This article is about the specific polity Umayyad Caliphate and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
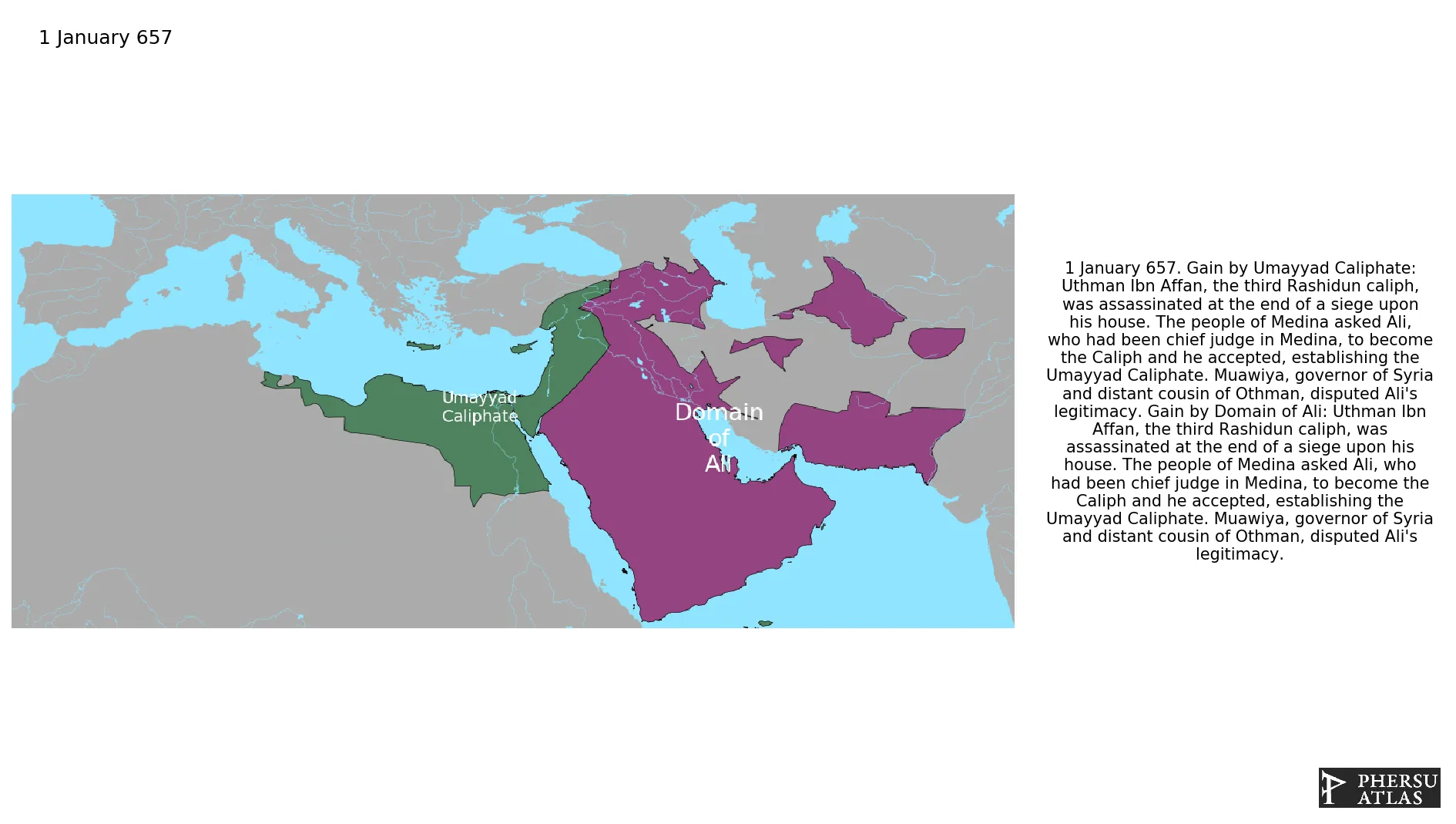
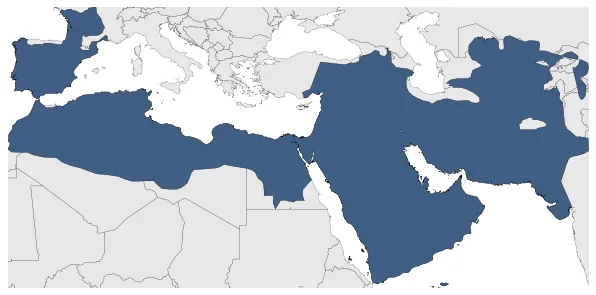
Was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, conquering Ifriqiya, Transoxiana, Sindh, the Maghreb and Hispania (al-Andalus). At its greatest extent, the Umayyad Caliphate covered 11,100,000 km2 (4,300,000 sq mi) making it one of the largest empires in history in terms of area.
