.svg.png.webp)
Data
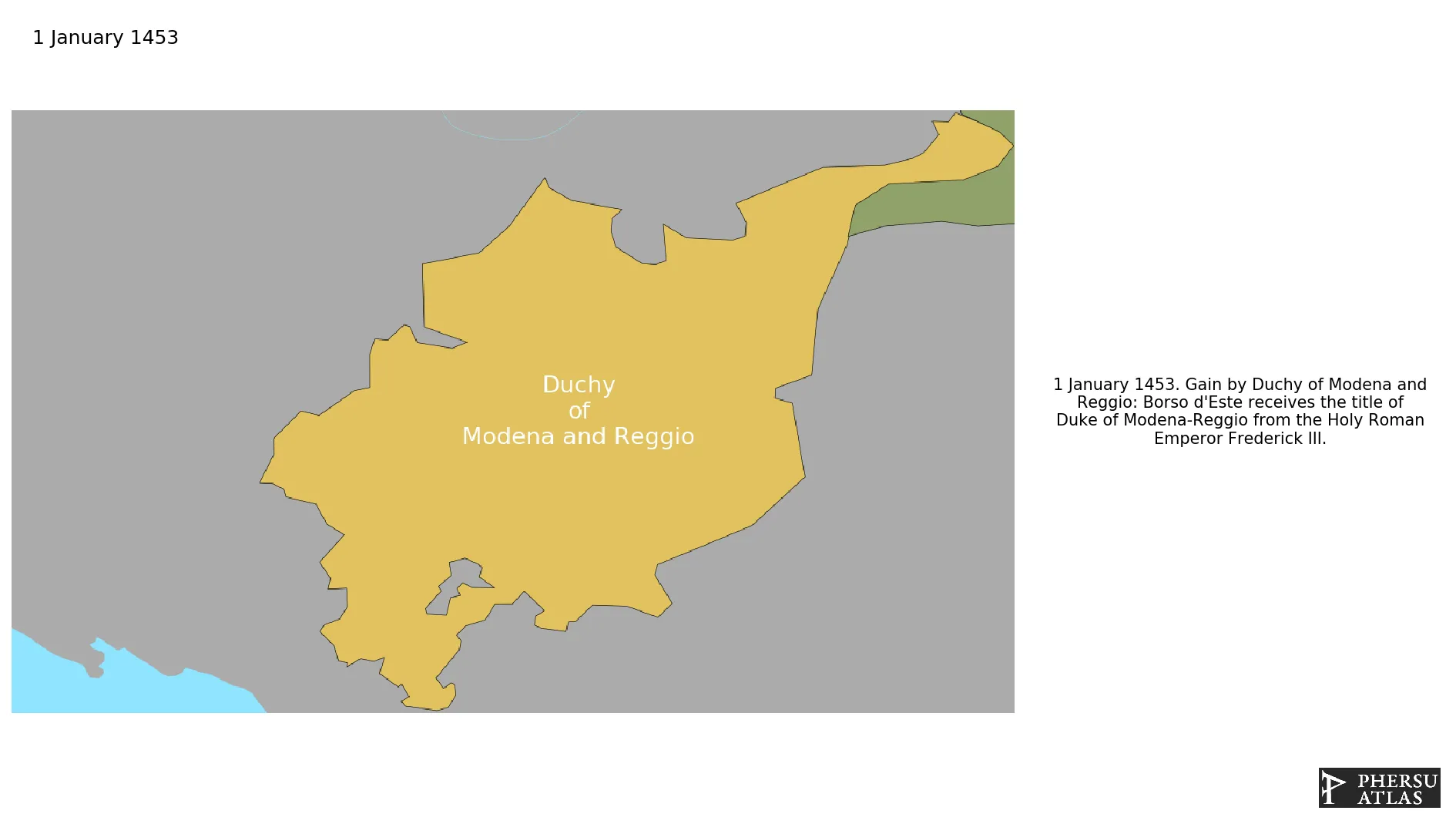
Name: Duchy of Modena and Reggio
Type: Polity
Start: 1453 AD
End: 1859 AD
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Duchy of Modena and Reggio
Duchy of Modena and Reggio
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and since 1814 by the Austria-Este branch of the family.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Italian Wars
Were a series of conflicts covering the period between 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the Valois kings of France, and their Habsburg opponents in the Holy Roman Empire and Spain.
