This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Macedonia and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an ancient kingdom centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty. During the reign of the Argead King Philip II (359-336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. Philip II's son Alexander the Great, campaigned in Asia and was able to conquer the Achaemenid Empire. He then campaigned further East as far as the Indus River. Alexander died in 323 BC. In the following years the Macedonian Empire was divided among the generals of Alexander. Macedonia continued to exist as a successor state of the Macedonian Empire in the region of Macedon and in Greece (see Antigonid Macedonia).
Establishment
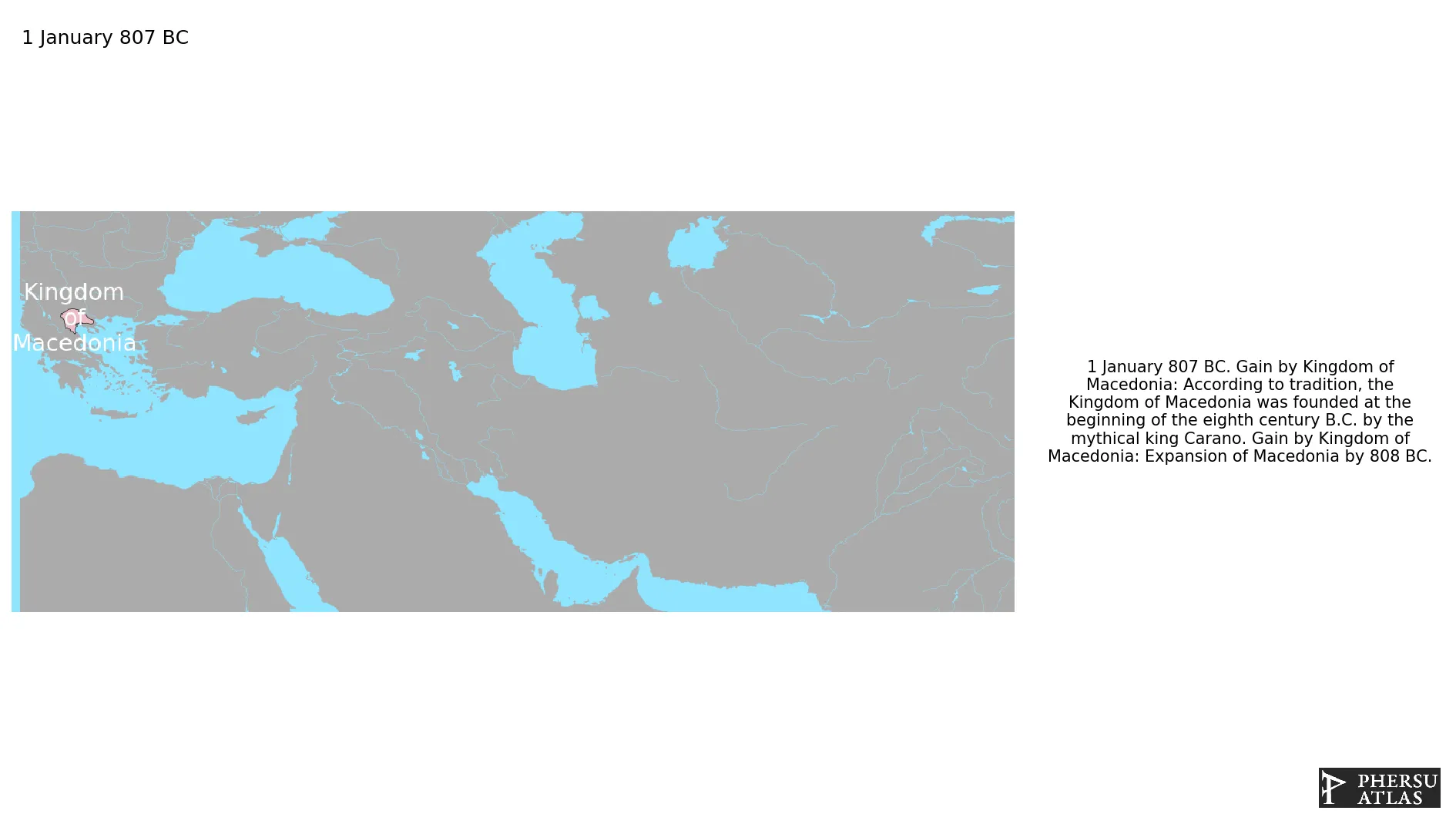
January 807 BC: According to tradition, the Kingdom of Macedonia was founded at the beginning of the eighth century B.C. by the mythical king Carano.
