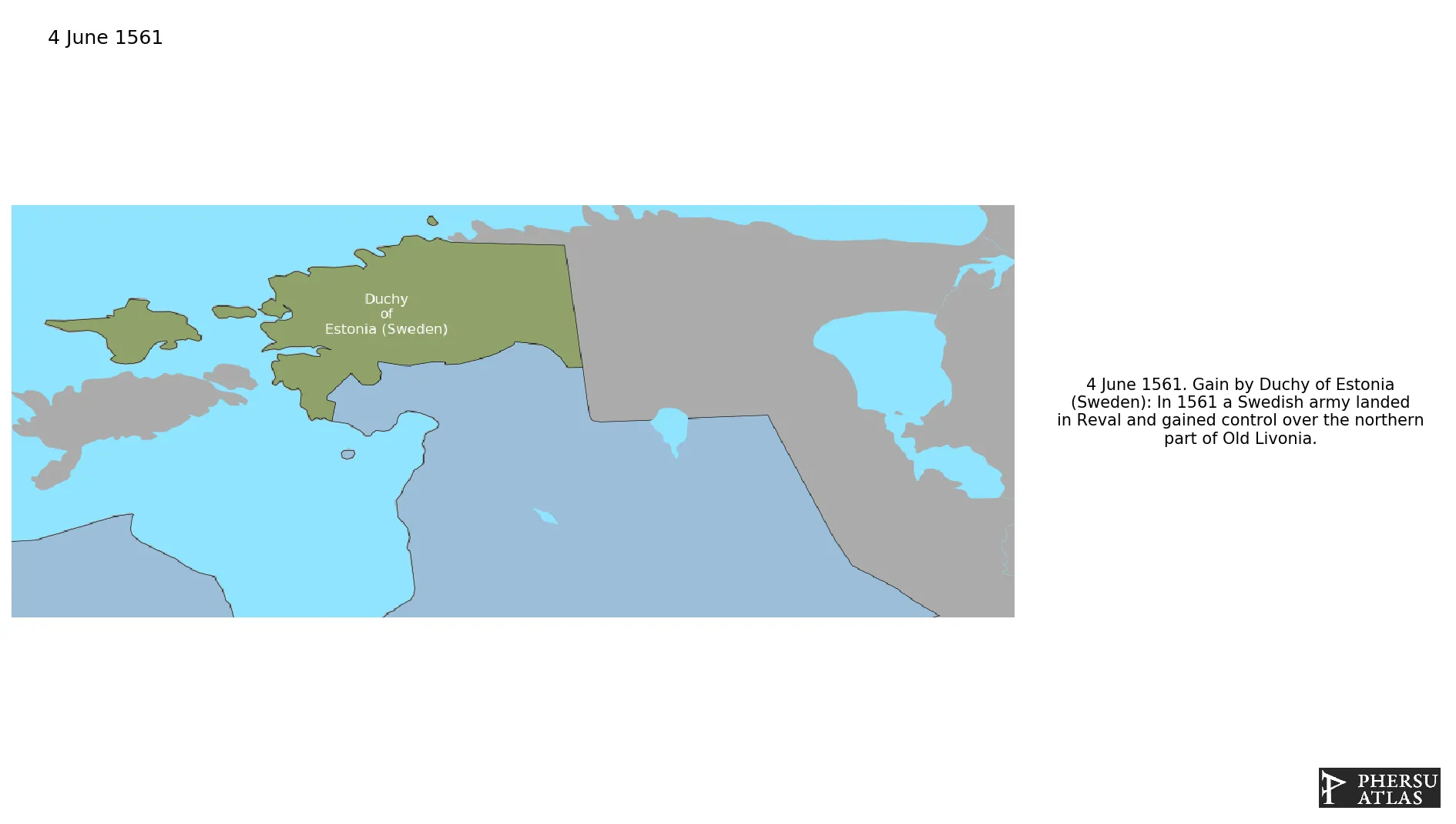
.png.webp)
Data
Name: Duchy of Estonia (Sweden)
Type: Polity
Start: 1561 AD
End: 1721 AD
Nation: estonia
Parent: sweden
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Duchy of Estonia (Sweden)
Duchy of Estonia (Sweden)
This article is about the specific polity Duchy of Estonia (Sweden) and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Sweden conquered the northern part of modern-day Estonia from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Northern Wars
A series of wars fought in northern and northeastern Europe from the 16th to the 18th century.
Was a war fought over the control of Old Livonia. The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom of Sweden, and the Union (later Commonwealth) of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. Old Livonia was finally partitioned between Sweden, Poland-Lithuania and Denmark-Norway.
1.1.1.Russian invasion of Livonia
Was a Russian invasion of Livonia by Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible).
Was the partition of Old Livonia between Denmark, Sweden and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
1.1.3.Polish and Swedish counterattack (Livonian War)
Were the military operations of Sweden and Poland-Lithuania against the Russian invasion.
Was a Truce concluded between Sweden and Russia that ended the Livonian War.
Was a war between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden (along with their respective allies) over the hegemony in the Baltic Sea.
1.2.1.Russo-Swedish War (1656-1658)
Was fought by Russia and Sweden as a theater of the Second Northern War.
Was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe.
1.3.1.Phase 1: Swedish Dominance
Was the first phase of the Great Northern War, characterized by Swedish victories.
1.3.1.1.Livonian-Estonian Frontier of the Great Northern War
Was the Livonian-Estonian theatre of war in the first phase of the Great Northern War.
1.3.2.Phase 2: Sweden Defending itself
Was the second phase of the Great Northern War. It consisted in the counterattack of all the countries that Sweden had invaded during the first phase of the war.
1.3.2.1.Russian Offensive in the East
Was a Russian military campaign against the territories occupied by Sweden in eastern Europe and the Baltic during the Great Northern War.
1.3.3.Peace Treaties of the Great Northern War
Were the peace treaties that ended the Great Northern War.
Was a treaty that ended the Great Northern War between the Tsardom of Russia and the Swedish Empire.
2. War against Sigismund
Was a war between Duke Charles, later known as King Charles IX of Sweden, and Sigismund, who was at the time the king of both Sweden and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The war led to the dissolution of the Polish-Swedish Union.
3. Polish-Swedish War (1600-11)
Was a war between Sweden and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth mainly over the control of Livonia and Estonia.
3.1.Polish Counterattack (Polish-Swedish War of 1600-1611)
Was the Polish counterattack against the Swedish invasion in the Polish-Swedish War (1600-1611).
4. European wars of religion
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
4.1.1.Thirty Years' War Minor Scenarios
A series of conflicts related to the Thirty Years' War.
Was a brief war between Sweden and Denmark-Norway.