Establishment
January 657: Uthman Ibn Affan, the third Rashidun caliph, was assassinated at the end of a siege upon his house. The people of Medina asked Ali, who had been chief judge in Medina, to become the Caliph and he accepted, establishing the Umayyad Caliphate. Muawiya, governor of Syria and distant cousin of Othman, disputed Ali's legitimacy.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a civil war at the end of the Rashidun Caliphate that led to the establishment of the Umayyad Caliphate.
1.1.Hasan-Muawiya treaty
Was a political peace treaty signed in 661 between Caliph Hasan ibn Ali and Mu'awiya I (r. 661-680) to bring the First Fitna (656-661) to an end.
January 662: In the Hasan-Muawiya treaty, Hasan ibn Ali handed over power to Muawiya.
Were a series of wars between a number of Muslim Arab dynasties and the Byzantine Empire from the 7th to the 11th century. Conflict started during the initial Muslim conquests, under the expansionist Rashidun and Umayyad caliphs, in the 7th century and continued by their successors until the mid-11th century.
November 670: The Muslim fleet, led by the Umayyad Caliphate, under the command of Muawiyah I, successfully navigated through the Sea of Marmara and established a base in Cyzicus in 670. This strategic move allowed them to expand their influence in the region and control key trade routes.
April 671: The Muslim fleet, led by the Arab commander Mu'awiya, had successfully penetrated into the Sea of Marmara by 670. They established a base at Cyzicus, a strategic location in present-day Turkey, where they stayed during the winter of 671. This marked a significant advancement in the Arab-Byzantine conflict during the early Islamic expansion.
January 676: A massive Muslim fleet reappeared in the Marmara and re-established a base at Cyzicus.
January 679: Constantine IV however used a devastating new weapon that came to be known as "Greek fire", invented by a Christian refugee from Syria named Kallinikos of Heliopolis, to decisively defeat the attacking Umayyad navy in the Sea of Marmara, resulting in the lifting of the siege in 678.
2.1.Byzantine occupation of Gaermanicea
Byzantine occupation of Gaermanicea.
January 747: Byzantine occupation of Gaermanicea.
Was a civil war in the Umayyad Caliphate where other regional dynasties challenged the Umayyads.
May 680: Upon Muawiyah's death in 680 CE, Yazid demanded allegiance from Husayn and other dissidents. Husayn did not give allegiance and traveled to Mecca. The people of Kufa, an Iraqi garrison town and the center of Ali's caliphate, were averse to the Syria-based Umayyad caliphs and had a long-standing attachment to the house of Ali.
October 680: The Battle of Karbala ensued on 10 October during which Husayn was killed along with most of his relatives and companions.
November 683: With the demise of Yazid and the withdrawal of Syrian troops, Ibn al-Zubayr was now de facto ruler of the Hejaz and the rest of Arabia.
November 683: Oman was independently ruled by the Banu Juland.
April 684: Soon afterwards, he was recognized in Egypt, as well as in Iraq where the Umayyad governor Ibn Ziyad had been expelled by the tribal nobility (ashraf). Coins bearing Ibn al-Zubayr's name were minted in parts of southern Persia (Fars and Kirman).
August 684: Battle of Marj Rahit: The victory consolidated the position of the Umayyads over Syria, paving the way for their eventual victory in the civil war against Ibn al-Zubayr.
January 685: Marwan and his son Abd al-Aziz expelled the Zubayrid governor of Egypt with the help of local tribes.
October 691: Battle of Maskin: Umayyads' victory and recapture of Iraq.
April 692: Mecca is besieged by the Umayyad Caliphate.
December 692: The city was bombarded with catapults and supplies were cut off, resulting in large scale desertions by the followers of Ibn al-Zubayr. He was killed along with his few remaining supporters in October 692. The siege brought an end to the decade-long civil war and the Caliphate was united under Abd al-Malik.
The northeast African Kingdom of Aksum invaded the region of Hejaz, in south Arabia.
January 703: In 702 Aksumite pirates were able to invade the Hejaz and occupy Jeddah.
January 704: Aksum regained control of ist coastal area and of the Dahlak Archipelago.
January 704: Jedda is reconquered by the Umayyads.
In the Battle of Varnakert (702) Armenian prince Smbat Bagratuni defeated the 8,000-strong Umayyad army from the garrison in Nakhichevan.
