This article is about the specific polity Republic of Genoa and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
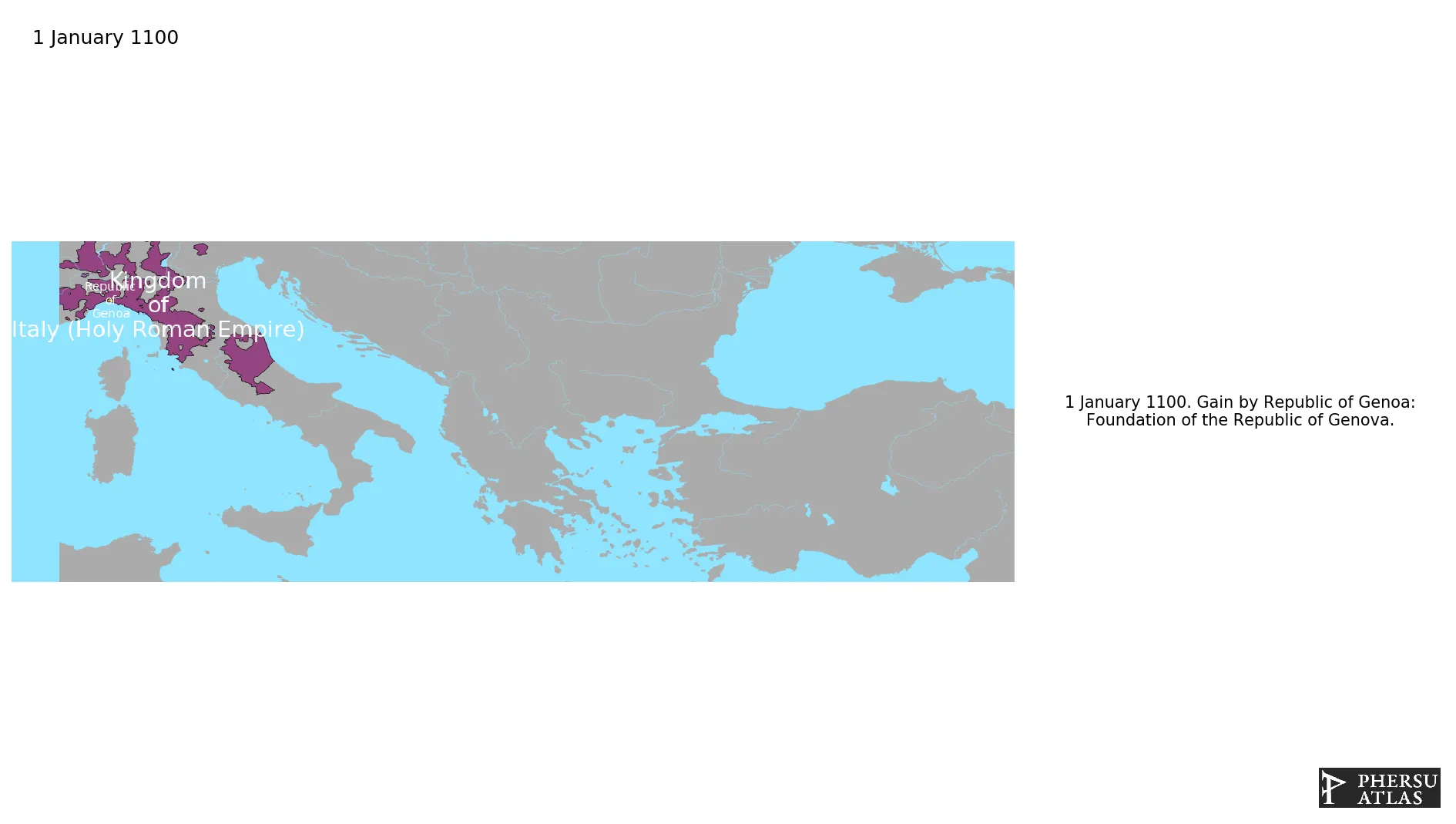
Was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria, on the northwestern Italian coast. Throughout its history, the Genoese Republic established numerous colonies throughout the Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
Establishment
January 1100: Foundation of the Republic of Genova.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Genoese took possession of island of Rhodes, a dependency of the Empire of Nicaea, in a surprise attack in 1248.