January 807 BC: Expansion of Macedonia by 808 BC.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Expansion of Macedonia under King Philip II.
January 357 BC: Expansion of Macedonia by 358 BC.
January 357 BC: Battle of Erigon Valley: took place in 358 BC between the Dardanians under Bardyllis and the Macedonians under Philip II. Macedonian northwestern frontier enlarged as far as Lake Lynkcesta (Lake Ohrid).
January 357 BC: The following year (358 BC), Philip heard that the Paionian king, Agis, had died. Taking advantage of their political disarray and transition of power, Philip marched his army into Paionia, where he defeated the Paionians. He then compelled the tribe to swear allegiance to Macedon. Macedonian northwestern frontier enlarged as far as Lake Lynkcesta.
January 355 BC: Galepsos (Thrace) was destroyed 356 BC by Philipp II of Macedon.
January 355 BC: Philip II of Macedonia conquered Oisyme in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: Pistyros was destroyed by Philipp II of Macedon in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: Sirra was destroyed by Philipp II of Macedon in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: It remained formally independent from the kingdom of Macedonia in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: Expansion of Macedonia by 356 BC.
January 355 BC: In 356 BC Philip of Macedon campaigned in Thrace, capturing the town of Krinides.
January 355 BC: Pydna, a city in ancient Macedonia, was captured by Philip II of Macedon in either 357 or 356 BC through treachery. This event marked an important conquest for Philip as he expanded his kingdom's territory.
January 355 BC: Philip II handed Potidea over to the Olynthians.
January 355 BC: According to Plutarch, an army under Parmenion defeated the Illyrian king Grabos in 356 BC, shortly after the conclusion of the siege of Potidea. Grabos then became a subject ally of Macedon.
January 355 BC: Crenides was close to Mount Pangaion with its rich gold veins and to another Thasian colony, Datos. The two colonies provoked the Thracians but at the same time gave Philip II of Macedon the justification for penetrating the area and founding Philippi in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: Krenides was close to Mount Pangaion with its rich gold veins and to another Thasian colony, Datos. The two colonies provoked the Thracians but at the same time gave Philip II of Macedon the justification for penetrating the area and founding Philippi in 356 BC
January 355 BC: Apollonia (Thrace) was destroyed 356 BC by Philipp II of Macedon.
January 355 BC: In 356 BC, Philip II besieged and captured Potidea.
January 355 BC: Phagres was destroyed by Philipp II of Macedon in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: Berga was destroyed by Philipp II of Macedon in 356 BC.
January 355 BC: Myrkinos was destroyed 356 BC by Philipp II of Macedon.
January 354 BC: By 355 BC, Elimiotis was part of the Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 353 BC: During the 355-354 BC siege of Methone, Philip II lost his right eye to an arrow wound, but managed to capture the city.
January 352 BC: Methone was besieged by the Macedonian king Philip II, who thereby lost his eye by an arrow (354/3 BC). After their surrender King Philip allowed the inhabitants to leave the city.
January 351 BC: In 352 BC Phillip II besieged the city of Heraion Teichos. Athens decided to send a fleet of forty triremes and to levy sixty talents in order to help the city, but the fleet never set sail. Only later a much smaller fleet of ten ships and money of five talents were sent. But Philip captured the city.
January 351 BC: The Thracian tribe of the agrianes, neighbors of Paioia, and their king, Langarus, appear from 352 BC as allies of Philip II.
January 350 BC: In 352/1 BC, the city of Perinthos, along with Byzantion and Amadokos, formed an alliance with Philip II of Macedonia. This alliance was significant as it strengthened Philip II's influence in the region and allowed for greater cooperation between the city-states.
January 350 BC: In 352/1 BC, Perinthos, Byzantion, and Amadokos formed an alliance with Philip II of Macedonia. Perinthos was a city in Thrace, Byzantion was an ancient Greek city, and Philip II was the king of Macedonia.
January 350 BC: In -351 BC, Daminon Teichos was part of the territory that went to the Kingdom of Macedonia. During the same period, Perinthos, Byzantion, and Amadokos formed an alliance with Philip II of Macedonia.
January 349 BC: Sale was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Around 350 BC, Philip II of Macedon took Neapolis.
January 349 BC: Around the year 350 BC, Philip II of Macedonia occupied the port of Abdera.
January 349 BC: Dikaia (Thrace) was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Stryme was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Some scholars date from 350 BC the Macedonian direct control of Tymphaea, another border area between Epirus and Macedon.