January 703: In the Battle of Varnakert (702) Smbat Bagratuni defeated the 8,000-strong Umayyad army from the garrison in Nakhichevan. Smbat, with the aid of Byzantine Empire, managed to re-conquer the majority of Armenia and drive the Arabs out of the country.
Were the military campaigns by the first three Islamic Caliphates (the Caliphate of Muhammad, the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate) that led to the Islamic conquest of most of the Middle East as well as the Iberian Peninsula.
6.1.Muslim conquest of the Maghreb
Was the Muslim conquest of Maghreb by the Rashidun and later Umayyad Caliphate.
January 709: The Christian Berber kingdoms were conquered by the Umayyads.
January 709: Kingdom of Cabaon conquered by the Arabs.
January 710: By 709, all of North Africa was under the control of the Umayyad Caliphate.
6.1.1.Second Muslim invasion of Maghreb
Was the Muslim conquest of territories in Tunisia.
January 671: In 670 the city of Kairouan (Tunisia) was established by the Umayyad Caliphate.
January 684: Battle of Tahouda: Expulsion of the Umayyads from present-day Tunisia.
January 689: Battle of Mammes (688): Capture of Kairouan by Umayyad forces.
6.1.2.Third Muslim Invasion of the Maghreb
Was the Muslim conquest of territories in Tunisia.
January 696: In 695, the Umayyad Caliphate conquered Carthage.
January 698: Emperor Leontius sent the navy under the command of John the Patrician and the droungarios Tiberius Apsimarus. They entered the harbor and successfully recaptured it in a stunning surprise attack in 697.
January 699: Battle of Carthage (698).
January 699: Battle of Wadi Nini: Expulsion of the Umayyads from Cyrenaica.
January 701: General Hasan ibn al-Nu'man advanced in the Maghreb, his armies taking the city of Icosium in 700.
January 704: Battle of Tabarka.
6.2.Arab-Khazar Wars
Were a series of conflicts fought between the armies of the Khazar Khaganate and the Rashidun, Umayyad, and Abbasid caliphates and their respective vassals.
6.2.1.Second Arab-Khazar War
Was a war between the Khazar Kahaganate and the Umayyad Caliphate.
August 722: Battle of Balanjar.
January 730: By 729, the Arabs had lost control of northeastern Transcaucasia.
December 730: The battle in 730 in Ardabil was between the Arab general al-Jarrah and the Khazars led by Barjik. The Khazars emerged victorious, defeating al-Jarrah's army of 25,000 soldiers. This victory solidified the Khazar Khaganate's control over the territory.
January 732: Sa'id ibn Yazid was a prominent Umayyad general who successfully recaptured the city of Akhlat on Lake Van in 731.
January 741: He restored the provinces of Albania to Muslim allegiance after meting out exemplary punishment to the inhabitants of Khaydhan, who resisted his advance, and reached Derbent, where he found a Khazar garrison of 1,000 men with their families installed. .
6.3.Muslim conquest of Transoxiana, Ferghana and Khorasan
Were the 7th and 8th century conquests, by Umayyad and Abbasid Arabs, of Transoxiana, the land between the Oxus (Amu Darya) and Jaxartes (Syr Darya) rivers, a part of Central Asia that today includes all or parts of Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
January 671: It was not until the appointment of Ziyad ibn Abi Sufyan to the government of Iraq and the eastern Caliphate that the Arabs undertook a systematic pacification campaign in Khurasan. Peroz was evicted and once again fled to China.
January 677: Sa'id ibn Uthman was a prominent military leader and governor under the Umayyad Caliphate. Samarkand was a key city in Central Asia known for its strategic location on the Silk Road. The capture of Samarkand by Sa'id ibn Uthman in 676 was a significant victory for the Umayyad Caliphate in expanding their territory and influence in the region.
January 716: Umayyad commander Qutayba ibn Muslim conquered the strategic Central Asian cities of Bukhara, Samarkand, Khwarezem and Farghana between 705 and 715 CE, annexing nearly the whole of Transoxiana north of the Iranian plateau and bordering the contemporary Tang dynasty of China.
January 716: The larger part of Transoxiana was conquered by the Umayyad leader Qutayba ibn Muslim in the reign of al-Walid I (r. 705-715).
January 717: The deposed king fled to Kucha (seat of Anxi Protectorate), and sought Chinese intervention. The Tang dynasty sent 10,000 troops under Zhang Xiaosong to Ferghana. He defeated Alutar and the Arab occupation force at Namangan and reinstalled the ikhshid on the throne.