January 1249: The Genoese took possession of the city and island of Rhodes, a dependency of the Empire of Nicaea, in a surprise attack in 1248.
January 1251: Rhodes is conquered by Nicaean forces.
Was the Byzantine reconquest of Kios from the Republic of Genoa.
July 1329: Reconquest of Chios by the Byzantines.
Expansion during the rule of Orhan in the Ottoman Beylik.
January 1351: In 1350, the territory of Yoros was taken over by the Ottoman Beylik from the Genoan rulers who had controlled it from 1300 to 1350. Yoros was a strategic location on the Bosphorus Strait, and its capture played a significant role in the expansion of the Ottoman Empire.
Was a military conflict fought in the Byzantine Empire between Byzantine Emperor John V Palaiologos and his son, Andronikos IV Palaiologos.
January 1377: Andronikos assumed control of Constantinople and imprisoned the Emperor John V and his younger brother Manuel. In return for their help, Andronikos IV now gave Tenedos to the Genoese.
Military campaigns of Timur (or Tamerlane), a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia.
5.1.Timurid invasion Anatolia
Was a Timurid campaign in Anatolia, which was occupied for several years.
June 1402: In the spring of 1402, Tamerlan advanced into central Anatolia.
January 1404: Fortunately for the Ottoman dynasty, in 1403 Tamerlane returned with his army to Samarkand, because he wanted to conquer China.
5.1.1.Battle of Ankara
Was a battle between the forces of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I and the Emir of the Timurid Empire, Timur. The battle was a major victory for Timur, and it led to the Ottoman Interregnum.
July 1402: Timurid decisive victory against the Ottomans in the Battle of Ankara (1402).
Byzantine reconquest of the Egean Islands.
January 1404: Byzantine reconquest of the Egean Islands.
Were a series of military campaign by the Crown of Aragon to conquer the island of Sardinia.
August 1420: Overhelmed by the Aragones forces, William II of Arborea reached an agreement with them on 17 August 1420 and what remained of the ancient Giudicato was sold to the Kingdom of Aragon for 100,000 gold florins.
7.1.Sardinian-Aragonese war
Was a late medieval conflict over the control of the island of Sardinia. It saw the Aragonese forces fighting against the Judicate of Arborea and the Republic of Genoa.
October 1353: Alghero was reoccupied by the Judicate of Arborea.
October 1353: Alghero wThe Monteleone fortress arose against Genoa.
February 1410: Pietro Torrelles occupied Bosa.
November 1411: By 1411 the Aragonese further expanded their control over Sardinia.
Expansion during the rule of Murad II in the Ottoman Sultanate.
January 1426: The Ottomans permanently conquered the town of Amisus (Simesso/Samsun).
January 1435: In 1434, Alušta was taken over by the Ottoman Sultanate from Venetian control.
Wars during the rule of Mehmed II in the Ottoman Sultanate.
January 1457: Samothrace conquered by Ottoman Empire.
January 1457: Thasos was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1456.
January 1457: Ainos conquered by Ottoman Empire.
January 1461: Amasra, the most important fortress of the Genoese on the Black Sea coast, was besieged and captured.
September 1462: The island of Lesbos was captured following a siege of its capital, Mytilene, and annexed.
June 1475: In May 1475, the Ottoman commander Gedik Ahmet Pasha conquered Caffa.
July 1475: Soldaia or Sugdeia (today's Sudak) - 1266/87-1322, 1358/65-1475 in the intermediate period she was Venetian.
January 1476: In 1475, the Genoese colony of Vosporo (modern-day Kerč, Crimea) was conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
January 1476: Genoese domination over Anapa lasted until the arrival of an Ottoman fleet in 1475.