January 349 BC: Zone was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Mesambria (Thrace) was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Maroneia was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Kypsela was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Drys was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Bergepolis was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 349 BC: Ainos was taken by Macedon around 350 BC.
January 343 BC: In around 344 BC, the city of Hypata, located in Thessaly, Greece, came under the rule of the Kingdom of Macedonia, led by King Philip II. This marked an expansion of Macedonian influence in the region.
January 343 BC: In around 344 BC, Hypata came under Macedonian rule.
January 341 BC: In 342 BC, Philip II of Macedonia conquered a Thracian city in modern-day Bulgaria, which was then renamed Philippopolis (modern Plovdiv). This strategic move expanded the territory of the Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 341 BC: Expansion of Macedonia by 342 BC.
January 339 BC: In 340 BC the Macedonians took over the island of Skyros.
January 338 BC: The year 339 BC proved a culminating year for the Second Scythian Kingdom, and the beginning of its decline. The war with Philip II of Macedon ended in a victory for Philip (the father of Alexander the Great).
January 337 BC: Panormos was conquered by the Kingdom of Macedon (338-146 BC).
January 337 BC: In 338 BC it was besieged by Philip II of Macedon. With the assistance of Corinth and Athens, it escaped complete domination at Philip's hands, but was nevertheless forced to accept a Macedonian garrison.
January 337 BC: It was eventually ceded to Philip in 338 BC.
January 337 BC: Peparethos was conquered by the Kingdom of Macedon (338-146 BC).
January 335 BC: Pandosia was conquered in -336 by Philip II of Macedonia.
January 335 BC: The territory referred to is the city of Thebes, which was conquered in -336 from Philip II of Macedonia by his son, Alexander the Great. This event marked the end of Theban independence and its incorporation into the Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 335 BC: Ikos passed to the dominance of Macedonia the following century, following the Greek conquests of King Philip II.
1.1.Third Sacred War
Was fought between the forces of the Delphic Amphictyonic League, principally represented by Thebes, and latterly by Philip II of Macedon, and the Phocians.
January 347 BC: Anthemous was given by Philip of Macedon to the Olynthians.
January 347 BC: The empty territory bordering Macedonia and Thessaly was probably controlled by Macedonia.
January 346 BC: Teithronion was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Dioikismos (dispersion of the inhabitants) of Stiris caused by the invasion by Macedonian forces.
January 346 BC: Phanoteus was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Parapotamioi was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Dioikismos (dispersion of the inhabitants) of Medeon caused by the invasion by Macedonian forces.
January 346 BC: Dioikismos (dispersion of the inhabitants) of Lilaia caused by the invasion by Macedonian forces.
January 346 BC: Abai was occupied a second time by the Boeotians in the Sacred or Phocian War in 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Antikyra was destroyed in 346 BC by Philip II of Macedon amid the Third Sacred War.
January 346 BC: Charadra was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Daulis was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Drymos was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Erochos was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Neon/Tithorea was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Elateia (Phokis) was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Dioikismos (dispersion of the inhabitants) of Troneia caused by the invasion by Macedonian forces.
January 346 BC: Dioikismos (dispersion of the inhabitants) of Ledon caused by the invasion by Macedonian forces.
January 346 BC: Hyampolis was destroyed in 480 BC and reappeared around 346 BC.
January 346 BC: Dioikismos (dispersion of the inhabitants) of Phlygonion caused by the invasion by Macedonian forces.
July 346 BC: Philip II made a truce with Phalaikos (ruler of Phocis) on 19 July. Phalaikos surrendered Phocis to Macedon, in return for being allowed to leave.
January 345 BC: Philip II of Macedon controlled the city of Nicaea, near Thermopylae, since 346 BC.
January 345 BC: By the end of 346 BC Philip II of Macedon left the territories occupied in Phocis.
January 345 BC: Some time after its inhabitants were dispersed during the Third Sacred War, the city of Medeon began to be resettled and came back into existence.
January 345 BC: Some time after its inhabitants were dispersed during the Third Sacred War, the city of Lilaia began to be resettled and came back into existence.
January 345 BC: Serrion Teichos was one of the fortresses conquered by Philip II in 346 BC.
January 345 BC: The Polis of Abai was destroyed in 480 BC during the Greco-Persian Wars. It was later reestablished around 346 BC.
January 345 BC: Reconstruction of Antikyra.
January 345 BC: Charadra was destroyed in 480 BC, but reappeared around 346 BC.
January 345 BC: Daulis was destroyed in 480 BC, but reappeared around 346 BC.
January 345 BC: Drymos was destroyed in 480 BC, but reappeared around 346 BC.
