If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire.
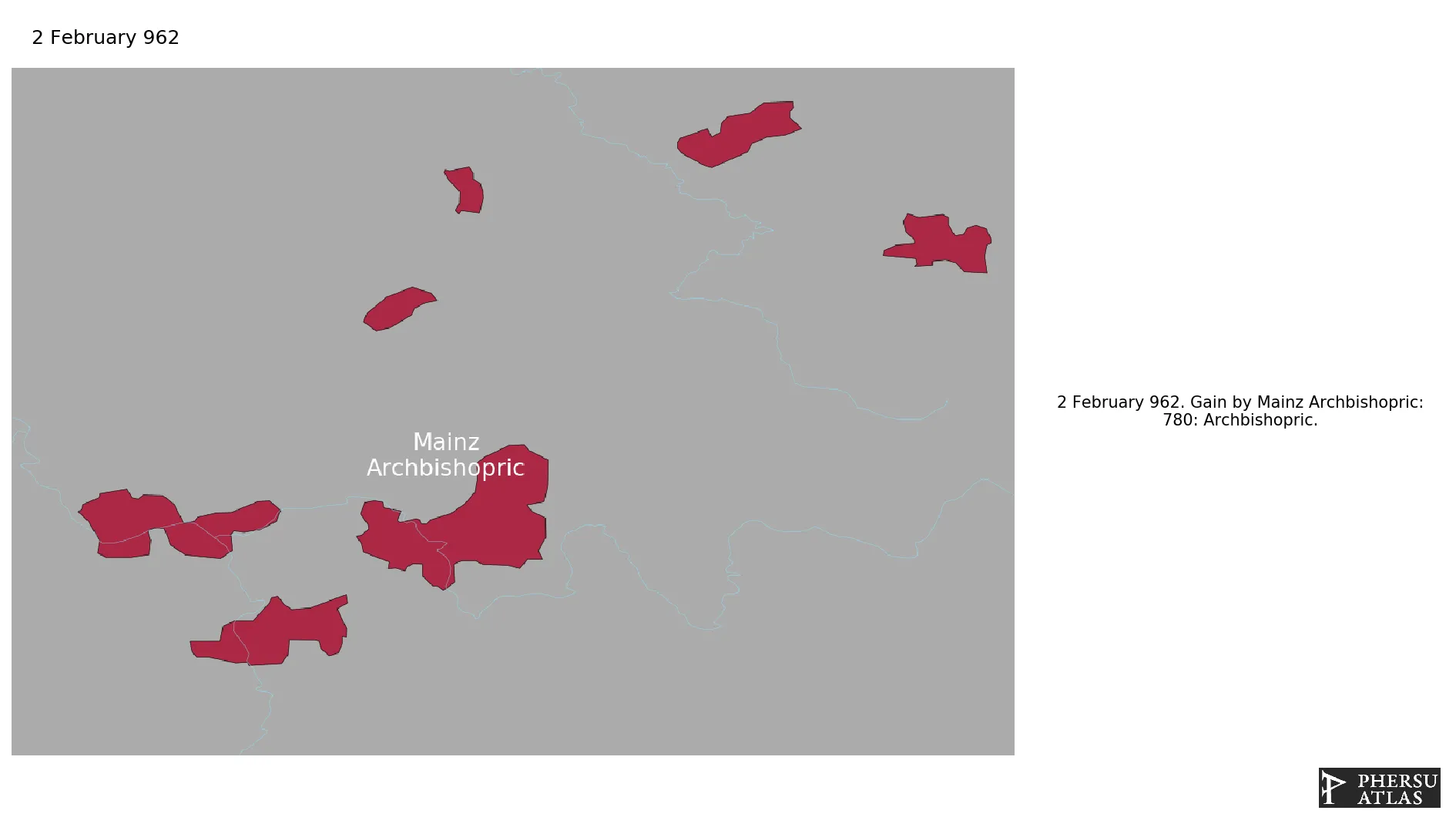
Establishment
February 962: 780: Archbishopric.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Frankish Kingdom was partitioned and reuinited several times as the Frankish rulers used to divide their territories equally among their heirs. This lead also to a number of wars and revolts.
1.1.Incoronation of Otto I
East Frankish King Otto I was crowned first Holy Roman Emperor.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
2.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
2.1.1.Bohemian-Palatine period
Was the first period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with a protestant revolt in Bohemia, at the time a territory of the Habsburg Domains.
2.1.1.1.War in Palatinate
Was the theatre of war in Palatinate during the first phase of the Thirty Years' War.
December 1621: German Protestant military leader Christian of Brunswick takes Amöneburg, not far from Mainz.
September 1622: From the summer of 1622, the territories of the Palatinate on the right bank of the Rhine were occupied by the troops of the Catholc League. Frederick V of the Palatinate eventually lost his electoral dignity on February 23, 1623, which was transferred to Maximilian of Bavaria.