January 1476: The Genoese outpost of Cembalo, now Balaklava, part of the city of Sevastopol in Crimea, was conquered by the Turks.
9.1.Fall of Constantinople
Was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 after a 53-day siege which had begun on 6 April. The conquest of Constantinople and the fall of the Byzantine Empire marked the effective end of the last remains of the Roman Empire.
May 1453: In 1453, during the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople, the Genoese territory of Galata was taken over by the Ottoman Sultanate under the leadership of Mehmed the Conqueror.
Were a series of conflicts covering the period between 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the Valois kings of France, and their Habsburg opponents in the Holy Roman Empire and Spain.
10.1.War of the League of Cambrai
Was one of the so-called Italian wars.
10.1.1.Third Phase - The Holy League
Was the third phase of the War of the League of Cambrai, one of the so-called Italian Wars.
June 1511: Genoa rebelled against the French, acclaiming doge Giano Fregoso.
June 1512: Genoese revolt against France suppressed.
10.2.Italian War of 1521-1526
Was one of the so-called Italian wars. The war pitted Francis I of France and the Republic of Venice against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, Henry VIII of England, and the Papal States.
May 1522: Colonna and d'Avalos, generals in the service of the Holy Roman Empire, proceeded to lay siege to Genoa, defended by 6,200 men, entering the city on May 30. Genoa was thus freed from the French yoke.
10.3.War of the League of Cognac
Was one of the so-called Italian Wars. It was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V —primarily the Holy Roman Empire and Spain— and the League of Cognac, an alliance including the Kingdom of France, Pope Clement VII, the Republic of Venice, the Kingdom of England, the Duchy of Milan, and the Republic of Florence.
10.3.1.French invasion of Lombardy
Was the French invasion of Lombardy during the War of the League of Cognac.
September 1527: The French army led by Lautrec takes Genoa in August 1527.
October 1527: French forces occupy Alessandria.
June 1529: In 1529, France suffered a defeat at the hands of the Imperial troops at Landriano, resulting in the loss of control over the Duchy of Milan, along with Lombardy and Liguria.
10.4.Italian War of 1551-1559
Was one of the so-called Italian Wars.
10.4.1.Mediterranean campaigns
Was a French and Ottoman naval campaign during the Italian War of 1551-1559.
10.4.1.1.Invasion of Corsica (Italian War of 1551-1559)
Was the French invasion of Corsica during the Italian War of 1551-1559.
August 1553: Bastia was captured by the French on 24 August 1553.
August 1553: With the help of the Ottomans, the French had managed to take strong positions on Corsica and finally occupied it almost completely by the end of the summer.
August 1553: French military commander Paulin de la Garde arrived in front of Saint-Florent.
October 1553: In 1553, the French military captured Bonifacio, a town in Corsica. This event was part of the ongoing conflict between France and the Republic of Genoa, which controlled the island at the time.
January 1556: In 1555, the French were expelled from the coastal area of Corsica by the forces of the Republic of Genoa, led by their admiral, Andrea Doria. This marked the end of French control in the region and the territory was subsequently claimed by Genoa.
10.4.2.Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis
Was the treaty that ended the Italian War of 1551-1559, the last of the Italian Wars (1494-1559).
April 1559: France ceded the island of Corsica to the Republic of Genoa.
Expansion during the rule of Selim II in the Ottoman Empire.
January 1567: The Genoese controlled the island of Chios from 1304 to 1329 and again from 1346 to 1566. In 1566, the territory was taken over by the Ottoman Empire. Chios was an important trading hub for the Genoese, known for its production of mastic resin.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
12.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
12.1.1.First Genoese-Savoyard War
Was the theatre of war in Liguria during the Thirty Years' War.
March 1625: The French captured Voltaggio.
March 1625: The French formed a 30,000-strong army that began operations against Genoa in February 1625. The attack caught the Genoese Republic unprepared. Most of the Republic was overrun.