January 345 BC: Elateia (Phokis) was destroyed in 480 BC, but reappeared around 346 BC.
January 345 BC: Erochos: Destroyed in 480 BC.
January 345 BC: Hyampolis: Destroyed in 480 BC.
January 345 BC: Some time after its inhabitants were dispersed during the Third Sacred War, the city of Ledon began to be resettled and came back into existence.
January 345 BC: Neon/Tithorea: Destroyed in 480 BC.
January 345 BC: Parapotamioi: Destroyed in 480 BC.
January 345 BC: Phanoteus was destroyed in 480 BC.
January 345 BC: Some time after its inhabitants were dispersed during the Third Sacred War, the city of Phlygonion began to be resettled and came back into existence.
January 345 BC: Some time after its inhabitants were dispersed during the Third Sacred War, the city of Troneia began to be resettled and came back into existence.
January 345 BC: Teithronion was destroyed in 480 BC.
January 345 BC: Some time after its inhabitants were dispersed during the Third Sacred War, the city of Stiris began to be resettled and came back into existence.
1.1.1.Olynthian War
Was a war between the Kingdom of Macedon and the Chalkidian League.
June 348 BC: Philip II seems to have methodically worked his way around the 32 cities of the League, leaving Olynthos to the end. By the spring of 348 BC, the western part of Chalkidiki had been lost.
October 348 BC: By September the siege was over, and the Chalkidian league had been annihilated.
November 348 BC: The same fate awaited the other Chalkidian cities that had not submitted to him. Philip then incorporated Chalkidike into the Macedonian state.
1.1.2.Peace of Philocrates
The Peace of Philocrates aknowledged the territorial conquests of Macedonia in Phocis and Thrace.
January 345 BC: On July 19, Philip II of Macedon made a truce with Phalaikos, the ruler of Phocis. As part of the agreement, Phalaikos surrendered the region to Macedonia.
1.2.Philip II's campaign in Greece (Fourth Sacred War)
Was the military campaign of Macedonia king Philip II in Greece during the Fourth Sacred War.
April 339 BC: The Thebans seized the town of Nicaea near Thermopylae.
August 338 BC: Philip II of Macedon advanced into Boeotia in an attempt to march on Thebes and Athens.
August 338 BC: The Island of Limnos is conquered by Macedonia.
August 338 BC: Athenai was subjugated by Philip II.
January 337 BC: The battle of Chaeronea (338 BC) was fought in 338 BC, in Boeotia, between Macedonia under Philip II and an alliance of city-states led by Athens and Thebes. The battle ended with a decisive victory of the Macedonians. Philip had no intention of conquering any territory and soon the Macedonian armies left southern Greece. After the battle, Macedon established hegemony over the majority of Southern Greece (except Sparta).
January 337 BC: Seleinous was conquered by the Kingdom of Macedon (338-146 BC).
Were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states.
2.1.Greek reconquests after the Second Persian Invasion of Greece
The final defeat of the Persians at Mycale during the Second Persian Invasion of Greece encouraged the Greek cities of Asia to revolt, and the Persians lost all of their territories in Europe.
January 478 BC: The Kingdom of Macedonia regained independence following the defeat and withdrawal of the Achaemenid Empire in 479 BC.
Was a war between Athens and the Kingdom of Macedonia that preceded the Peloponnesian War of 431-404 BC.
January 432 BC: The Athenian Empire captured the Macedonian cities Therma and Beroea.
January 432 BC: King Perdiccas II retaliated against Athens by supporting the rebellion of their allies in Chalcidice. As a result, he was able to gain control of the strategic city of Potidaea in -433.
January 430 BC: Sitalces was a Thracian king who brokered a peace treaty in -431 between Athens and Potidaea, a city in Chalcidice. As a result of the treaty, much of Chalcidice's territory was ceded to the Athenian Empire.
January 430 BC: Therma was returned to Macedonia.
January 430 BC: Macedonian conquest of Kyrrhos.
January 430 BC: Macedonian conquest of Ichnai.
January 430 BC: Macedonian conquest of Edessa.
Was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world.
January 429 BC: Herakleion passed into Athenian control in the years 430/29, 425/4.
January 428 BC: Herakleion conquered by Macedon.
January 424 BC: Platamon passed into Athenian control.
January 423 BC: Platamon conquered by Macedonia.
January 412 BC: After Athenian alliance with Perdiccas II in 413 BC it became again a city of Macedon.
January 409 BC: King Archelaus I of Macedonia besieged the city by Pydna.
Mygdonia was conquered by Macedonia in the V Century BC.