2.1.2.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
September 1631: On September 17, 1631, the Swedish army under Gustav Adolf met the troops of the Catholic League under Tilly in the Battle of Breitenfeld north of Leipzig.
December 1631: Gustav Adolf II of Sweden crosses the Rhine with his army and besieges Mainz.
December 1631: Mainz conquered by sweden.
December 1632: Swedes under Wolf Heinrich von Baudissin take Deutz.
March 1633: The Swedish troops of Georg von Braunschweig-Lüneburg capture the city of Hameln.
June 1634: Conquest of Philippsburg by Sweden.
2.1.3.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
2.1.3.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1637: After the death of Swedish King Ferdinand II, his son and successor Ferdinand III brought the Swedish troops back to Pomerania, leaving the territories occupied by Sweden in Germany.
August 1640: In 1640, the Swedes led by field marshal Banér moved through Thuringia via Saalfeld into Hesse and further near the town of Fritzlar, which was reached on August 31, 1640.
October 1640: When 14 regiments arrived to reinforce the imperial army at the end of September 1640, the Swedish army left the territories it occupied in Germany (with the exception of Pomerania).
June 1648: In May 1648, there was the last major field battle of the Thirty Years' War between French-Swedish and Imperial-Bavarian armies near Augsburg.
2.1.3.2.Rhineland Front (France)
Was the Rhineland front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
May 1645: French General Thurenne advanced up to Bad Mergentheim, where a battle with German field Marshal Franz von Mercy would take place on May, 5 1645.
November 1645: The French evacuate their ephemeral conquests in Germany, systematically devastating them.
2.1.4.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
October 1648: With the Peace of Westphalia Sweden received Western Pomerania (henceforth Swedish Pomerania), Wismar, and the Prince-Bishoprics of Bremen and Verden as hereditary fiefs. Sweden evacuated the remnant territories it had occupied in the Holy Roman Empire.
2.2.Nine Years' War
Was a conflict between France and the Grand Alliance, a coalition including the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, and Savoy. It is considered the first war that saw fighting globally because battles occured in Europe, America, Africa and India.
2.2.1.Rhineland Theatre (Nine Years' War)
Was the Rhineland Theatre of the the Nine Years' War.
January 1689: Several towns fell to the French without resistance, including Oppenheim, Worms, Bingen, Kaiserslautern, Heidelberg, Speyer and, above all, the key fortress of Mainz.
June 1689: The French left the Rhineland region.
September 1689: In 1689, during the Nine Years' War, Charles V, Duke of Lorraine, cleared away the French threat on Frankfurt and besieged Mainz, which was under the control of the Mainz Archbishopric. The Marquis of Huxelles surrendered the town on September 8 after a two-month siege.
2.2.2.Peace of Ryswick
Were a series of treaties that ended the Nine Years' War.
September 1697: Peace of Ryswick (1697): France kept Strasbourg but returned Freiburg, Breisach, Philippsburg and the Duchy of Lorraine to the Holy Roman Empire.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
3.1.Central German Theatre
Was the theatre of war in central Germany of the Seven Years' War.
3.1.1.Rhineland Theatre (Seven Years' War)
Was the theatre of War in the Rhineland during the Seven Years' War.
July 1760: French general de Broglie launched an offensive in the direction of Hesse, defeating Duke Ferdinand of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel's forces on July 10 at the Battle of Korbach.
July 1760: The Battle of Warburg was fought on 31 July 1760 during the Seven Years' War. The battle was a victory for the Hanoverians and the British against the French army.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1803: Several exclaves of the Mainz Archibishopric, including Erfurt, are given to the Kingdom of Prussia.
February 1803: Reichsdeputationsschluss: the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the Reichstag (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Empire. The law secularized nearly 70 ecclesiastical states and abolished 45 imperial cities to compensate numerous German princes for territories to the west of the Rhine that had been annexed by France as a result of the French Revolutionary Wars.
January 1804: In 1803, the princes of the Leiningen-Dagsburg-Hardenburg line were compensated for their lost possessions in the Palatinate on the left bank of the Rhine with a new territory, which became part of the Principality of Leiningen. This territory was located in present-day Germany.
January 1804: With the secularization of the Archbishopric of Mainz in 1803, Karl Theodor Anton Maria von Dalberg was compensated by receiving the newly created principalities of Aschaffenburg and Regensburg and the County of Wetzlar.
August 1806: The Duchy of Nassau, named for its historical core city, Nassau, was founded in 1806.
January 1807: Several scattered territories of other German polities were added to the Grand Duchy of Berg, including Berg, Dortmund, Steinfurd, Werden, and Wildenburg.
4.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
January 1795: The French armies drove the Austrians, British, and Dutch beyond the Rhine, occupying Belgium, the Rhineland, and the south of the Netherlands.
4.1.1.Rhineland campaign of 1792
Was a French military campaign in the Rhineland.
October 1792: French general Custine captured Mainz on 21 October 1792.