March 1625: French forces led by the Duke of Lesdiguières stormed the towns of Capriata, Novi, and Rossiglione in Italy.
September 1625: In 1625, the Republic of Genoa, led by the Doge Giovanni Giacomo Imperiale, marched against Casale, reclaiming the territories of Gavi and Novi from the Duchy of Savoy.
November 1625: By October the Republic of genoa recuperated all the territories lost to the French (with the exception of the castle of La Penna) and additionally conquered Oneglia, Ormea, and a number of localities in Piedmont.
November 1625: Albenga is occupied by the Duchy of Savoy.
January 1627: In 1626, the territory of Albenga returned to the Republic of Genoa.
12.1.2.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
January 1649: Genova gave Pontremoli back to Spain.
Was a short war fought between the Duchy of Savoy and the Republic of Genoa.
January 1673: The Savoyards occupied Pieve di Teco.
January 1673: Pieve di Teco conquered by Republic of Genoa.
Was a European conflict caused by the succession to the Habsburg Domains. Maria Theresa succeeded her father Charles VI, and the opposition to female inheritance of the throne was a pretext for starting a war. It was a global conflict that saw fight in Europe, Asia, America and Africa.
14.1.Italian Theatre (War of the Austrian Succession)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the Austrian Succession.
October 1746: On 6 September 1746, Genoa was besieged by the Austrians who had crossed the territories of the King of Sardinia. The Austrians, led by General Brown and the Genoese exile Antoniotto Botta Adorno, had presented themselves in Sampierdarena imposing excruciating peace conditions on the Genoese. Among these conditions was the dismantling of the city fortifications and their transfer to the Austrians.
December 1746: The revolt in the city lasted three days, as on 9 December Botta Adorno agreed to the negotiations and left the city almost immediately.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
15.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
15.1.1.Italian theatre (War of the first coalition)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
November 1795: In northern Italy the victory at the Battle of Loano in November gives France access to the Italian peninsula.
April 1796: Napoleon won at the Second Battle of Dego, driving the Austrians northeast, away from their Piedmontese allies.
June 1797: In 1797, Napoleon Bonaparte deposed Giacomo Maria Brignole, the last doge of the Republic of Genova. This marked the end of the Republic of Genova and the territory was incorporated into the Ligurian Republic.
15.2.War of the Sixth Coalition
Was a war between France and a a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States. The coalition emerged after the decimation of the French army in the French invasion of Russia. The coalition ultimately invaded France and forced Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile.
May 1814: Republic's revival in Genoa.
15.2.1.Treaty of Paris (1814)
Was the treaty that ended the war between France and the Sixth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1814: By the Treaty of Paris, May 30, 1814, the House of Savoy was restored to its rights.
15.3.Congress of Vienna
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
February 1815: Geona was eventually annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia in 1815.
January 1151: The territory controlled by Genoa was already very large by the mid of the XII Century.
May 1191: Holy Roman Emperor Heinrich VI grants suzerainty over the area of Ventimiglia to Genoa.
January 1198: During the break-up of the Byzantine Empire the island of Corfu was occupied by Genoese privateers.
January 1199: Genoa conquers Lavagna.
September 1202: Deed of transfer of the Gavi Marquisate to the Republic of Genoa.
January 1205: Expansion of the Genoese colonies in Crimea.
January 1208: Corfu was captured by Venice from its Genoese ruler.
January 1252: Albenga became part of the Republic of Genova.
January 1256: Foundation of the County of Loano by Oberto I Doria.
January 1259: Passage of the Municipality of Ventimiglia under the jurisdiction of the Republic of Genoa.
January 1260: The kingdom of Logudoro came to an end in 1259, when the queen Adelasia died without an heir. After this, Logudoro was effectively ruled by the Genoese families of Doria and Malaspina, and the ruling family of Arborea.
January 1262: Amastris (Amasra) was a Genoese colony from 1261.