January 399 BC: Mygdonia was conquered by Macedonia in the Vth Century BC.
Was a war between Sparta and the Chalcidian League.
January 399 BC: The Macedonian capital of Pella fall into the hands of the Chalcidicean League's forces.
January 378 BC: As a result of the Olynthian War, the Chalkidiki League was dissolved by Sparta, and most of the cities of Chalkidike and the Chalkidiki League came under the sovereignty of the Macedonian king Amyntas III.
Was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire.
January 361 BC: The Macedonian king Perdiccas succeeded in 362 BC ultimately to establish Macedonia as the protecting power of the city.
Was a war between the Second Athenian League and the allied city-states of Chios, Rhodes, Cos and Byzantion.
January 356 BC: King Philip II of Macedon, father of Alexander the Great, used the war as an opportunity to further the interests of his Macedonian kingdom in the Aegean region. In 357 BC, Philip captured Amphipolis.
January 356 BC: Traïlos: assumed to be conquered at the same time of Amphipolis.
January 355 BC: In 356 BC, Philip II of Macedon took the city of Crenides, refounding it as Philippi.
January 355 BC: Both Pydna and Potidaea were conquered over the winter and occupied by Macedonia.
In 336 BC Philip II of Macedon was authorized by the League of Corinth as its Hegemon to initiate a sacred war of vengeance against the Persians for desecrating and burning the Athenian temples during the Second Persian War, over a century before.
January 335 BC: In 336 BC Philip II of Macedon was authorized by the League of Corinth as its Hegemon to initiate a sacred war of vengeance against the Persians for desecrating and burning the Athenian temples during the Second Persian War, over a century before.
Were a series of conquests that were carried out by Alexander III of Macedon (known as Alexander "The Great") from 336 BC to 323 BC. Alexander conquered the Persian Empire and also expanded his kingdom into the Indian Subcontinent.
January 331 BC: Naukratis was integrated into the Macedonian Empire.
10.1.Alexander's Balkan campaign
Was a campaign waged by Alexander the Great in the Balkan against a number of rebellious vassals of the Macedonian kingdom.
June 335 BC: Shortly before the battle of Pelion in -335, the city of Pelion was occupied by the Dardani, a Illyrian tribe. The battle took place between the Dardanian forces and the Macedonian army led by King Philip II of Macedon.
September 335 BC: Siege of Pelium.
January 334 BC: Odessos surrendered to Alexander the Great in 335 BC.
January 334 BC: In 335 BC, Alexander the Great, the king of Macedonia, defeated the Thracian tribe of the Triballi at Haemus Mons and along the Danube. This victory led to the surrender of the Triballi on Peuce Island.
10.2.Alexander's War in Persia
Were the military campaigns by Alexander the Great King of Macedon in the territories of the Achaemenid Empire.
10.2.1.Conquest of the Achaemenid Empire
Was a military campaign by Alexander the Great King of Macedon in Asia that resulted in the conquest of the Achaemenid Empire.
June 334 BC: Troy conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 334 BC: Battle of the Granicus.
July 334 BC: Sardes conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 334 BC: Ephesus conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 334 BC: Siege of Miletus.
October 334 BC: Siege of Halicarnassus.
January 333 BC: Phaselis conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 333 BC: Lycia conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
February 333 BC: Perge conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
February 333 BC: Termessos conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
May 333 BC: Gordion conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
October 333 BC: Tarsus conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
November 333 BC: Soli conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
November 333 BC: Battle of Issus. Alexander the Great decisively defeats the Persian army of Darius.
December 333 BC: Alexandretta or Alexandria near Issus conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: Cilician Gates conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: The various kingdoms of Cyprus became allies of Alexander following his victorious campaigns at Granicus (334 BC) and Issus (333 BC).
January 332 BC: Aradus Island conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: Cydnos River conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: Ankyra (Ankara, Turkey) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: Kelainai (near Dinar, Turkey) in Pisidia conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: Side conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 332 BC: Aspendos conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
February 332 BC: Byblos (40 km north of Beirut, Lebanon) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
February 332 BC: Sidon (Lebanon), Phoenicia, conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 332 BC: Siege of Tyre. The city fell to the Macedonians.
November 332 BC: Siege of Gaza. The city fell to the Macedonians.
January 331 BC: Damascus conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 331 BC: Pelusium (Port Said, Egypt) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 331 BC: Jerusalem conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
February 331 BC: Memphis conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
February 331 BC: Foundation of Alexandria.