January 717: The deposed king fled to Kucha (seat of Anxi Protectorate) and sought Chinese intervention. The Chinese sent 10,000 troops under Zhang Xiaosong to Ferghana. He defeated Alutar and the Arab occupation force at Namangan and reinstalled Ikhshid on the throne.
6.4.Arab occupation of Amorium
Arab occupation of Amorium.
6.5.Arab occupation of Cappadocia and Cylicia
Arab conquest of Byzantine Cappadocia and Cylicia.
6.6.Umayyad conquest of Hispania
Was an Umayyad Caliphate invasion of the Iberian Peninsula from c. 710-780. The conquest resulted in the defeat of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.
6.6.1.Revolt of Asturias
The Hispano-Visigothic nobleman Pelagius began a revolt against the Islamic rule of Hispania and established the Kingdom of Asturias.
6.6.2.Campaign of Septimania
Umayyad military campaign in Septimania (southern France).
6.7.Islamic conquest of Sindh
Was the invasion of Sindh (Pakistan) initiated by the Umayyad Caliphate.
January 713: In the year 712, Muhammad bin Qasim, an Umayyad general, sailed from the Persian Gulf into Sindh and conquered both Sindh and the lower Punjab (corresponding to Multan), both regions in northwestern India straddling the course of the Indus River.
6.8.Arab occupation of Amasea and Mishtia
Arab conquest of Byzantine Amasea and Mishtia.
6.9.Umayyad campaigns in India
Were a series of expansionistic military campaigns by the umayyad Caliphate in the Indian subcontinent.
6.9.1.Campaign by Muhammad bin Qasim
Campaign in India by Umayyad commander Muhammad bin Qasim.
January 716: Campaign by Muhammad bin Qasim.
6.9.2.Campaign by Al Junayd
Campaign in India by Umayyad commander Muhammad Al Junayd.
January 727: In 726, the Umayyad Caliphate subdued territories including Qassa (Kutch), al-Mandal (perhaps Okha), Dahnaj, Surast (Saurashtra), and Barus or Barwas (Bharuch) in the Indian subcontinent. These regions were important centers of trade and commerce during this time.
6.10.Second Arab Siege of Constantinople
A combined land and sea offensive by the Muslim Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate against the capital city of the Byzantine Empire.
6.11.Islamic conquest of Deccan
Was the invasion of Deccan (India) initiated by the Umayyad Caliphate.
January 734: Arab invaders who had established themselves in the Sindh made a push into the Deccan.
Were a series military campaigns from the 8th century until 1492 by the Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula to reconquer the region from the Islamic rulers that had conquered it during the Umayyad conquest of Hispania.
January 726: 725: Muslim raids reach Autun in the Frankish Empire.
February 726: End of Muslim raid in Autun (Frankish Empire).
January 741: Umayyad conquest of Galicia.
Were the military campaigns of the Umayyad Caliphate in modern-day Spain, Portugal and France.
8.1.Frankish-Umayyad Wars
Were a series of wars between the Umayyad Caliphate, which had conquered the Iberian Peninsula, and the Frankish Kingdom.
June 732: 732: A Muslim army under Abd ar-Rahman defeats an army of Duke Eudos of Aquitaine (or Odo the Great) near Bordeaux. The Moors then sack Aquitaine.
December 732: End of the sack of Aquitaine by the Muslim army.
In the VIII century Muktapida, an Indian king of the Karkota dynasty of Kashmir, created a short-lived empire covering most of India.
January 741: Karkota ruler Lalitaditya Muktapida conquered extensive territories in India and Central Asia.
January 761: Karkota ruler Lalitaditya Muktapida conquered extensive territories in India and Central Asia.
Was the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE), the second of the four major Caliphates in Islamic history, by the third, the Abbasid Caliphate (750-1517 CE).
February 748: Abu Muslim successfully initiated an open revolt against Umayyad rule. On February 14, 748 he established control of Merv.
September 749: Yazid had been forced to abandon Kufa due to a rebellion by Abbasid sympathizers, and fled to Wasit.
October 749: Wasit is besieged by the Abbasid Caliphate.
January 750: The rebels where in control of Khorasan by march 749.
January 750: On January 16, 750 the two forces met on the left bank of a tributary of the Tigris in the Battle of the Zab, and nine days later Marwan II was defeated and his army was completely destroyed.
May 750: Damascus fell to the Abbasids in April.
August 750: Al-Fazari, the Umayyad commander at Wasit, held out even after the defeat of Marwan II in January. The Abbasids promised him amnesty in July, but immediately after he exited the fortress they executed him instead.
January 666: The Turk Shahis or Kabul Shahis were a dynasty of Western Turk, or mixed Western Turk-Hephthalite, origin, that ruled from Kabul and Kapisa to Gandhara in the 7th to 9th centuries CE.