January 1262: Amisus (Simesso/Samsun) was one of the Genoese colonies on the Black Sea from 1261.
January 1267: Caffa (today Feodosia) - 1266-1475 was the main Genoese station in Crimea.
January 1274: Galata was Genoese from 1273 to 1453.
January 1276: Around the middle of the 13th century, the fiefdom of Savignone, which also included Croce, passed under the rule of the Fieschis, counts of Lavagna. In 1275, the territory was acquired by the Republic of Genoa.
January 1276: Around the middle of the 13th century, the fiefdom of Savignone, which also included Croce, passed under the rule of the Fieschis, counts of Lavagna. In 1275, Crocefieschi became part of the Republic of Genoa.
January 1277: Dolceacqua under Doria's rule.
August 1284: The Island of Corsica and the Island of Capraia definitively passed under the control of Genoa after the defeat of the Republic of Pisa in the battle of Meloria.
January 1289: The territory of Castellaro is ceded to the Republic of Genoa.
January 1289: Albenga is occupied by the March of Finale.
January 1291: Moncastro (today: Bilhorod-Dnistrovsky) became a center of Genoese commercial activity from c. 1290 on.
January 1295: Aigeai (heute Ayas) 1294-1347.
January 1295: In 1294 it Sassari became a Free Commune, confederated to Genoa (after an initial pro-Pisan period), following the promulgation of the Sassari Statutes.
January 1301: Genoan Yoros 1300-1350.
January 1301: At the end of the thirteenth century, the Marquises del Bosco were definitively removed by arms from Masone which, from that moment, became a fief of the Genoese Republic.
January 1305: The island of Chios was under the control of the Republic of Genoa from 1304.
January 1305: The island of Samos was under the control of the Republic of Genoa from 1304.
January 1309: In 1308, Caffa was plundered by the Mongols.
January 1311: Vosporo (today's Kerč) was a Genoese colony since 1310.
January 1330: In 1329, the Island of Samos was reconquered by the Byzantine Empire.
January 1334: The Island of Lesbos is acquired by Genoa.
January 1337: The Island of Lesbos is acquired by the Byzantines.
January 1347: Genoese Chios (1304-1329 und 1346-1566).
January 1347: Genoese Samos (1304-1329 und 1346-1475).
January 1348: The city of Ayas was increasingly oppressed by the Mamluks and fell definitively into their hands in 1347.
January 1351: Genoan Yoros 1300-1350.
January 1354: Domain of Milan over Genoa 1353-1356.
January 1355: Thasos (1354-1457) Genoese Colony.
January 1356: Samothrace conquered by Republic of Genoa.
January 1356: The Gattilusi family established a number of fiefs, under nominal Byzantine suzerainty, over the island of Lesbos (1355-1462).
January 1357: Genoa becomes independent from Milan.
January 1358: The Republic of Genoa controlled Cembalo (present day Balaklava) in Crimea from 1357.
July 1365: On 19 July 1365, a Genoese force from Kaffa seized the city of Sudak.
January 1366: In 1365, Alušta, known as Lusta at the time, came under the control of the Republic of Genoa.
January 1368: Sanremo declares itself Free Commune.
January 1377: Ainos conquered by Republic of Genoa.
January 1378: Venetian colony in Bozcaada Island (Tenedo) from 1377.
January 1380: In 1379, the city of Albenga returned to the control of the Republic of Genoa.
January 1388: At the time of the heirless death of Manuel II (1387), the Clavesana Marquisate ceased to exist.
January 1393: Genova conquers Novi.
January 1395: Period of French domination over the Republic of Genoa from 1394 to 1409.
January 1400: The settlement of Anapa was acquired by the Genoese and renamed Mapa at the turn of the 14th century.
January 1403: After the passage of Tamerlane in Anatolia in 1402 and the ensuing period of troubles, the Beylik of Aydin was able to reaffirm its independence.
January 1410: Genoa came under the control of the Visconti of Milan.
January 1413: Milano conquers Novi.
