 1621: German Protestant military leader Christian of Brunswick takes Amöneburg, not far from Mainz.
September 1622: From the summer of 1622, the territories of the Palatinate on the right bank of the Rhine were occupied by the troops of the Catholc League. Frederick V of the Palatinate eventually lost his electoral dignity on February 23, 1623, which was transferred to Maximilian of Bavaria.
1.1.2.Thirty Years' War Minor Scenarios
A series of conflicts related to the Thirty Years' War.
1.1.2.1.Invasion of Franche Comté (Ten Years War)
Was French invasion of modern-day Franche-Comté, at the time a possession of the Habsburg, during the Thirty Years' War.
January 1645: Following a treaty concluded with Cardinal Mazarin in 1644, France committed to cease hostilities in Franche-Comté, in exchange for the considerable sum of 40,000 écus, thus guaranteeing the region's neutrality once again. The year 1644 thus marked the end of the Ten Years' War in Franche-Comté.
1.1.3.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
December 1632: Swedes under Wolf Heinrich von Baudissin take Deutz.
1.1.4.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
1.1.4.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1637: After the death of Swedish King Ferdinand II, his son and successor Ferdinand III brought the Swedish troops back to Pomerania, leaving the territories occupied by Sweden in Germany.
1.1.4.2.Low Countries Front (France)
Was the Low Countries front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
January 1636: Spanish occupation of Philippsbourg, Speyer, Landau and Treviri.
1.1.5.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
January 1649: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of Thirty Years' War.
January 1649: The region of Saarwerden returned to the Nassau-Saarbrücken line except Bockenheim.
1.2.Nine Years' War
Was a conflict between France and the Grand Alliance, a coalition including the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, and Savoy. It is considered the first war that saw fighting globally because battles occured in Europe, America, Africa and India.
1.2.1.Rhineland Theatre (Nine Years' War)
Was the Rhineland Theatre of the the Nine Years' War.
January 1689: Several towns fell to the French without resistance, including Oppenheim, Worms, Bingen, Kaiserslautern, Heidelberg, Speyer and, above all, the key fortress of Mainz.
1.2.2.Peace of Ryswick
Were a series of treaties that ended the Nine Years' War.
September 1697: Peace of Ryswick (1697): France kept Strasbourg but returned Freiburg, Breisach, Philippsburg and the Duchy of Lorraine to the Holy Roman Empire.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
2.1.Central German Theatre
Was the theatre of war in central Germany of the Seven Years' War.
2.1.1.Rhineland Theatre (Seven Years' War)
Was the theatre of War in the Rhineland during the Seven Years' War.
July 1760: French general de Broglie launched an offensive in the direction of Hesse, defeating Duke Ferdinand of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel's forces on July 10 at the Battle of Korbach.
July 1760: The Battle of Warburg was fought on 31 July 1760 during the Seven Years' War. The battle was a victory for the Hanoverians and the British against the French army.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
February 1803: Reichsdeputationsschluss: the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the Reichstag (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Empire. The law secularized nearly 70 ecclesiastical states and abolished 45 imperial cities to compensate numerous German princes for territories to the west of the Rhine that had been annexed by France as a result of the French Revolutionary Wars.
January 1804: The Fulda Prince-Bishopric is secularised to Nassau.
March 1806: On 15 March 1806, the French emperor created the Granduchy of Berg and put it under the rule of his brother-in-law Joachim Murat. The Grand Duchy was a Napoleonic creation on territories formally part of several German states. Its capital was Düsseldorf.
August 1806: Established.
3.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
January 1795: The French armies drove the Austrians, British, and Dutch beyond the Rhine, occupying Belgium, the Rhineland, and the south of the Netherlands.
3.1.1.Peace of Basel
Were a series of Treaties between the French Republic and Prussia, Spain and Hesse-Kassel that ended the War of the First Coalition with these countries.
April 1795: Peace of Basel of 1795 at the end of the War of the First Coalition between the Kingdom of Prussia and the French Republic. France gained the left bank of the Rhine.
3.1.2.Rhine campaign of 1796
Were a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
July 1796: French forces occupied the city of Giessen.
August 1796: On 17 August the French took Sulzbach.
3.1.3.Rhine campaign of 1797
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
September 1796: Wiesbaden conquered by france.
3.1.4.Rhine campaign of 1798
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
September 1796: On 16-18 September Charles of Brunswick defeated the French Army of Sambre & Meuse in the Battle of Limburg.
