Data
Name: Liege Prince-Bishopric
Type: Polity
Start: 986 AD
End: 1794 AD
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Liege Prince-Bishopric
Liege Prince-Bishopric
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
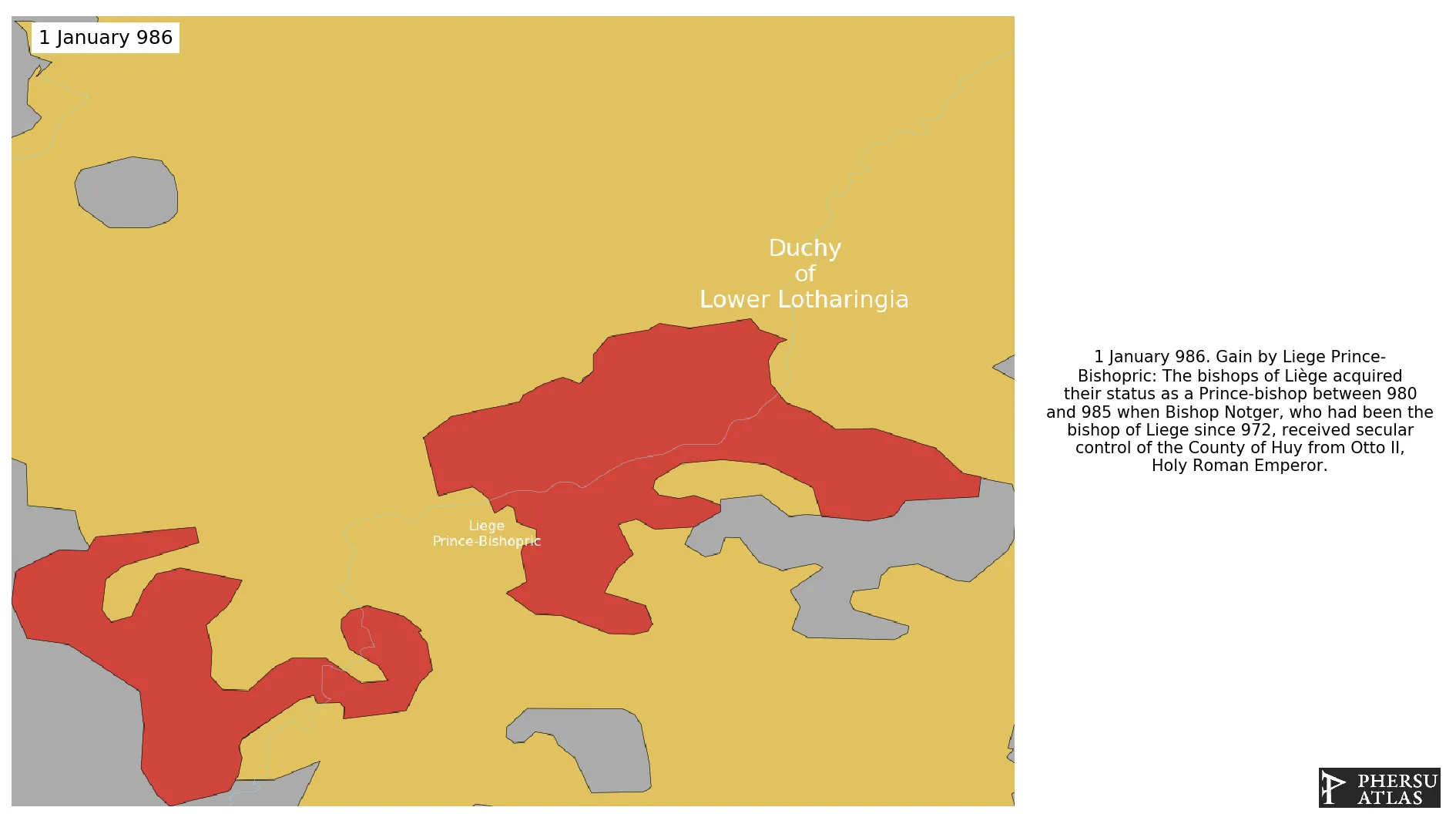
Was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. War of the Cow
Was a conflict in the Holy Roman Empire between the Prince-Bishopric of Liège under Bishop John of Enghien and the Marquisate of Namur under Marquis Guy of Dampierre. What began as a dispute over stolen property.
2. European wars of religion
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
2.1.1.Thirty Years' War Minor Scenarios
A series of conflicts related to the Thirty Years' War.
2.1.1.1.Invasion of Franche Comté (Ten Years War)
Was French invasion of modern-day Franche-Comté, at the time a possession of the Habsburg, during the Thirty Years' War.
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
2.1.2.1.Low Countries Front (France)
Was the Low Countries front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
Was a conflict between France and the Grand Alliance, a coalition including the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, and Savoy. It is considered the first war that saw fighting globally because battles occured in Europe, America, Africa and India.
2.2.1.Low Countries Theatre (Nine Years' War)
Was the Low Countries Theatre of the the Nine Years' War.
3. Franco-Dutch War
Was a war between the Kingdom of France and the Dutch Republic.
Were a series of treaties that ended various interconnected wars, notably the Franco-Dutch War.
4. War of the Spanish Succession
The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters. It was a global war, with fighting taking place in Europe, Asia, and America. At the end of the war, Philip II, who was the successor chosen by Charles II as a descendant of Charles' paternal half-sister Maria Theresa, became King of Spain and of its overseas empire. The Spanish possessions in Europe were partitioned between various European Monarchies.
4.1.Dutch and German Theatre (War of the Spanish Succession)
Was the theatre of war of the War of the Spanish Succession in Germany and the Low Countries.
Were a series of treaties to end the War of the Spanish Succession.
Was a treaty between France and the Holy Roman Empire, to end the War of the Spanish Succession.
5. War of the Austrian Succession
Was a European conflict caused by the succession to the Habsburg Domains. Maria Theresa succeeded her father Charles VI, and the opposition to female inheritance of the throne was a pretext for starting a war. It was a global conflict that saw fight in Europe, Asia, America and Africa.
5.1.Low Countries Theatre (War of the Austrian Succession)
Was the theatre of war in the Low Countries during the War of the Austrian Succession.
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
6. French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
6.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
Was a French military campaign in the Flanders.