January 1415: Lemnos conquered by Republic of Genoa.
January 1415: Thasos conquered by Republic of Genoa.
January 1417: In 1416, the territory of Rocchetta-Suvero was taken over by the Republic of Genoa.
January 1417: Genoa conquers Castevoli.
January 1420: In 1419, the Republic of Genoa gained control of Tmutarakan, a strategic trading outpost on the Black Sea. The Genoese presence in the region lasted until 1482, when the territory was eventually lost to the expanding Russian Empire.
January 1422: Domain of Milan over Genoa 1421-1435.
January 1436: End of the domain of Milan over Genoa.
January 1438: In 1437, Lucca, not being able to pay a debt of 150,000 scudi contracted a few years earlier with Genoa, allowed it to occupy the seaport of Motrone and some nearby castles.
January 1439: Sarzana falls under the domination of the Republic of Genoa.
January 1448: Rocchetta-Suvero reverts to the control of the Malaspinas.
January 1448: Genova conquers Novi.
January 1459: Threatened by Alfonso V of Aragon, the Doge of Genoa ceded the Republic to the French in 1458.
January 1462: Genoa regained independence from France.
January 1464: In the period 1463-1478 Genoa was part of the Sforza domains.
January 1465: In 1464, during the First Ottoman-Venetian War,the Venetians seized Lemnos and other former Gattilusi possessions.
January 1465: Castevoli remained in the Genoese domain until 1464.
January 1480: From 1479 Genoa was again independent from Milan.
January 1483: Genoese colony established in the city of Tmutarakan.
January 1485: Corvaia and Pietrasanta were part of the Genoese state until 1484 when they were conquered by the Republic of Florence.
January 1486: Bagnaria becames an independent feudality under the Doria family.
August 1487: Moncastro (today: Bilhorod-Dnistrovsky) fell to Ottoman conquest.
January 1489: Genea was part of the Sforza domanis between 1488 and 1499.
January 1530: The struggles with Genoa ended tragically for Savona in 1528.
January 1548: Fieschi conquers Torriglia.
May 1560: Foundation of the County of Tassarolo by Marcantonio Spinola.
January 1567: Alfonso II, lord of Arnasco, was driven out by his subjects for his tyrannical rule.
September 1641: Honoré II, Prince of Monaco secured recognition of his independent sovereignty from Spain in 1633, and then from Louis XIII of France by the Treaty of Péronne (1641). Since then the area has remained under the control of the Grimaldi family.
January 1644: The Duchy of Savoy conquers Dolceacqua.
January 1648: Pontremoli (about 6,000 inhabitants) was bought by the Republic of Genoa in November 1647.
January 1711: Calice briefly returned to the hands of the Malaspinas (1710).
January 1714: Marquisate of Finale enfeoffed to the Republic of Genoa.
January 1729: Genoa conquers Busalla.
January 1744: Bagnaria is annected to the Kingdom of Sardinia.
January 1747: Albenga is occupied by the Duchy of Savoy.
January 1748: In 1747, Albenga, a territory in Italy, returned to the control of the Republic of Genoa.
January 1749: Genoa conquers Sanremo.
December 1755: In November 1755, Pasquale Paoli proclaimed Corsica a sovereign nation, the Corsican Republic (Italian: Repubblica Corsa), independent from the Republic of Genoa.
Disestablishment
February 1815: Geona was eventually annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia in 1815.
Selected Sources
Ducas: Historia turco-bizantina 1341-1462, XXII [6]
Repetti, E. (1833), Dizionario geografico, fisico, storico della Toscana: contenente la descrizione di tutti i luoghi del granducato, ducato di Lucca, Garfagnana e Lunigiana, Volume 1, Florence (Italy), p. 826
Repetti, E. (1843), Dizionario geografico, fisico, storico della Toscana: contenente la descrizione di tutti i luoghi del granducato, ducato di Lucca, Garfagnana e Lunigiana, Volume 5, Florence (Italy), p. 185
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.139

 Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa