If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
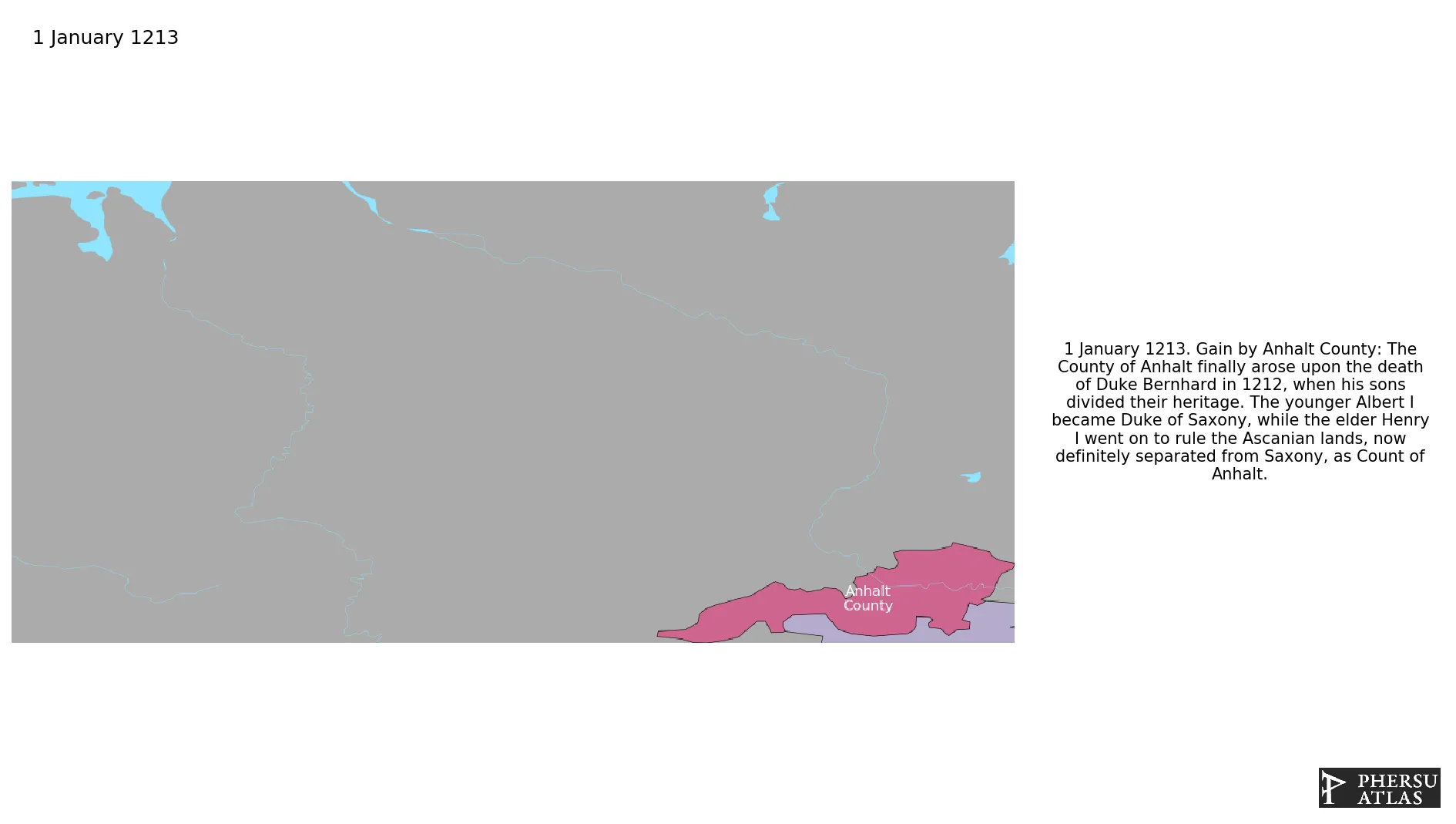
Anhalt County
Anhalt Duchy
Establishment
January 1213: The County of Anhalt finally arose upon the death of Duke Bernhard in 1212, when his sons divided their heritage. The younger Albert I became Duke of Saxony, while the elder Henry I went on to rule the Ascanian lands, now definitely separated from Saxony, as Count of Anhalt.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
1.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
1.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1241: The Mongols invaded the Holy Roman Empire without major clash of arms.The army invaded eastern Germany, and crossed the March of Moravia in April-May 1241.
June 1241: The Mongols left eastern Germany and Moravia.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
2.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
2.1.1.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
May 1631: After the Swedish occupation of Frankfurt an der Oder in April 1631, Pomerania, Mecklenburg, Brandenburg and Saxony signed alliance treaties with Sweden.
September 1631: On September 17, 1631, the Swedish army under Gustav Adolf met the troops of the Catholic League under Tilly in the Battle of Breitenfeld north of Leipzig.
