If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
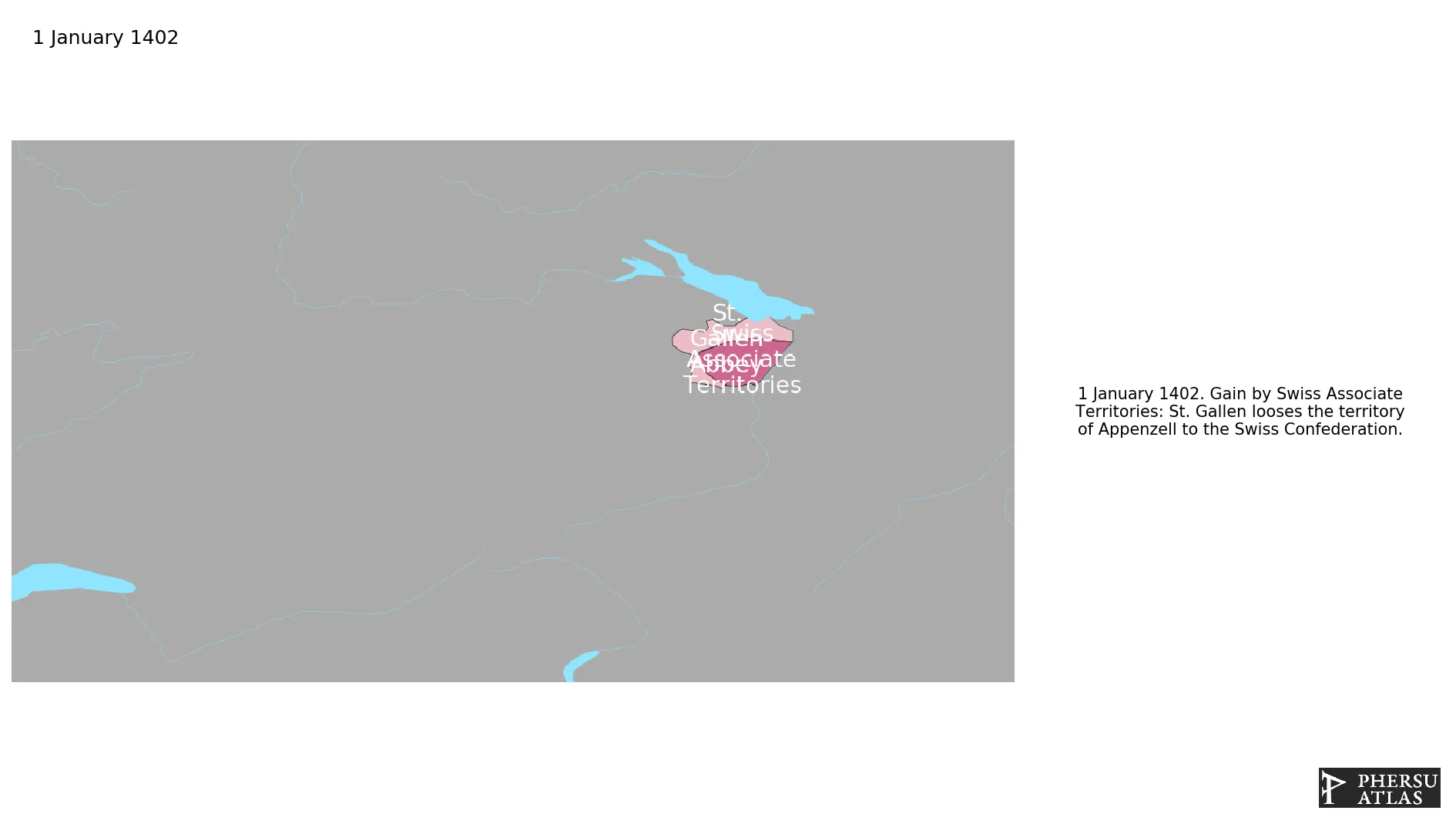
Were territories linked to the Old Swiss Confederation by treaties.
Establishment
January 1402: St. Gallen looses the territory of Appenzell to the Swiss Confederation.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies.
February 1476: Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, took the town of Grandson, which was controlled by troops from Bern and Freiburg.
March 1476: In the battle of Grandson Charles the Bold of Burgundy suffered a defeat against the Swiss infantry.
Was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg.
February 1499: In January 1499, the Habsburg governor of Tyrol, Sigismund of Austria, militarily occupied Vinschgau and Münstertal to assert his claim against the episcopal rights and the church association led by Bishop Georg of Chur.