January 670: Garama was conquered by Arab general Uqba ibn Nafi in 669 AD.
January 671: Under Mu'awiya's direction, the Muslim conquest of Ifriqiya (central North Africa) was launched by the commander Uqba ibn Nafi in 670, which extended Umayyad control as far as Byzacena (modern southern Tunisia), where Uqba founded the permanent Arab garrison city of Kairouan.
January 674: The island of Rhodes was captured by the Umayyad Caliphate in 673 during their first attack on Constantinople. The Umayyad Caliphate was a powerful Islamic empire ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, and Constantinople was the capital of the Byzantine Empire at the time.
January 677: The Principality of Khuttal was a local Iranian dynasty, which ruled the Khuttal region from the early 7th century to 750.
January 681: The island of Rhodes was evacuated in 679/80 as part of the Byzantine - Umayyad peace treaty.
January 681: The Zunbils ruled the region of Zabul in present-day Afghanistan from the early 7th century.
January 682: The Bukhar Khudahs were a local Sogdian dynasty, which ruled the city of Bukhara from an unknown date.
June 683: The Ansar and Quraysh of Medina took up the anti-Umayyad cause and in 683 expelled the Umayyads from the city.
July 683: Yazid's Syrian troops routed the Medinese at the Battle of al-Harra and subsequently plundered Medina before besieging Ibn al-Zubayr in Mecca.
January 689: In 688, the emperor Justinian II and the caliph Abd al-Malik reached an unprecedented agreement. The Arabs evacuated Cyprus, and for the next 300 years, the island was ruled jointly by both the Caliphate and the Byzantines as a condominium, despite the nearly constant warfare between the two parties on the mainland.
January 700: Türgeshes emerged as an independent power after the demise of the Western Turks and established a khaganate in 699.
January 701: With the collapse of the Kingdom of Aksum around the year 700 CE, Beja clans invaded and established several kingdoms in present-day Eritrea.
January 701: Tashkent was conquered by the Umayyad Caliphate.
January 706: Despite this success, the Umayyad generals Muhammad ibn Marwan and Maslamah ibn Abd al-Malik soon restored Armenia to subject status, and secured Muslim control by organizing a large-scale massacre of the princely families (nakharar) within the cathedral of Nakhchivan in 705.
January 706: In 705, the Arab general Qutayba ibn Muslim managed to make the Chaghan Khudah, whose name is mentioned as Tish, acknowledge Umayyad authority.
January 711: The Emirate of Nekorwas was founded in 710 CE.
January 712: In 711 the Türk forces, led by Tonyukuk, crossed the Mongolian Altai, clashed with the Türgesh army in Dzungaria, on the River Boluchu, and won an outright victory. Tonyukuk forced a crossing over the Syr Darya in pursuit of the retreating Türgesh, leading his troops to the border of Tokharistan.
January 736: The Saindhavas, also known as Jayadrathas, ruled western Saurashtra (now in Gujarat, India) from c. 735 CE to c. 920 CE, probably in alliance with Maitrakas in early years.
January 738: In 737, the Tibetans launched an attack against the king of Bru-za (Gilgit), who asked for Chinese help, but was ultimately forced to pay homage to Tibet.
January 740: Avanijanashraya Pulakeshin, a son of Vikramaditya I's brother Jayasimhavarman who was the governor of the Lata branch (Gujarat) fought and defeated them in 739 CE.
January 741: Chalukya king Vikramaditya II captured the Khetaka region from the Maitrakas with the help of Jayabhatta IV, the Gurjara king of Lata.
January 743: A revolt of the Zenata tribe of the Banu Ifran broke out. The rebels proclaimed their leader Abu Qurra to be the Caliph, and he established a Sufri state in Tlemcen.
January 744: In 742 or 743, the Barghwata removed themselves from the rebel alliance, and retreated to the Tamesna region, on the Atlantic coast of Morocco, where they founded their new independent state and abandoned their Sufri Kharijitism.
January 746: In 745, Gao Xianzhi marched across the Pamirs with 10,000 men and conquered Little Balur (Gilgit), a client state of the Tibetan Empire.
Disestablishment
January 761: Some territories still controlled by the Umayyads were inglobated into the Abbasid Caliphate.
January 761: Karkota ruler Lalitaditya Muktapida conquered extensive territories in India and Central Asia.
Selected Sources
Schwartzberg, J. E. (1992); A Historical Atlas of South Asia, Chicago (USA), p. 146
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.94
.png.webp)
 Umayyad Caliphate
Umayyad Caliphate