March 331 BC: Siwa conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 331 BC: Tigris conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 331 BC: Thapsacus (Tipsah) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 331 BC: Edessa, or Urhai (Urfa, Turkey), conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 331 BC: Harran conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
October 331 BC: Battle of Gaugamela. Alexander's decisive victory leading to the collapse of the Persian Empire.
November 331 BC: Arbela (Arbil/Irbil, Iraq) in Mesopotamia conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
November 331 BC: Babylon conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 330 BC: Alep conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 330 BC: Susa conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 330 BC: Battle of the Persian Gate.
February 330 BC: Persepolis conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 330 BC: Caspian Gates (between modern Eyvanakey and Aradan or Tehran and Semnan, Iran, Media/Parthia border) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 330 BC: Deh Bid Pass conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 330 BC: Rhagae (Rey, Iran) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 330 BC: Ecbatana (Hamadan, Iran) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 330 BC: Thara is the city where the Persian king Darius III was killed. Although Alexander appeared as the Achaemenid ruler, there is no doubt that the Achaemenid Empire had come to an end at the latest with the assassination of Darius by the satrap Bessos (330 BC).
August 330 BC: Alexander's detour from modern Semnan to the Dasht-e-Kavir desert ―Parthia.
January 329 BC: Pasargad conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
10.2.2.Campaigns of Alexander the Great against the Achaemenid rebel Satrapies
Were a series of military campaign by Alexander the Great, King of Macedon, in the regions of the Achaemenid Empire that had become de facto independent after the collapse of the Empire.
August 330 BC: Hecatompylos conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 330 BC: Zadracarta conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
September 330 BC: Hyrcanian campaign.
October 330 BC: Susia conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
October 330 BC: Artacoana conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
November 330 BC: Phrada and Alexandria Prophthasia (Farah, Afghanistan) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 329 BC: Alexandria and whole Egypt including Cyrenaica conquered by Rashidun Caliphate.
January 329 BC: Nisa-Alexandroupolis (probably Bagir Village, 18 km southwest of Ashgabat, Turkmenistan) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
May 329 BC: Kapisa, Alexandria in the Caucasus conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
May 329 BC: Ortospana and Kabura conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
May 329 BC: Cophen River conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 329 BC: Foundation of Alexandria Tarmita (Termez/Termiz, Uzbekistan) - Sogdia (or Transoxiana).
June 329 BC: Bactra conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 329 BC: Oxus River conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 329 BC: The Kambojas entered into conflict with Alexander the Great as he invaded Central Asia.
June 329 BC: Khawak Pass (leading from Badakhshan to Panjshir valley, 100 km northeast of Kabul, Afghanistan) conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 329 BC: Drapsaca conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 329 BC: Nautaca conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
July 329 BC: Maracanda conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 329 BC: Jaxartes River conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
August 329 BC: Fergana Valley conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
November 329 BC: Territories north of the Jaxartes River are conquered by the Kingdom of Macedonia.
December 329 BC: Bactra conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
December 329 BC: Tribactra conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 328 BC: Alexander the Great founded the city of Alexandria in Arachosia (modern-day Ghazni, Afghanistan) as part of his conquests in the region.
January 328 BC: Kingdom of Kapisa conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 328 BC: Foundation of Alexandria Oxiane (perhaps modern-day Ai Khanum).
December 328 BC: Sogdian campaigns and attack of the Sogdian settlements in the Gissarskiy Range.
January 327 BC: Nautaca conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 327 BC: Alexandria in Margiana was founded by Craterus and refounded by Antiochus I and called Antiochia.
April 327 BC: Siege of the Sogdian Rock or Rock of Sisimithres (where Oxyartes and Roxana were located).
December 327 BC: Shang-La Pass, Pakistan, conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 326 BC: Cophen River conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
June 326 BC: The Rebel Achaemenid Satrapies are conquered by the Kingdom of Macedonia.
January 325 BC: Modern Hund, Pakistan, conquered by Kingdom of Macedonia.
10.3.Alexander's War in India
After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the Indian subcontinent.
June 326 BC: Battle of Hydaspes River against Purava king Porus. Alexander the Great annexed large areas of the Punjab region from the Hydaspes to the Hyphasis (the entire Purava reign of Porus).
August 326 BC: In 326 BC, its king Puru (Por) was defeated by the Macedonian conqueror Alexander the Great in the Battle of Hydaspes.
January 325 BC: The King of Patala came to Alexander and surrendered. Alexander let him keep possession of his own dominions, with instructions to provide whatever was needed for the reception of the army.