2.1.2.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
2.1.2.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1637: After the death of Swedish King Ferdinand II, his son and successor Ferdinand III brought the Swedish troops back to Pomerania, leaving the territories occupied by Sweden in Germany.
December 1643: In 1643 Swedish general Torstensson invaded Moravia for the second time.
January 1644: In 1643, when the Torstensson War broke out, the Swedish military focused entirely on Denmark and thus enabled an imperial offensive to Jutland.
November 1644: In 1644 Swedish field marshal Torstenson led his army for the third time into the heart of Germany and routed the imperials at the battle of Jüterbog.
July 1647: The Imperial Army liberated the fortress of Egra (today known as Cheb in the Czech Republic) from Swedish occupation.
June 1648: In May 1648, there was the last major field battle of the Thirty Years' War between French-Swedish and Imperial-Bavarian armies near Augsburg.
2.1.3.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
October 1648: With the Peace of Westphalia Sweden received Western Pomerania (henceforth Swedish Pomerania), Wismar, and the Prince-Bishoprics of Bremen and Verden as hereditary fiefs. Sweden evacuated the remnant territories it had occupied in the Holy Roman Empire.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
May 1806: In April 1806, Alexius Friedrich Christian von Anhalt-Bernburg became the first of the princes of Anhalt to become duke.
3.1.War of the Fourth Coalition
Was a war between the French Empire and a coalition of European monarchies, mainly Prussia and Russia.
3.1.1.Prussian Campaign (War of the Fourth Coalition)
Was a French military campaign in Prussia during the War of the Fourth Coalition.
October 1806: Napoleon entered Berlin on 27 October 1806.
3.1.2.Peace of Tilsit
Were a series of treaties that ended the War of the Fourth Coalition.
July 1807: The treaty signed between Prussia and France at Tilsit, following the War of the Fourth Coalition, was highly disadvantageous to Prussia. As a result of this agreement, the Kingdom lost most of its Polish territories to the newly created Duchy of Warsaw. Additionally, it ceded most of its territories in central Germany and the Rhineland to France, the Grand Duchy of Berg, and the Kingdom of Westphalia. The remnant territories occupied by France in Germany were evacuated.
3.2.War of the Sixth Coalition
Was a war between France and a a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States. The coalition emerged after the decimation of the French army in the French invasion of Russia. The coalition ultimately invaded France and forced Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile.
August 1813: In the Battles of Großbeeren and neighboring Blankenfelde and Sputendorf an allied Prussian-Swedish army under Crown Prince Charles John - formerly Marshal of France Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte - defeated the French.
3.3.Congress of Vienna
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
June 1815: Territories awarded to the Duchy of Anhalt by the Congress of Vienna.
Were a series of wars that resulted in the creation of the German Empire under Prussian leadership in 1871.
4.1.Franco-Prussian War
Was a war that saw the Second French Empire fight against an alliance of German states led by the Kingdom of Prussia. The war was caused by the struggle over dominance in continental Europe between Prussia and France. The German states were victorious and in 1871 merged to form the German Empire. France was occupied and forced to cede Alsace-Lorraine to Germany.
4.1.1.Unification of Germany (1871)
Was the unification of 25 German states into the German Empire under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
January 1871: Unification of Germany into a German Empire with tight political and administrative integration, replacing the decentralized German Confederation and Holy Roman Empire, was officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
January 1316: The family ruling in Aschersleben became extinct in 1315, and this district was subsequently incorporated in the neighboring Bishopric of Halberstadt.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
January 1668: Jever is annexed to Anhalt-Zerbst.
January 1794: Jever is annexed to Russia.
Disestablishment
January 1871: Unification of Germany into a German Empire with tight political and administrative integration, replacing the decentralized German Confederation and Holy Roman Empire, was officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France.
Selected Sources
Dreißigjähriger Krieg. Austria Forum. Retrieved on 30 march 2024 on https://austria-forum.org/af/AustriaWiki/Drei%C3%9Figj%C3%A4hriger_Krieg
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, C.H. Beck München, pp. 28-31
O'Mahony, C. I. (2013). War within the Walls: Conflict and Citizenship in the Murals of the Hôtel de Ville, Paris. Journal of War & Culture Studies, 6(1), 6-23.
Schmidt, G. (2006): Der Dreißigjährige Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 65
Spindler, M. (2017): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, Munich (Germany), p. 266
Strakosh-Grassmann, G. (1893): Der Einfall der Mongolen in Mitteleuropa in den Jahren 1241 und 1242, Innsbruck (Austria), pp. 53-67
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.191-195
Westfälischer Friede - Vertrag von Osnabrück, https://de.wikisource.org/wiki/Westf%C3%A4lischer_Friede_%E2%80%93_Vertrag_von_Osnabr%C3%BCck
.svg.png.webp)
 anhalt
anhalt