March 1499: The Swabian War of 1499 brought the Belfort's downfall: in order to eliminate it as an Austrian base, the people of Graubünden burned down the castle on March 14, 1499.
April 1499: On April 17, the Confederates moved to the Klettgau and the Hegau and plundered several towns, such as Tiengen and Stühlingen.
May 1499: Swiss forces left Klettgau and Hegau.
2.1.Treaty of Basel
Was the treaty that ended the Swabian War.
September 1499: On September 22, 1499, the Peace of Basel was sealed between Maximilian and the Confederates. Jurisdiction over Thurgau, previously an Imperial loan to the city of Constance, which was to pass to the Swiss Confederacy.
Was an armed conflict between the federation of the Three Leagues, which functioned as an associate state of the Old Swiss Confederacy, and the Duchy of Milan early in the 16th century.
January 1532: In the Milan Wars from 1512 to 1531, the Three Leagues under Conrad von Planta succeeded in conquering Cläven together with Bormio (Worms) and the Veltlin (Valtellina).
January 1533: The League forces were able to drive the Milanese out of the Valtellina. In a peace treaty concluded the next year, Chiavenna and the Valtellina were granted to the Three Leagues. Only the tre pievi came under the control of Milan.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
4.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
4.1.1.Thirty Years' War Minor Scenarios
A series of conflicts related to the Thirty Years' War.
4.1.1.1.War of Valtellina
Was a war over the control of Valtellina (today in northern Italy) mainly between Spain and France.
August 1620: The Grisons were forced to retreat north of the Alps and the Valtellina was militarily invaded by the Spaniards.
4.1.1.2.Invasion of Franche Comté (Ten Years War)
Was French invasion of modern-day Franche-Comté, at the time a possession of the Habsburg, during the Thirty Years' War.
January 1645: Following a treaty concluded with Cardinal Mazarin in 1644, France committed to cease hostilities in Franche-Comté, in exchange for the considerable sum of 40,000 écus, thus guaranteeing the region's neutrality once again. The year 1644 thus marked the end of the Ten Years' War in Franche-Comté.
4.1.2.Bündner Wirren
Was a war in in what is now the Swiss canton of Graubünden that started as a revolt by local Catholics against their Protestant overlords.
October 1621: Emboldened by the murder of Pompeius Planta, the Protestant forces in the Three Leagues assembled an army to retake the Valtellina and other subject lands. This attempted invasion gave the Spanish and Austrians an excuse to invade the Leagues. By the end of October, Spain and Austria had occupied all of Graubunden.
February 1622: In January 1622, Graubünden had to cede the Müstair, the Lower Engadine, and Prättigau valleys to the Swiss Associate Territories.
September 1639: On 24 January 1639, Jürg Jenatsch was killed. On 3 September 1639 the Leagues agreed with Spain to bring the Valtellina back under League sovereignty, but with the promise to respect the free exercise of the Catholic faith. Treaties with Austria in 1649 and 1652, brought the Müstair and Lower Engadine valleys back under the authority of the Three Leagues.
4.1.3.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
4.1.3.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1648: When in November Gustaf of Sweden received a report about the signed peace, he ordered his troops to leave. Also the French troops started leaving the occupied territories in the Holy Roman Empire.
4.1.3.2.Rhineland Front (France)
Was the Rhineland front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
January 1638: France occupies Laufenberg.
March 1638: France occupies Neuenburg.
November 1643: Battle of Tuttlingen: a surprise attack by Imperial forces caused the French army to retreat across the Rhine.
May 1648: The French returned to Swabia and then to Bavaria. They defeated the Imperial forces at Zusmarshausen (May 17, 1648) and drove Maximilian of Bavaria out of Munich.
4.1.4.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
January 1649: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of Thirty Years' War.
Was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland.
5.1.French Invasion of northern Italy
Was the French invasion of northern Italy during the War of the Polish Succession.
September 1734: Following their defeat at Guastalla at the hands of the French, which resulted in heavy casualties, the Austrians retreated to the Oglio River. They maintained this position for the remainder of the year.
January 1735: The French army entered winter quarters in December 1734, leaving the North Bank of the Po River.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1799: On April 12, 1798, 121 cantonal deputies proclaimed the Helvetic Republic under the auspices of the French occupying forces. The Helvetic Republic was a centralized state based on the ideas of the French Revolution.