1.1.War of the League of Cambrai
Was one of the so-called Italian wars.
1.1.1.Second Phase - Alliance between Venice and the Papal States
Was the second phase of the War of the League of Cambrai, one of the so-called Italian Wars.
1.1.2.Fourth Phase - Alliance between Venice and France
Was the fourth phase of the War of the League of Cambrai, one of the so-called Italian Wars.
1.2.War of the League of Cognac
Was one of the so-called Italian Wars. It was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V —primarily the Holy Roman Empire and Spain— and the League of Cognac, an alliance including the Kingdom of France, Pope Clement VII, the Republic of Venice, the Kingdom of England, the Duchy of Milan, and the Republic of Florence.
2. War of the Polish Succession
Was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland.
2.1.French Invasion of northern Italy
Was the French invasion of northern Italy during the War of the Polish Succession.
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Polish Succession. Augustus III was officially confirmed as King of Poland.
3. War of the Austrian Succession
Was a European conflict caused by the succession to the Habsburg Domains. Maria Theresa succeeded her father Charles VI, and the opposition to female inheritance of the throne was a pretext for starting a war. It was a global conflict that saw fight in Europe, Asia, America and Africa.
3.1.Italian Theatre (War of the Austrian Succession)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the Austrian Succession.
Was a joint Austrian and Savoyard invasion of Modena during the War of the Austrian Succession.
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
4. French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
4.1.War of the First Coalition
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
4.1.1.Italian theatre (War of the first coalition)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
4.2.War of the Sixth Coalition
Was a war between France and a a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States. The coalition emerged after the decimation of the French army in the French invasion of Russia. The coalition ultimately invaded France and forced Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile.
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
4.4.War of the Seventh Coalition (The Hundred Days)
Napoleon escaped the exile he had been forced after the War of the Sixth Coalition and reorganized the French army. He was defeated by a coalition that included Great Britain, Austria, Prussia and Russia and sent into permanent exile on the island of Saint Helena.
Was a conflict between the Napoleonic Kingdom of Naples and the Austrian Empire during the War of the Seventh Coalition. Naples, which was still ruled by the Napoleonic general Joachim Murat, decided to side with Napoleon. The Austrian won the war and reinstated Ferdinand IV as King of Naples and Sicily.
4.4.1.1.Neapolitan attack (Neapolitan War)
Was the invasion of central and northern Italy launched by the Neapolitan armies during the Neapolitan War.
4.4.1.2.Austrian counterattack (Neapolitan War)
Was the Austrian invasion of Italy during the Neapolitan War.
5. Treaty of Florence (1844)
Was a treaty between the Grans Duchy of Tuscany, the Duchy of Modena and Reggio, and the Duchy of Parma and Piacenza where the borders between these countries were simplified though the exchange of several exclaves/enclaves in their territories.
6. Revolutions of 1848
Was a revolutionary wave in Europe that started in France. The revolutions were essentially democratic and liberal in nature, with the aim of removing the old monarchical structures and creating independent nation-states, as envisioned by romantic nationalism.
6.1.First Italian War of Independence
Was the first of the three traditional Italian Wars of Independence. It was fought by the Kingdom of Sardinia against the Austrian Empire but it did not led to any territorial modification.
6.1.1.Modena and Parma Operation
Was an Austrian military operation by prince Franz Joachim von Liechtenstein to restore the deposed dukes of Parma and Modena. .
7. Wars of Italian Unification
Was a series of conflicts that led to the unification of the Italian Peninsula into the Kingdom of Italy. It includes the three wars considered the three independency wars of Italy, in addition to a series of military operations like the Expedition of the Thousand and the Sardinian military campaign in Central Italy.