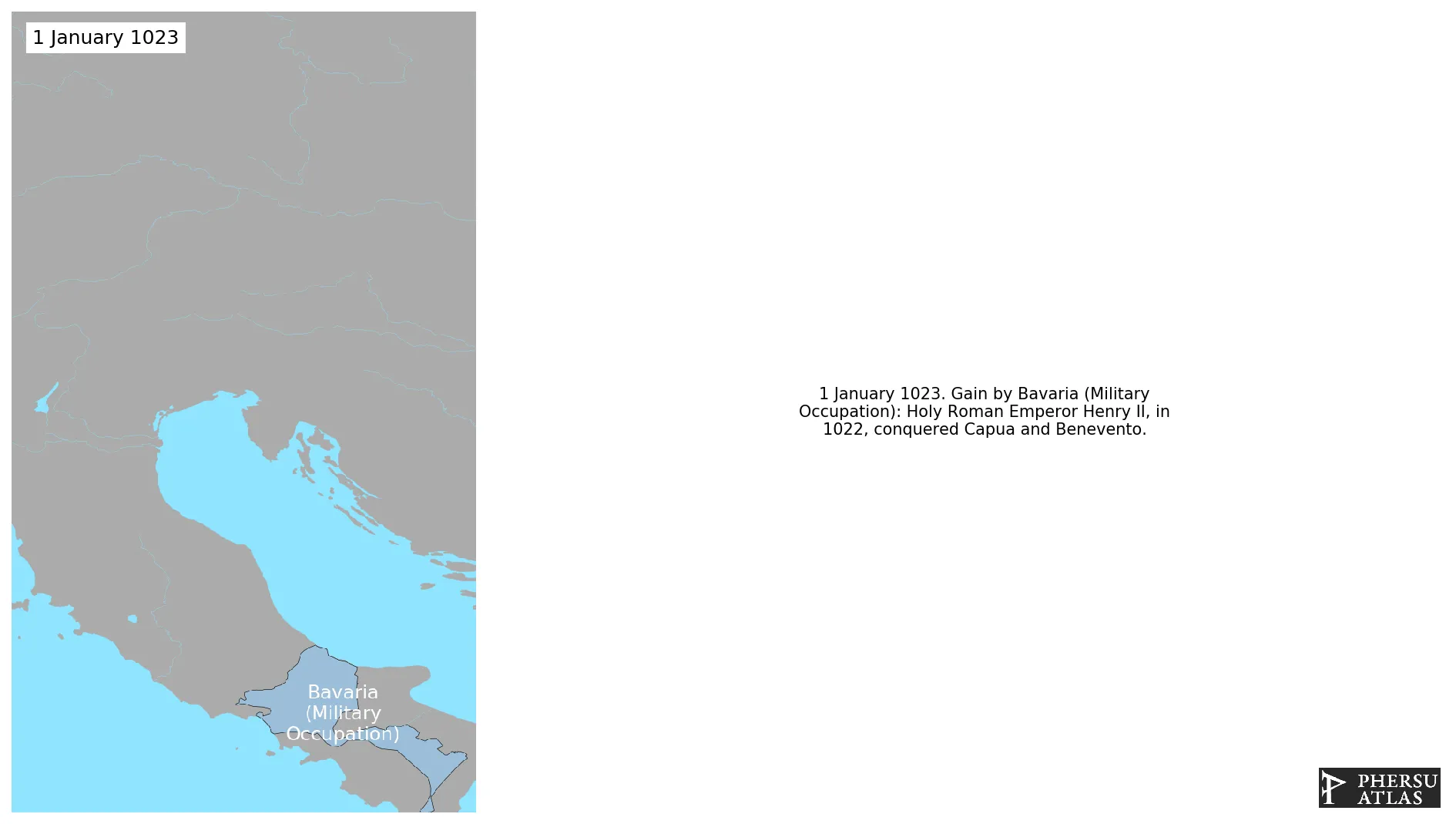
.png.webp)
Data
Name: Bavaria (Military Occupation)
Type: Polity
Start: 1023 AD
End: 1743 AD
Parent: bavaria
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Bavaria (Military Occupation)
Bavaria (Military Occupation)
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Polity that includes all territories militarly occupied by Bavaria that are not part of a specific military territory.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Indipendance of Capua and Benevento
Was the end of a period of Bavarian domain over Benevento and Capua.
2. European wars of religion
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
2.1.1.Bohemian-Palatine period
Was the first period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with a protestant revolt in Bohemia, at the time a territory of the Habsburg Domains.
Was the theatre of war in Palatinate during the first phase of the Thirty Years' War.
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
2.1.3.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
2.1.3.2.Rhineland Front (France)
Was the Rhineland front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
3. War of the Spanish Succession
The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters. It was a global war, with fighting taking place in Europe, Asia, and America. At the end of the war, Philip II, who was the successor chosen by Charles II as a descendant of Charles' paternal half-sister Maria Theresa, became King of Spain and of its overseas empire. The Spanish possessions in Europe were partitioned between various European Monarchies.
3.1.Dutch and German Theatre (War of the Spanish Succession)
Was the theatre of war of the War of the Spanish Succession in Germany and the Low Countries.
4. Silesian Wars
Were a series of wars between the Habsburg Domains and Prussia for the control of Silesia. The war started during the War of the Austrian Succession, when Frederick the Great of Prussia invaded Habsburg-held Silesia.
Was the first of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was part of the War of the Austrian Succession. The war started when Prussia invaded Silesia. The possession of the region by Prussia was aknowledged by Austria at the end of the war.
4.1.1.Bohemian Theatre (First Silesian WarWar)
Was the Bohemian theatre of the First Silesian War.
Was the Bavarian theatre of the First Silesian War.