March 325 BC: Mallian Campaign against the Malli of the Punjab. Alexander was defining the eastern limit of his power by marching down-river along the Hydaspes to the Acesines (now the Jhelum and Chenab), but the Malli and the Oxydraci combined to refuse passage through their territory. Alexander sought to prevent their forces meeting, and made a swift campaign against them which successfully pacified the region between the two rivers.
Military campaign of Chandragupta Maurya, founder of the Mauryan Empire.
January 322 BC: The Maurya Empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya, with help from Chanakya, at Taxila, a noted center of learning.
January 316 BC: Expansion of the Magadha Kingdom until 317 BC.
January 316 BC: The Greek generals Eudemus and Peithon ruled in the Indus Valley until around 317 BC, when Chandragupta Maurya (with the help of Chanakya, who was now his advisor) orchestrated a rebellion to drive out the Greek governors, and subsequently brought the Indus Valley under the control of his new seat of power in Magadha.
Were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule his empire following his death.
12.1.Lamian War
Was a war fought by a coalition of cities including Athens and the Aetolian League against Macedon and its ally Boeotia. The war broke out after the death of the King of Macedon, Alexander the Great, and was part of a series of attempts to challenge Macedonian hegemony over mainland Greece.
January 321 BC: In 323 BC, Euphron the Younger, grandson of the tyrant Euphron, reintroduced democracy in Sikyon. However, the city was soon conquered by the Macedonians during the Lamian War, leading to the territory being incorporated into the Kingdom of Macedonia in -322.
12.2.Conquest of Cappadocia
Was a Macedonian military campaign against the Kingdom of Cappadocia that was still controlled by the Achaemenid ruler Ariarthes I.
April 322 BC: Eumenes conquered the province of Cappadocia Cappadocia, which was still held by the Persian prince Ariarathes I.
12.3.Second War of the Diadochi
Was the conflict between the coalition of Polyperchon (as regent of the Macedonian Empire), Olympias and Eumenes and the coalition of Cassander, Antigonus, Ptolemy and Lysimachus following the death of Cassander's father, Antipater (the old regent).
September 318 BC: Eumenes is allowed to withdraw from Nora and immediately allies himself with Polyperchon. Eumenes occupies Phenicia and builds a fleet.
September 318 BC: Polyperchon, the new Regent of the Empire, who decided to march his army south to force the Greek cities to side with him against Cassander and Antigonus.
November 318 BC: Eumenes secured the loyalty of 6,000 of Alexander's veterans, the Argyraspides and the Hypaspists, who were stationed in Cilicia.
September 317 BC: From Athens Polyperchon marched on Megalopolis which had sided with Cassander and besieged the city. The siege failed and he had to retreat losing a lot of prestige and most of the Greek cities.
November 317 BC: Polyperchon retreated to Epyrus and along with Olympia was able to reinvade Macedonia.
April 316 BC: Cassander's victory: Olympias surrenders and is executed; Alexander IV Aigos and Roxane are placed under house arrest, Polyperchon retreats to the Peloponnese.
November 316 BC: Antigonus bribed the Argyraspides who arrested and handed over Eumenes. Antigonus had Eumenes and a couple of his officers executed. With Eumenes's death, the war in the eastern part of the Empire ended.
12.3.1.Consolidation of the borders after the Second War of the Diadochi
Were a series of events and military operations after the Second war of the Diadochi that led to the consolidation of the borders between the successor states of the Macedonian Empire.
April 315 BC: Lysimachus controlled Thrace.
April 315 BC: Cassander controlled Macedon and large parts of Greece.
April 315 BC: Antigonus controlled Asia Minor and the eastern provinces.
April 315 BC: The kings of Cyprus, including Praxippos of Lapithos and Kyrenia, the Poumiaton of Kition and Stasioikos of Marion, allied themselves with Antigonus.
April 315 BC: Ptolemy controls Egypt, Syria, Cyrene and Cyprus.
January 731 BC: According to Plutarch, Methone was founded as a Greek colony in the year 733/732 BC.
January 699 BC: The year of foundation of the polity of Stolos/Skolos is based on peer group of similar polities in the same region (Phersu Atlas assumption).
January 699 BC: The year of foundation of the polity of Kalindoia is based on peer group of similar polities in the same region (Phersu Atlas assumption).
January 699 BC: The year of foundation of the polity of Strepsa is based on peer group of similar polities in the same region (Phersu Atlas assumption).
January 699 BC: The polity of Gonnos was established during classical times - earliest date due to mixed information (Phersu Atlas assumption).
January 699 BC: The excavations at Leibethra reveal that the acropolis was inhabited from the 8th century BC.