October 1792: The French army penetrated as far as Frankfurt, which surrendered.
4.1.2.Flanders Campaign
Was a French military campaign in the Flanders.
July 1793: During the French Revolutionary Wars, the Prussians, led by Duke of Brunswick, besieged Mainz, held by French revolutionary forces under General Custine. The siege lasted from 14 April to 23 July 1793.
June 1795: Territory evacuated by the French at the end of the Flanders Campaign. The surrender of Luxembourg on 7 June 1795 concluded the French conquest of the Low Countries, thus marking the end of the Flanders Campaign.
4.1.3.Peace of Basel
Were a series of Treaties between the French Republic and Prussia, Spain and Hesse-Kassel that ended the War of the First Coalition with these countries.
April 1795: Peace of Basel of 1795 at the end of the War of the First Coalition between the Kingdom of Prussia and the French Republic. France gained the left bank of the Rhine.
4.1.4.Rhine campaign of 1796
Were a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
June 1796: French General Kléber defeated the Duke of Württemberg in the Battle of Altenkirchen.
July 1796: French forces occupied the city of Giessen.
4.1.5.Treaty of Campo Formio
Was a treaty between France and Austria that ended the War of the First Coalition.
January 1798: The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI). The treaty transferred the Austrian Netherlands to France. The territories of Venice were partitioned, most were acquired by Austria. Austria recognized the Cisalpine Republic and the newly created Ligurian Republic. Extension of the borders of France up to the Rhine, the Nette, and the Roer.
4.2.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
4.2.1.Suvorov Swiss campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Switzlerand.
October 1799: The Russian troops were forced by the French to abandon their hold on the left bank of the Rhine.
4.2.2.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
4.3.Congress of Vienna
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
June 1815: Rieneck is ceded to Bavaria.
January 1075: Worms is declared a Free Imperial City.
January 1153: In 1152, the castle of Schöneberg was acquired by the Mainz Archbishopric.
January 1171: The archbishops of Mainz granted the castle of Schöneberg as a fief to the Eberschütz family.
January 1295: Gleichenstein County is sold to the Archbishopric of Mainz.
January 1310: Parts of the Dürne possessions fell to the archbishopric of Mainz.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
January 1419: Sömmerda was sold to Erfurt, which belonged to the Archbishopric of Mainz.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
January 1505: In 1504 there was a larger-scale exchange of territory between the Counts of Hanau-Lichtenberg and Kurmainz, in which Klingenberg fell to Mainz.
January 1548: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of the Reformation.
September 1559: Count Philip III. von Rieneck died as the last male member of his family on September 3, 1559. Count Philipp III. von Hanau-Münzenberg was unable to enforce his inheritance claims, so the fiefs reverted to Electoral Mainz and the Bishopric of Würzburg.
August 1581: The last lord of the county, Count Christoph zu Stolberg, died on August 5, 1581. In 1581 Königstein came under the archbishopric of Mainz.
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
January 1795: The Wildenburg Lordship is acquired by the Mainz Archbishopric.
Disestablishment
June 1815: Rieneck is ceded to Bavaria.
Selected Sources
Addington, L. (1994): The Patterns of War Since the Eighteenth Century, Bloomington (USA), p.24
Articles secrets et convention additionelle du traité de Campo Formio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2024 on https://books.google.de/books?id=SStJAAAAcAAJ&dq=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&hl=de&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&f=false
Battle of Warburg. BritishBattles.com. Retrieved on 30 march 2024 on https://www.britishbattles.com/frederick-the-great-wars/seven-years-war/battle-of-warburg/
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 48
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 38-39
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Exshaw, A. (1763): A Compleat History of the Late War, pp. 282-283
Frieden von Campoformio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2014 on https://books.google.de/books?id=UbGMtENHaBIC&pg=PA9#v=onepage&q&f=false
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Jorio, M. (2002): Basel, Frieden von (1795). Historisches Lexikon der Schweiz. https://hls-dhs-dss.ch/de/articles/044887/2002-05-01/
Kreins, J. (2003): Histoire du Luxembourg, Paris (France), p. 63
Krumenacker, Y. (2008): La Guerre de Trente Ans, Paris, Ellipses, pp. 144-145
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Schmidt, G. (2006): Der Dreißigjährige Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 65
Spindler, M. (2017): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, Munich (Germany), p. 266
Swiss campaign of Suvorov and his wonder-heroes. Top War. 30 September 2011. https://en.topwar.ru/7227-shveycarskiy-pohod-suvorova-i-ego-chudo-bogatyrey.html
Treaty of Ryswick (English version), https://bonoc.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/tratado-ryswick.pdf
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.191-195
Westfälischer Friede - Vertrag von Osnabrück, https://de.wikisource.org/wiki/Westf%C3%A4lischer_Friede_%E2%80%93_Vertrag_von_Osnabr%C3%BCck
.png.webp)
 Mainz Archbishopric
Mainz Archbishopric