3.1.5.Treaty of Campo Formio
Was a treaty between France and Austria that ended the War of the First Coalition.
January 1798: The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI). The treaty transferred the Austrian Netherlands to France. The territories of Venice were partitioned, most were acquired by Austria. Austria recognized the Cisalpine Republic and the newly created Ligurian Republic. Extension of the borders of France up to the Rhine, the Nette, and the Roer.
3.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
3.2.1.Suvorov Swiss campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Switzlerand.
October 1799: The Russian troops were forced by the French to abandon their hold on the left bank of the Rhine.
3.2.2.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
January 1253: Friedberg is declared a Free Imperial City.
January 1295: The Nassau Domains acquired Weilburg.
January 1379: The County of Münzenberg had a complex joint administration. The simplified version of the territories in Droysen's Holy Roman Empire Maps (1886) is adopted. Part of its territorie were acquired by Falkenstein.
January 1382: Saarbruecken County is acquired by the Nassau Dynasty.
January 1387: The dynasty of the Counts of Diez died out in 1386 and their county was acquired by Nassau.
January 1411: Nordhausen annexed to the Nassau Domains.
January 1411: Through his granddaughter Anna von Hohenlohe († 1410) and her husband Philipp I von Nassau-Saarbrücken-Weilburg, Kirchheimbolanden and the entire Sponheim-Bolander family estate finally fell to the House of Nassau.
January 1412: Through his granddaughter Anna von Hohenlohe († 1410) and her husband Philipp I von Nassau-Saarbrücken-Weilburg, Kirchheimbolanden and the entire Sponheim-Bolander family estate finally fell to the House of Nassau.
August 1505: On August 6, 1505, the brothers Eberhard, Georg and Philipp, who belonged to the House of Eppstein, received the right from the Roman-German king and later Emperor Maximilian I to use the title "Counts of Königstein". Thus the County of Königstein was founded.
January 1575: Nassau acquired Saarbrücken, Saarwerden and Stauf.
January 1630: Saarwerden is acquired by the Duchy of Upper Lotharingia.
February 1766: In 1766, the French king Louis XV. the rule of Püttlingen against the strategically more favorable territory of the Wadgassen Abbey with Prince Wilhelm Heinrich von Nassau-Saarbrücken and Prince Christian Ludwig zu Wied-Runkel (1762-1791), Lord of Püttlingen, in the so-called exchange agreement of February 15, 1766 France renounced the Metz enclave.
January 1788: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
March 1806: On 15 March 1806, the French emperor created the Granduchy of Berg and put it under the rule of his brother-in-law Joachim Murat. The Grand Duchy was a Napoleonic creation on territories formally part of several German states. Its capital was Düsseldorf.
August 1806: Established.
Selected Sources
Addington, L. (1994): The Patterns of War Since the Eighteenth Century, Bloomington (USA), p.24
Articles secrets et convention additionelle du traité de Campo Formio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2024 on https://books.google.de/books?id=SStJAAAAcAAJ&dq=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&hl=de&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&f=false
Battle of Warburg. BritishBattles.com. Retrieved on 30 march 2024 on https://www.britishbattles.com/frederick-the-great-wars/seven-years-war/battle-of-warburg/
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany)
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 48
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 42-43
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Exshaw, A. (1763): A Compleat History of the Late War, pp. 282-283
Frieden von Campoformio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2014 on https://books.google.de/books?id=UbGMtENHaBIC&pg=PA9#v=onepage&q&f=false
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Jorio, M. (2002): Basel, Frieden von (1795). Historisches Lexikon der Schweiz. https://hls-dhs-dss.ch/de/articles/044887/2002-05-01/
Livet, G. (1994): La Guerre de Trente Ans, Paris (France), p. 37
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Schmidt, G. (2006): Der Dreißigjährige Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 65
Swiss campaign of Suvorov and his wonder-heroes. Top War. 30 September 2011. https://en.topwar.ru/7227-shveycarskiy-pohod-suvorova-i-ego-chudo-bogatyrey.html
Treaty of Ryswick (English version), https://bonoc.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/tratado-ryswick.pdf
Zeller, O. (2024): La Bresse et le pouvoir: Le Papier journal de Jean Corton, syndic du tiers état (1641-1643), Dijon (France), p. 12

 Nassau Domains
Nassau Domains