January 630 BC: In the VII Century Leibethra and this part of Pieria were conquered by the Makedonians.
January 599 BC: Pydna: assumed to be founded in similar times to other cities.
January 599 BC: Europos was a greek polis in ancient Makedonia. Assumed to be founded in similar times to other cities.
January 599 BC: Kyrrhos was a polis already in the IV Century BC.
January 599 BC: The year of foundation of the polity of Edessa is based on peer group of similar polities in the same region (Phersu Atlas assumption).
January 599 BC: Therme was a Greek city founded by Eretrians or Corinthians in late 7th century BC.
January 599 BC: Ichnai was a greek polis in ancient Makedonia from 600 BC.
January 510 BC: In 512/511 BC, the Persian general Megabyzus forced the Macedonian king Amyntas I to make his kingdom a vassal of the Achaemenids.
January 498 BC: Achaemenid Persian hegemony over Macedonia was briefly interrupted by the Ionian Revolt (499-493 BC).
January 491 BC: In 492 BC, following the Ionian Revolt, the Persian general Mardonius firmly re-tightened the Persian grip in the Balkans.
January 420 BC: Heracleium passed under Athenian control.
January 398 BC: After Archelaus's death, the inhabitants of Pydna moved back to their old seaside site.
January 391 BC: Bardylis, king of the Dardanian Kingdom, defeated Macedonians and Molossians several times. At this time they were strong enough to rule Macedonia through a puppet king in 392-391 BC.
January 390 BC: Bardylis, a powerful king of the Dardanian Kingdom, defeated the Macedonians and Molossians multiple times. As a result, they were able to exert control over Macedonia by installing a puppet king in 392-391 BC. This period marked a significant shift in power dynamics in the region.
January 355 BC: Philip II handed Potidea over to the Olynthians.
January 329 BC: Pandosia conquered by Epirus.
January 322 BC: A smalle (northern) region, which had been the sub-satrapy of Matiene, became Media Atropatene under Atropates, the former Achaemenid governor of all Media, who had by then become father-in-law of Perdiccas, regent of Alexander's designated successor.
January 322 BC: In 323 BC, Alexander the Great annexed Calindea and three neighboring territories to the kingdom of Macedonia.
January 322 BC: During the reign (336-323 BC) of Alexander the Great, son of Philip II, Byzantium was forced to recognize Macedonian suzerainty, but it regained its independence under the successors of Alexander the Great.
Disestablishment
April 315 BC: The kings of Cyprus, including Praxippos of Lapithos and Kyrenia, the Poumiaton of Kition and Stasioikos of Marion, allied themselves with Antigonus.
April 315 BC: Lysimachus controlled Thrace.
April 315 BC: Ptolemy controls Egypt, Syria, Cyrene and Cyprus.
April 315 BC: Cassander controlled Macedon and large parts of Greece.
April 315 BC: Antigonus controlled Asia Minor and the eastern provinces.
Selected Sources
Assumption: most of the Chalcidian cities aren't citied after the Olynthian war, so we interpret the dissolution of the League with most of the Chalcidian Peninsula falling into the sphere of influence of Macedon.
Buckley, T. (1996): Aspects of Greek History, 750-323 BC: A Source-based Approach, Psychology Press, p. 330
Cawkwell, G. (1978): Philip II of Macedon, London (UK), p. 142
Cawkwell, G. (1978): Philip II of Macedon, London (UK), pp. 147-166
Hansen, M. G. / Nielsen, T. H. (2004): An inventory of archaic and classic polities, Oxford University Press, pp. 1363-1364
Schwartzberg,J. E. (1992): A Historical Atlas of South Asia, Minneapolis (USA), Plate III.B.4b (p.18) and Plate XIV.1a-c (p.145).
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.37-39
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.40-42
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.43-45
Xenophon. Greek History, V, 2, 13

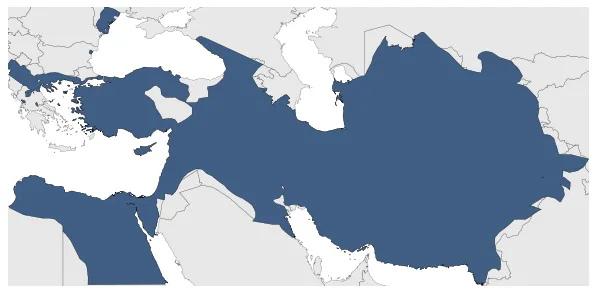
 Kingdom of Macedonia
Kingdom of Macedonia