Data
Name: Transcaucasian Commissariat
Type: Polity
Start: 1917 AD
End: 1918 AD
Nation: transcaucasia
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
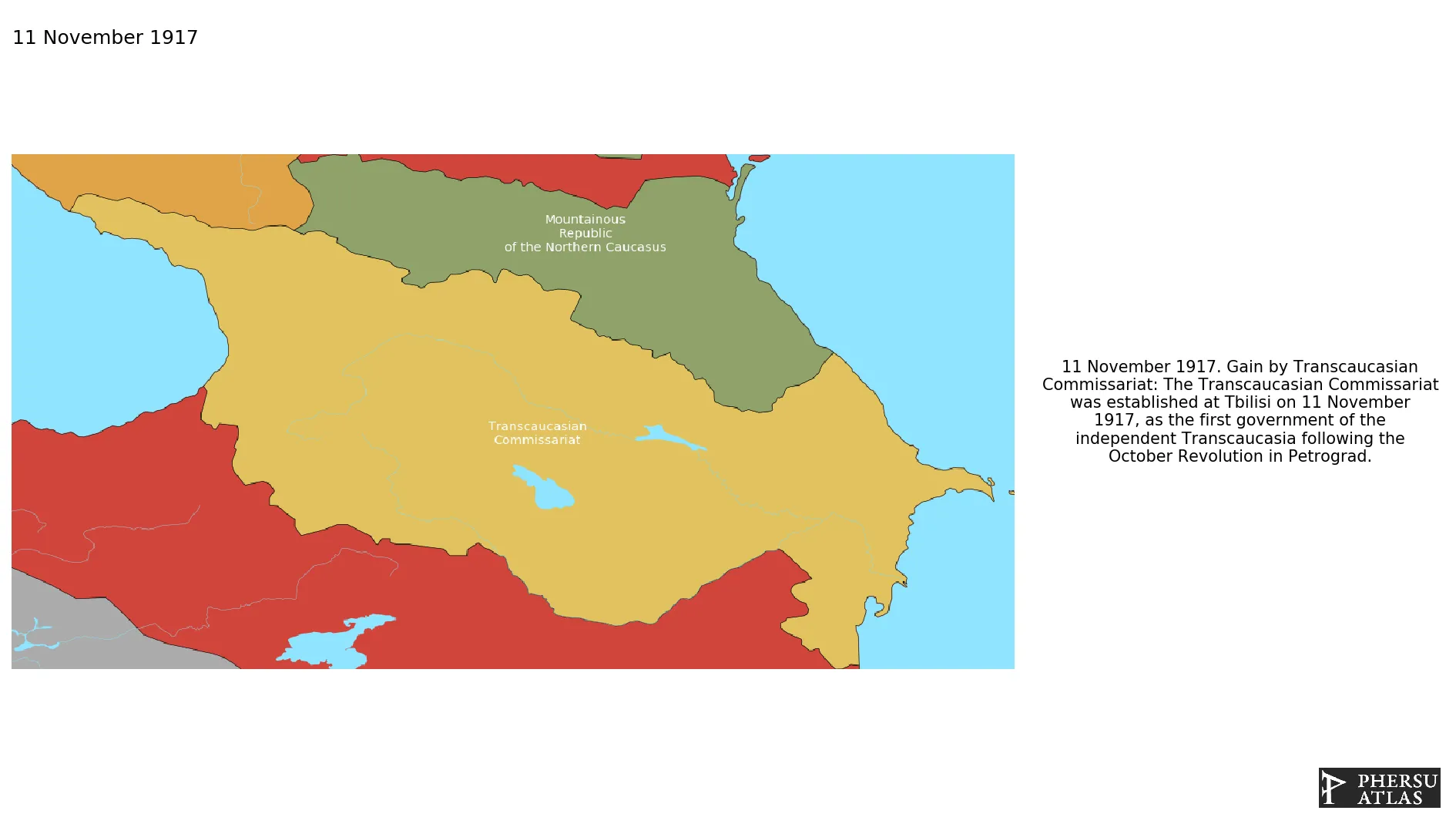
 Transcaucasian Commissariat
Transcaucasian Commissariat
This article is about the specific polity Transcaucasian Commissariat and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
The Transcaucasian Commissariat was established at Tbilisi on 11 November 1917, as the first government of independent Transcaucasia following the October Revolution in Petrograd.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. World War I
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
Was the theatre of war in eastern Europe during World War I.
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Brest Peace in Russia) was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, between the new Bolshevik government of Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's participation in World War I.
1.2.World War I Middle East Theatre
Was the theatre of war in the Middle East during World War I.
1.2.1.Caucasus campaign (World War I)
Was an armed conflict mainly between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire in the Caucasus area during World War I.
1.2.1.1.Russian Conquest of Armenia
Was the Russin offensive in Armenia during World War I.
1.2.1.2.Ottoman offensive (Caucasus campaign)
Was the Ottoman military offensive during the Caucasus campaign of World War I.
1.2.1.3.Transcaucasian Front of World War I
Was the theatre of war in Transcaucasia during World War I.
2. Russian Civil War
Was a Civil War in Russia that involved varios factions but mainly the Bolsheviks and the conservative White Army in the core Russian territories, as well as a multitude of local secessionist states. At the end of war the Bolsheviks were victorious and established the Soviet Union.
2.1.Pro-independence movements in the Russian Civil War
Local independence movement caused several secessions and revolts during the Russian Civil War.
2.1.1.Pro-independence and White movements in the Caucasus during the Russian Civil War
Were a series of revolts and secessions in the Caucasus during the Russian Civil War.