January 1803: Rottweil acquired by the Duchy of Württemberg.
6.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
December 1792: Secession of the Rauracian Republic, partly composed of territories belonging to the Abbey of Basel.
March 1797: On 9 December 1797, Frédéric-César de La Harpe, a member of the Helvetian Club from Vaud, asked France to invade Bern to protect Vaud. Seeing a chance to remove a feudal neighbor and gain Bern's wealth, France agreed. By February 1798, French troops occupied Mulhouse and Biel/Bienne. Meanwhile, another army entered Vaud, and the Lemanic Republic was proclaimed.
October 1797: In 1797, the districts of Chiavenna, Valtellina, and Bormio, dependencies of the Three Leagues (an associate of the Confederation), revolted under the encouragement of France. They were quickly invaded and annexed to the Cisalpine Republic on 10 October 1797.
6.1.1.Italian theatre (War of the first coalition)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
February 1797: French troops advanced directly toward Austria over the Julian Alps. General Barthélemy Joubert invaded Tyrol.
6.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
6.2.1.German Front (War of the Second Coalition)
Was the German theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
May 1800: After French general Claude Lecourbe had captured Stockach, the Austrians led by general Paul Kray retreated to Messkirch, where they enjoyed a more favourable defensive position.
6.3.French invasion of Switzerland
French invasion of the Old Swiss Confederacy.
April 1798: On April 12, 1798, 121 cantonal deputies proclaimed the Helvetic Republic under the auspices of the French occupying forces. The Helvetic Republic was a centralized state based on the ideas of the French Revolution.
January 1404: Freiburg im Üechtland renews an alliance treaty with Bern ("Burgrecht treaty").
January 1407: The county of Neuchâtel signs a treaty of association with Bern and Solothurn.
January 1437: The county of Toggenburg becomes a protectorate of Schwyz and Glarus.
January 1438: The county of Sargans signs a treaty of association with Glarus and Schwyz.
January 1452: St. Gallen Abbey becomes a protectorate of the Swiss Confederation.
January 1455: The city of Schaffhausen allied with six of the Swiss confederates in 1454.
January 1459: The Barons of Sax-Forstegg made an alliance with the Old Confederation in 1458.
January 1464: The Imperial City of Rottweil becomes an ally of the Swiss Confederation.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
January 1482: Freiburg joined the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1481.
January 1484: Sargans is sold to the Swiss Confederation.
January 1499: In 1497 and 1498 the Three Leagues allied with the Old Swiss Confederacy after the Habsburgs acquired the possessions of the extinct Toggenburg dynasty in 1496, siding with the Confederacy in the Swabian War three years later.
January 1502: Schaffhausen became a full member of the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1501.
January 1514: The canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden, like Ausserrhoden, has been a member of the Confederation since 1513.
January 1516: Mühlhausen (Alsace) becomes an ally of the Swiss Confederation.
January 1548: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of the Reformation.
January 1549: From 1548, the County of Gruyeres was a part of the Swiss Confederation.
January 1554: The lavish lifestyle of the Counts of Gruyeres gradually led to financial difficulties. After 1500, various areas had to be sold: the Lordship of Aigremont to Bern, the Lordship of Jaun and the Lordship of Corbières to Fribourg.
January 1580: Prince-Bishop of Basel Jakob Christoph Blarer von Wartensee allied himself with the seven Catholic towns of the Old Confederation in 1579.
January 1616: In 1615 the city of Zurich acquired the County of Sax-Forstegg.
June 1707: In 1707, following the death of Marie de Nemours, Duchess of Nemours and Princess of Neuchâtel, the city, which was on the border of the Swiss Confederation, had to choose her successor from among fifteen claimants.the Protestant cantons of the Swiss Confederation encouraged Neuchâtel to select the Protestant King Frederick I of Prussia.
Disestablishment
January 1803: Rottweil acquired by the Duchy of Württemberg.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 38-39
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 42-43
Krumenacker, Y. (2008): La Guerre de Trente Ans, Paris, Ellipses, pp. 146-147
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, Munich (Germany), p. 281
Schmiele, E. (1887): Zur Geschichte des schwedisch-polnischen Krieges von 1655 bis 1660, Berlin (Germany), p. 5
Zeller, O. (2024): La Bresse et le pouvoir: Le Papier journal de Jean Corton, syndic du tiers état (1641-1643), Dijon (France), p. 12

 Swiss Associate Territories
Swiss Associate Territories